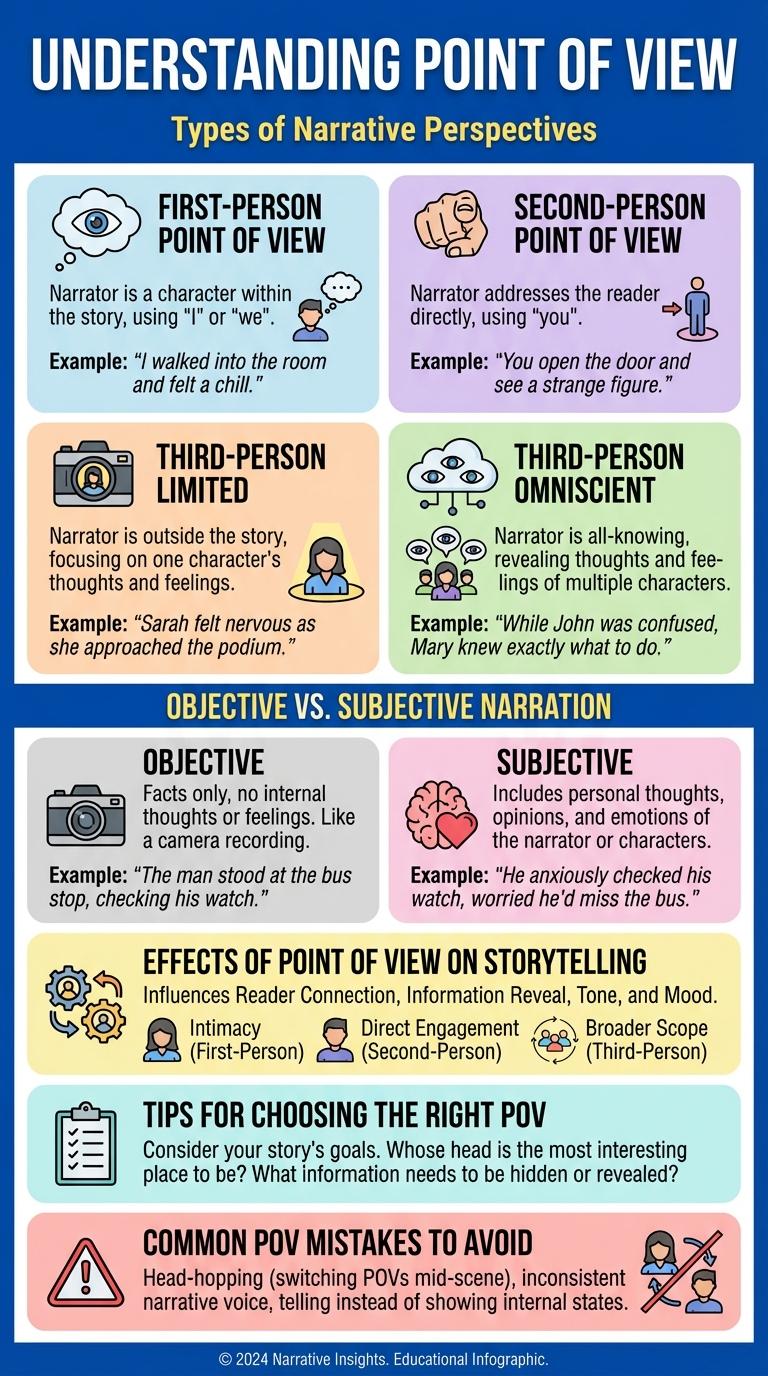
Understanding point of view is essential for interpreting narratives and analyzing perspectives in storytelling. This infographic visually breaks down the different types of point of view, highlighting first-person, second-person, and third-person perspectives. Grasping these concepts enhances comprehension and enriches the reading experience.
Understanding Point of View
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Point of view (POV) refers to the perspective from which a story is narrated or information is presented. |
| Common Types | First-person, Second-person, Third-person limited, Third-person omniscient |
| First-Person | Uses "I" or "we"; story told from the narrator's personal perspective. |
| Third-Person Omniscient | All-knowing narrator offering insights into multiple characters' thoughts and feelings. |
| Impact on Audience | Shapes how readers perceive characters, events, and biases within the narrative. |
Types of Narrative Perspectives
What are the main types of narrative perspectives used in storytelling? Narrative perspectives include first-person, second-person, and third-person points of view. Each type offers a unique way to experience the story and connect with characters.
How does first-person point of view affect the reader's experience? First-person narration uses "I" or "we," providing intimate insight into the narrator's thoughts and feelings. This perspective creates a personal and immersive storytelling experience.
What distinguishes second-person point of view in narratives? Second-person narration addresses the reader as "you," making them a direct participant in the story. It is less common and creates a unique, immersive effect by involving the reader personally.
What are the variations within third-person point of view? Third-person narration includes limited, omniscient, and objective perspectives. The limited point of view focuses on one character's thoughts, omniscient knows all characters' thoughts, and objective reports only observable actions.
Why is the choice of narrative perspective important in writing? The narrative perspective shapes how the story is told and influences the reader's connection to the plot and characters. Selecting the right point of view enhances clarity, engagement, and emotional impact.
First-Person Point of View
The first-person point of view provides a direct insight into the narrator's thoughts and feelings. It uses pronouns like "I" and "we," creating a personal connection with the reader.
- Subjective Experience - The narrator shares personal thoughts, emotions, and perceptions, offering an intimate perspective.
- Limited Knowledge - Information is restricted to what the narrator knows or observes.
- Unreliable Narration - The narrator's bias or limited understanding may influence the story's interpretation.
Second-Person Point of View
The second-person point of view directly addresses the reader using the pronoun "you," creating an immersive and engaging experience. This perspective is commonly found in instructional texts, interactive fiction, and choose-your-own-adventure stories. It allows readers to feel involved as active participants in the narrative or directions.
Third-Person Limited
Third-person limited point of view presents the story through the lens of a single character. The narrator reveals only that character's thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
This perspective creates a deep connection with one protagonist while maintaining an external narrator. Readers gain insight into the character's inner world without accessing others' minds.
Third-Person Omniscient
Third-person omniscient point of view provides a comprehensive perspective by revealing the thoughts and feelings of multiple characters. This narrative style offers an all-knowing presence throughout the story.
The narrator knows every character's internal experiences, motivations, and emotions, allowing for a rich and detailed understanding of the plot. This viewpoint can shift focus seamlessly between characters, enhancing plot complexity and depth. Writers often use third-person omniscient to build a broad, interconnected world within their stories.
Objective vs. Subjective Narration
Point of view in narration shapes how a story is perceived by the audience. Objective and subjective narrations offer distinct perspectives that influence reader interpretation.
- Objective Narration - Presents facts and events without personal bias or emotional influence.
- Subjective Narration - Conveys the narrator's personal thoughts, feelings, and opinions.
- Impact on Story - Objective narration enhances neutrality, while subjective narration deepens emotional connection.
Understanding the difference between objective and subjective narration helps readers analyze narrative intent and reliability.
Effects of Point of View on Storytelling
Point of view shapes the reader's experience by determining whose perspective guides the narrative. It influences how information is revealed and how characters are understood throughout the story.
- Emotional Connection - First-person point of view creates intimacy by allowing direct access to the narrator's thoughts and feelings.
- Reliability and Bias - A limited third-person point of view can introduce subjective interpretation, affecting the trustworthiness of the narrative.
- Scope of Knowledge - Omniscient narration provides a comprehensive understanding of all characters and events, shaping the story's depth and complexity.
Tips for Choosing the Right POV
Choosing the right point of view (POV) is essential for effective storytelling and audience engagement. POV shapes how readers perceive characters and the narrative's emotional impact.
First-person POV offers intimacy by revealing a character's inner thoughts and feelings. Third-person limited allows insight into one character while maintaining narrative flexibility.
