Nuclear energy harnesses the power of atomic reactions to generate electricity with high efficiency and low greenhouse gas emissions. This infographic illustrates the key components, processes, and benefits of nuclear power, highlighting its role in sustainable energy development. Understanding nuclear energy's mechanisms and safety measures is essential for appreciating its potential in meeting global energy demands.
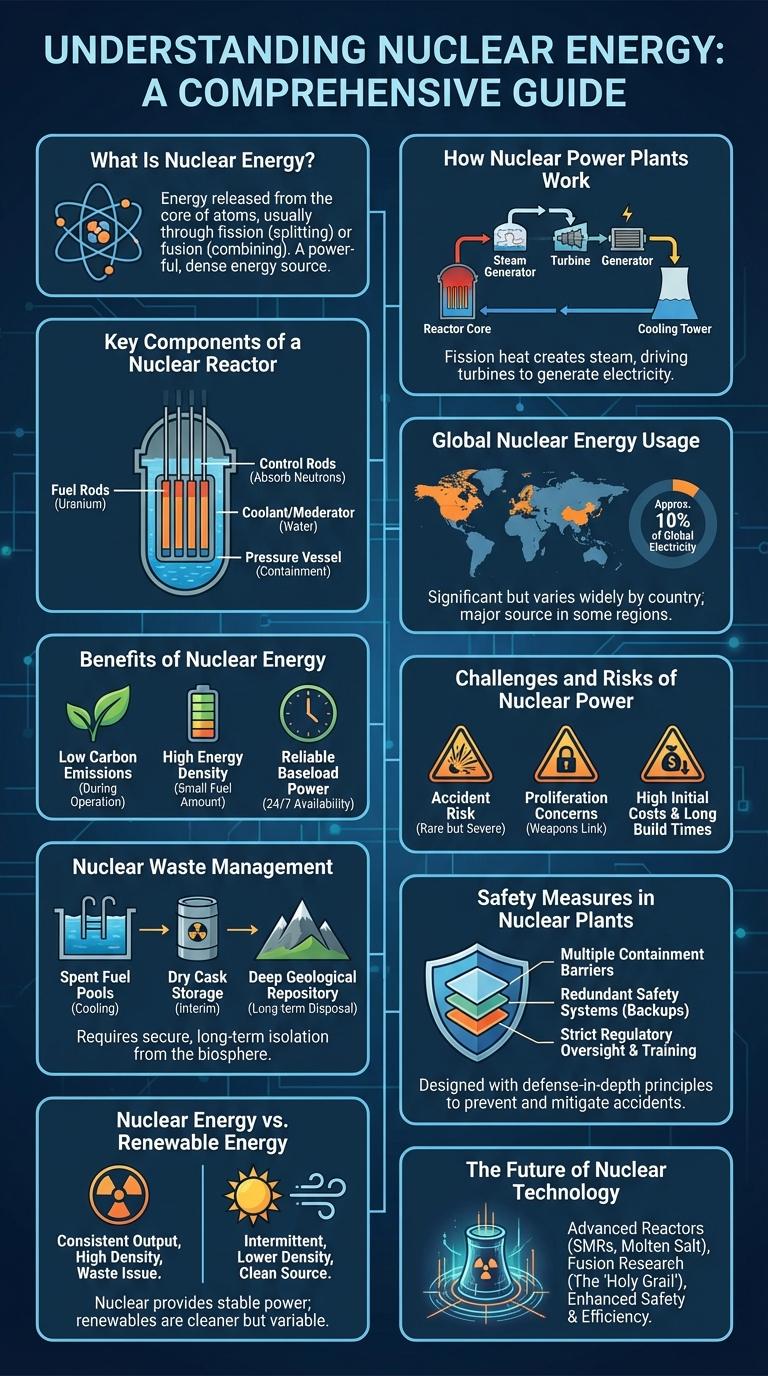
What Is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy is the power derived from splitting the nucleus of an atom through a process called nuclear fission. It generates large amounts of energy used primarily for electricity production worldwide.
- Nuclear Fission - The process involves breaking atomic nuclei, releasing significant energy.
- Energy Density - Nuclear fuel has a much higher energy density compared to fossil fuels.
- Electricity Generation - Nuclear reactors convert nuclear energy into electrical power for homes and industries.
How Nuclear Power Plants Work
Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear fission, where uranium atoms split and release heat. This heat produces steam that drives turbines connected to electrical generators. The process emits minimal greenhouse gases, making it a low-carbon energy source.
Key Components of a Nuclear Reactor
Nuclear reactors generate energy through controlled nuclear fission, where atomic nuclei split to release heat. This heat produces steam that drives turbines, generating electricity.
The key components include the reactor core, where fuel rods containing uranium or plutonium undergo fission. Control rods regulate the reaction by absorbing neutrons, maintaining safe energy output levels.
Global Nuclear Energy Usage
Nuclear energy powers approximately 10% of the world's electricity, making it a critical component of global energy strategies. Over 440 nuclear reactors operate across 30 countries, demonstrating widespread adoption.
The United States leads with 93 reactors, followed by France with 56 and China rapidly expanding its fleet. Nuclear energy offers a low-carbon alternative, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. Despite challenges, nuclear power remains vital for meeting global energy demands sustainably.
Benefits of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is a powerful source of clean electricity that supports global energy demands. It offers significant environmental and economic advantages over fossil fuels.
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions - Nuclear power plants produce minimal carbon dioxide, helping to combat climate change.
- High Energy Density - A small amount of nuclear fuel generates a large amount of energy, making it highly efficient.
- Reliable Power Supply - Nuclear reactors provide consistent and stable electricity regardless of weather conditions.
Nuclear energy plays a critical role in achieving sustainable and low-carbon energy systems worldwide.
Challenges and Risks of Nuclear Power
Nuclear energy offers a powerful source of electricity with low greenhouse gas emissions. Despite its benefits, the technology presents significant challenges and risks that must be carefully managed.
One major risk is the potential for catastrophic accidents, such as core meltdowns, which can release harmful radiation. Managing radioactive waste remains a critical challenge due to its long-term environmental impact and storage requirements.
Nuclear Waste Management
How is nuclear waste managed to ensure safety and environmental protection? Nuclear waste from nuclear energy production is carefully stored and treated to prevent radioactive contamination. Specialized facilities use methods like deep geological repositories to isolate waste for thousands of years.
What are the main types of nuclear waste? Nuclear waste is classified into low-level, intermediate-level, and high-level waste based on radioactivity. High-level waste, including spent nuclear fuel, requires long-term storage solutions due to its intense radioactivity and heat generation.
How does deep geological storage work for nuclear waste? Waste is sealed in corrosion-resistant containers and buried deep underground in stable rock formations. This method minimizes the risk of radioactive leakage into the environment over millennia.
What technologies are used to reduce nuclear waste volume? Advanced reprocessing recovers usable materials from spent fuel, reducing waste volume. New reactor designs also aim to generate less waste and utilize existing waste as fuel.
Why is public safety a priority in nuclear waste management? Strict regulatory frameworks monitor and control all stages of waste handling. Continuous research improves storage methods, guaranteeing protection of people and ecosystems worldwide.
Safety Measures in Nuclear Plants
| Safety Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Containment Structures | Thick steel-reinforced concrete buildings encase reactors to prevent radioactive leaks during accidents. |
| Emergency Core Cooling Systems (ECCS) | Automatic systems activate to supply cooling water to the reactor core if normal cooling fails, preventing meltdown. |
| Redundant Safety Systems | Multiple backup systems ensure critical functions continue even if one system malfunctions, enhancing operational reliability. |
| Radiation Monitoring | Continuous surveillance of radiation levels inside and around the plant to detect and respond to leaks promptly. |
| Regular Safety Drills | Routine emergency preparedness exercises for staff to ensure quick, coordinated responses to potential incidents. |
Nuclear Energy vs. Renewable Energy
Nuclear energy and renewable energy are two key sources in the transition to sustainable power. Each has unique advantages and challenges that influence energy policy worldwide.
Nuclear energy provides large-scale, low-carbon electricity with high reliability. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind offer clean power but face variability and storage challenges.
- Energy Output - Nuclear plants deliver consistent, high-capacity power compared to the intermittent output of solar and wind.
- Environmental Impact - Nuclear energy produces radioactive waste, while renewables generate minimal waste but require significant land and materials.
- Cost and Investment - Nuclear projects have high upfront costs and long development times, whereas renewable technologies have declining costs with faster installation.
