Jazz music blends rich cultural roots with innovative improvisation, creating a unique and dynamic sound that has influenced countless genres worldwide. This infographic highlights key milestones, legendary artists, and essential elements that define jazz's evolution. Explore how rhythm, harmony, and storytelling come together to shape this timeless musical tradition.
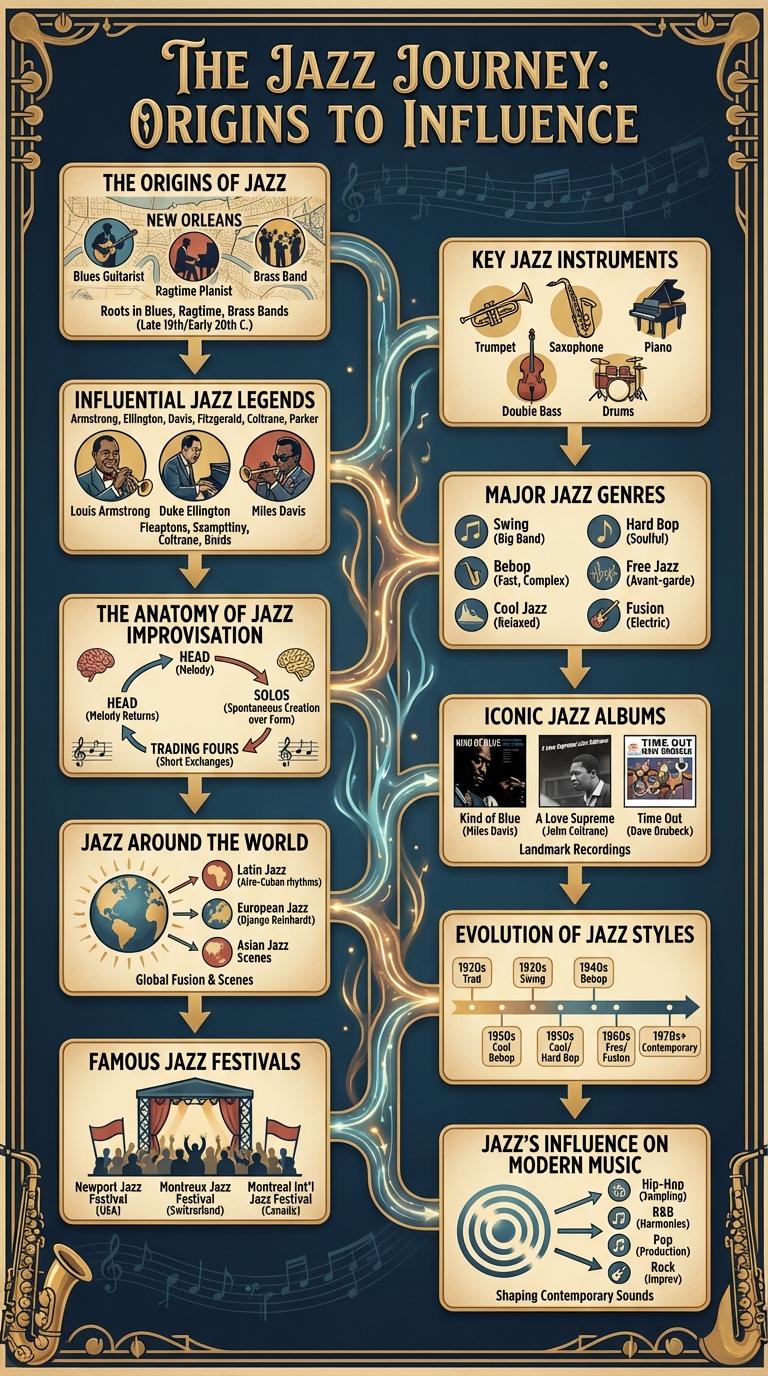
The Origins of Jazz
Jazz music originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the Southern United States, blending African and European musical traditions. It is characterized by improvisation, syncopation, and strong rhythms that reflect its diverse cultural roots.
- African Rhythms Influence - Jazz incorporates complex rhythms and call-and-response patterns derived from African musical traditions.
- Blues and Ragtime Foundations - Early jazz developed from blues and ragtime, combining emotive melodies with syncopated beats.
- New Orleans Origins - The city of New Orleans served as a cultural melting pot where jazz emerged, fueled by diverse communities and musical styles.
Key Jazz Instruments
Jazz music is characterized by its rich use of diverse instruments that create its unique sound. Key jazz instruments form the foundation of this dynamic genre, blending melody, harmony, and rhythm.
Trumpet and saxophone are central to jazz, known for their expressive tones and improvisational capabilities. The piano and double bass provide harmonic support and groove, while drums drive the rhythm and energy of jazz performances.
Influential Jazz Legends
Jazz music has shaped the cultural landscape with its rich history and innovative sounds. Influential jazz legends have pioneered styles and inspired generations of musicians worldwide.
Louis Armstrong revolutionized jazz with his virtuosic trumpet playing and charismatic stage presence. Miles Davis pushed boundaries through his groundbreaking albums and evolving musical styles.
Major Jazz Genres
Jazz music encompasses a variety of major genres, each with unique styles and cultural origins. Key genres include Swing, Bebop, Cool Jazz, Hard Bop, and Free Jazz, reflecting the evolution of jazz over the 20th century. These genres highlight different rhythms, improvisational techniques, and instrumental arrangements.
| Genre | Description |
|---|---|
| Swing | Upbeat, dance-oriented style popular in the 1930s and 1940s. |
| Bebop | Complex, fast-paced style emphasizing improvisation, emerged in the 1940s. |
| Cool Jazz | Relaxed and smooth, developed in the late 1940s and 1950s. |
| Hard Bop | Incorporates blues and gospel influences, popular in the 1950s. |
| Free Jazz | Atonal and avant-garde, focusing on free improvisation from the 1960s onward. |
The Anatomy of Jazz Improvisation
Jazz improvisation is the spontaneous creation of melodies over a harmonic framework. It is a core element that defines the genre's expressive and dynamic nature.
The process involves real-time invention using scales, chords, and rhythmic patterns. Musicians rely on deep knowledge of music theory and active listening to fellow players. This interaction produces unique and evolving performances every time.
Iconic Jazz Albums
| Album | Artist & Year |
|---|---|
| Kind of Blue | Miles Davis, 1959 |
| A Love Supreme | John Coltrane, 1965 |
| Time Out | Dave Brubeck Quartet, 1959 |
| Blue Train | John Coltrane, 1957 |
| Ellington at Newport | Duke Ellington, 1956 |
Jazz Around the World
Jazz music has influenced cultures worldwide, blending local sounds with traditional jazz elements. Countries like the United States, Brazil, Japan, France, and South Africa contribute unique styles such as bebop, bossa nova, jazz fusion, gypsy jazz, and kwela. Jazz festivals in cities like New Orleans, Tokyo, and Cape Town celebrate the genre's global impact and evolving creativity.
Evolution of Jazz Styles
How has jazz music evolved over the decades? Jazz originated in the early 20th century, blending African rhythms with European harmonic structures. It continuously transformed through influential styles like Dixieland, Swing, Bebop, and Fusion.
What defines the Dixieland jazz style? Dixieland jazz, emerging in New Orleans around 1910, features collective improvisation and a lively, upbeat tempo. It is characterized by instruments such as trumpet, clarinet, trombone, piano, and drums.
How did Swing jazz impact popular music? Swing dominated the 1930s and 1940s with big bands and danceable rhythms, emphasizing strong brass sections and smooth arrangements. This style helped make jazz a mainstream form of entertainment.
What distinguishes Bebop from earlier jazz styles? Bebop appeared in the 1940s with fast tempos, complex chord progressions, and virtuosic solos. It shifted jazz from dance music to an art form focused on improvisation and technical skill.
How does Fusion integrate different musical elements? Fusion combines jazz improvisation with rock, funk, and electronic instruments, gaining popularity in the 1970s. It expanded jazz's sonic palette and reached new audiences with innovative sounds.
Famous Jazz Festivals
Jazz music is celebrated worldwide through numerous renowned festivals that showcase legendary performances and innovative talents. These events offer immersive experiences for jazz enthusiasts and contribute significantly to the genre's global influence.
- Montreux Jazz Festival - Held annually in Switzerland, it is one of the largest and most prestigious jazz festivals globally.
- Newport Jazz Festival - Founded in 1954 in Rhode Island, USA, it played a crucial role in popularizing jazz music.
- North Sea Jazz Festival - Based in the Netherlands, this festival attracts international artists and tens of thousands of visitors each year.
These jazz festivals continue to inspire and unite audiences, preserving the rich heritage of jazz music.
