Martial law is a temporary imposition of direct military control over civilian functions during emergencies or unrest. It grants armed forces the authority to maintain order, suspend certain civil liberties, and enforce laws. This infographic breaks down key aspects, historical contexts, and implications of martial law worldwide.
What is Martial Law?
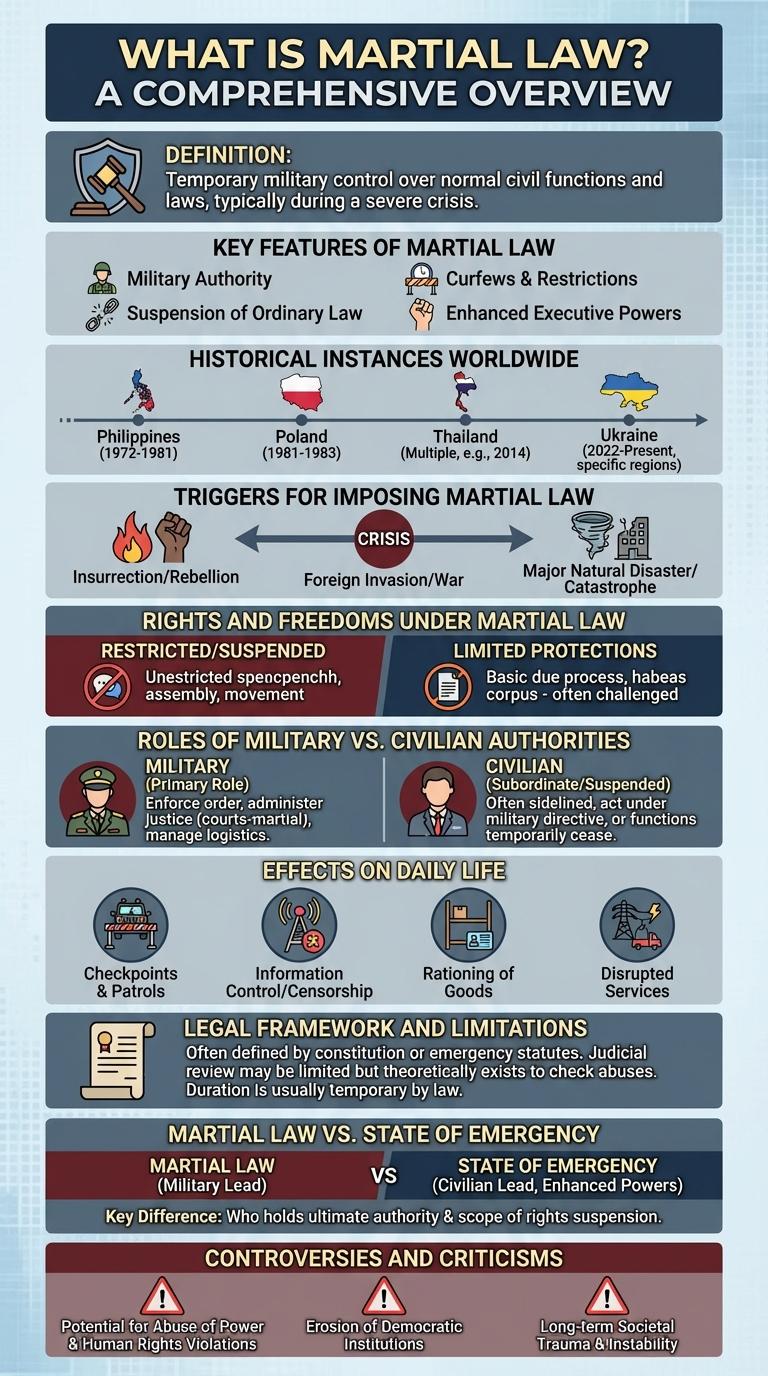
Martial law is the temporary imposition of direct military control over normal civilian functions by a government, usually during emergencies. It replaces civilian authority with military authority to restore order and ensure security. Under martial law, certain civil liberties and rights may be suspended to maintain public safety.
Key Features of Martial Law
Martial law refers to the temporary imposition of direct military control over normal civilian functions of government, typically during emergencies or periods of civil unrest. It grants military authorities the power to enforce laws and maintain order.
Key features of martial law include suspension of ordinary law, curfews, and restrictions on civil liberties such as freedom of movement and assembly. Military tribunals often replace civilian courts, and law enforcement duties shift to military personnel. These measures aim to restore stability swiftly during crises.
Historical Instances Worldwide
Martial law refers to the temporary imposition of direct military control over civilian functions, often during emergencies. Various countries have enforced martial law at critical historical moments for maintaining order and security.
- Poland (1981) - General Wojciech Jaruzelski imposed martial law to suppress political opposition and the Solidarity movement.
- Philippines (1972) - President Ferdinand Marcos declared martial law to extend his rule and control civil unrest.
- Thailand (2014) - The military seized power under martial law following months of political turmoil and protests.
Triggers for Imposing Martial Law
Martial law is imposed during times of severe civil unrest, natural disasters, or threats to national security that overwhelm regular law enforcement. Key triggers include widespread riots, armed insurrections, or the breakdown of public order that endangers citizens and property. Governments use martial law to restore stability by granting military authorities temporary control over civilian functions.
Rights and Freedoms Under Martial Law
Martial law is a temporary imposition of military authority over civilian functions during emergencies. It often involves significant restrictions on civil liberties to maintain order and security.
- Suspension of Habeas Corpus - Individuals can be detained without immediate court intervention under martial law.
- Restriction on Freedom of Movement - Curfews and travel bans are commonly enforced to control populations.
- Limited Freedom of Speech and Assembly - Public gatherings and expressions critical of authorities may be prohibited or censored.
Rights and freedoms under martial law are curtailed to prioritize national security but are meant to be temporary and subject to legal oversight.
Roles of Military vs. Civilian Authorities
| Military Authorities | Civilian Authorities |
|---|---|
| Enforce martial law directives and maintain public order | Implement laws and uphold civil governance under normal conditions |
| Control curfews, checkpoints, and security checkpoints | Manage law enforcement agencies and local government functions |
| Possess the power to detain individuals for security reasons | Protect civil rights and ensure due process through judiciary systems |
| Use military tribunals for violation cases related to martial law | Handle civilian courts and legal proceedings outside martial law enforcement |
| Override civilian authority during emergency situations | Regain full administrative control once martial law is lifted |
Effects on Daily Life
How does martial law impact daily routines? Martial law imposes strict curfews and checkpoints, restricting freedom of movement. Residents often face limited access to essential services and goods during enforcement periods.
What changes occur in communication under martial law? Communication channels may be monitored or restricted by authorities, leading to limited access to information. Internet and phone services can be intermittently disrupted to control the flow of news.
How is personal safety affected during martial law? Military presence increases in public areas, enhancing security but also creating a tense environment. Civilians may experience increased searches and detentions, influencing their sense of safety.
What impact does martial law have on economic activities? Many businesses operate under reduced hours or shut down temporarily. Supply chains face interruptions, causing shortages and price fluctuations in everyday products.
How are educational institutions influenced by martial law? Schools and universities often close or switch to remote learning to comply with restrictions. Students and educators face challenges maintaining normal academic schedules and activities.
Legal Framework and Limitations
Martial law refers to the temporary imposition of direct military control over civilian functions, usually in times of emergency or civil unrest. It is governed by a strict legal framework that outlines the circumstances under which it can be declared and enforced.
The primary legal basis for martial law varies by country but often includes constitutional provisions, emergency laws, and military codes. Limitations on martial law typically ensure protection of fundamental rights, specify its duration, and provide for legislative or judicial oversight.
Martial Law vs. State of Emergency
Martial Law is the imposition of direct military control over normal civilian functions by a government, typically during times of war, rebellion, or severe emergencies. It often involves the suspension of civil liberties and the enforcement of military justice.
A State of Emergency is a governmental declaration that temporarily enhances executive powers to restore order during crises like natural disasters, civil unrest, or pandemics. Unlike Martial Law, it usually retains civilian law enforcement and legal processes.
