Visualizing complex legal concepts through an infographic simplifies understanding and enhances retention. Clear, concise illustrations break down intricate laws into digestible segments, making legal information accessible for everyone. This approach transforms dense legal jargon into engaging and educational content.
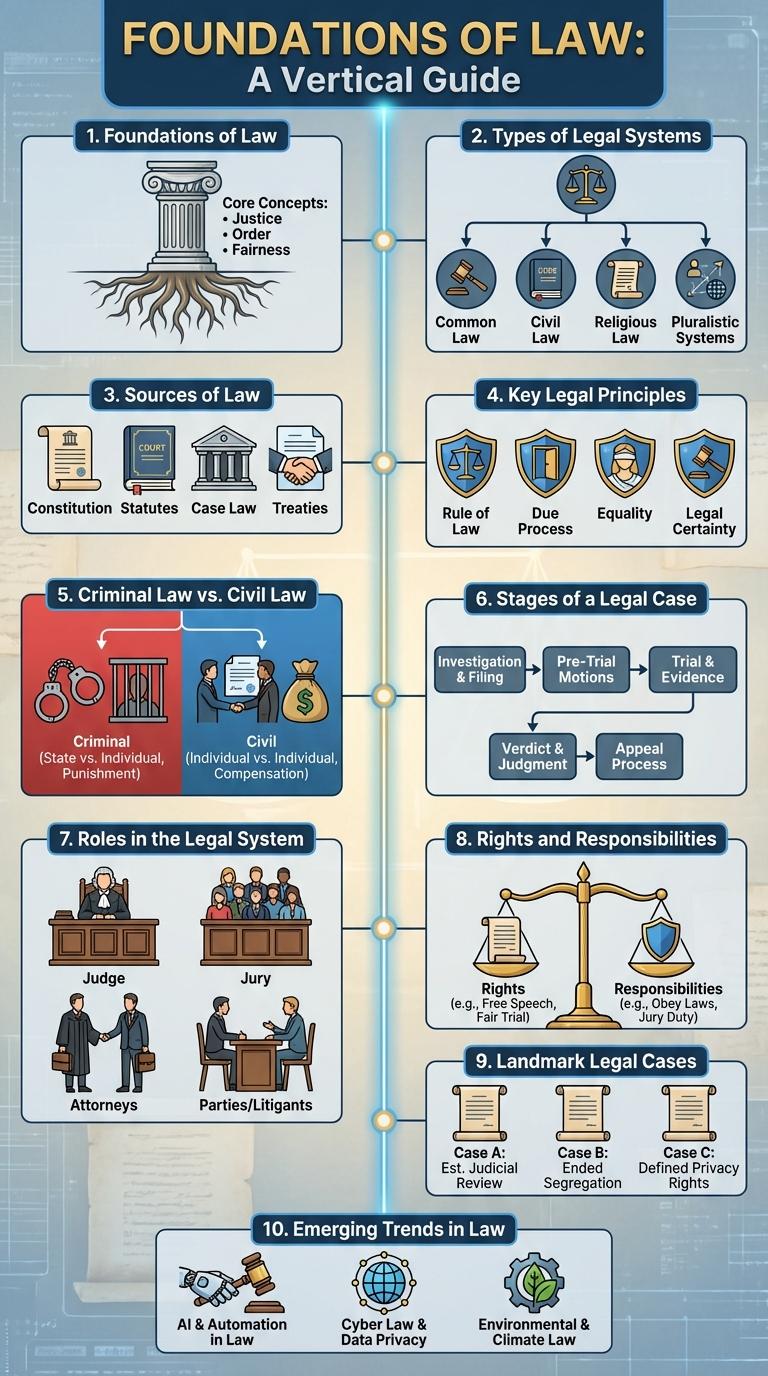
Foundations of Law
The foundations of law are essential principles that provide structure and order to societies. Understanding these core elements is crucial for grasping how legal systems develop and function effectively.
- Natural Law - Asserts that certain rights are inherent and universally recognizable through human reason.
- Constitutional Law - Establishes the framework and authority of government based on a nation's constitution.
- Statutory Law - Comprises laws enacted by legislative bodies to regulate behavior within society.
- Common Law - Develops from judicial decisions and precedents rather than written statutes.
- International Law - Governs relations and agreements between sovereign states and international entities.
The interplay of these foundational elements shapes the rule of law and ensures justice and fairness in legal systems worldwide.
Types of Legal Systems
Legal systems around the world define how laws are created, interpreted, and enforced. Understanding different types helps in comprehending global legal frameworks and cultural contexts.
Common types include Civil Law, Common Law, Religious Law, and Customary Law. Each system has unique principles, procedures, and sources of authority.
Sources of Law
Law is derived from multiple sources that establish legal standards and frameworks within a jurisdiction. Understanding these sources helps clarify how laws are created, interpreted, and enforced.
- Constitution - The foundational legal document outlining the structure of government and fundamental rights.
- Statutory Law - Laws enacted by legislatures to regulate behavior and provide specific rules.
- Case Law - Judicial decisions that interpret statutes and legal principles, creating binding precedents.
- Administrative Law - Rules and regulations issued by government agencies to implement legislative policies.
- Customary Law - Traditional practices recognized as legally binding within certain communities or regions.
Key Legal Principles
Understanding key legal principles is essential for navigating the complexities of law. These principles form the foundation of legal systems worldwide, ensuring justice and fairness.
Rule of Law guarantees that all individuals and institutions are accountable under the law. Due Process ensures fair treatment through the judicial system. Equity provides remedies that are not available under strict legal rules.
Criminal Law vs. Civil Law
Criminal law and civil law serve distinct purposes within the legal system, addressing different types of legal issues. Understanding their differences helps clarify the nature of legal actions and the rights involved.
Criminal law involves offenses against the state, while civil law deals with disputes between private parties.
- Purpose - Criminal law aims to punish wrongful acts that harm society, whereas civil law seeks to resolve disputes and provide compensation.
- Burdens of Proof - Criminal cases require proof beyond a reasonable doubt; civil cases rely on the preponderance of the evidence.
- Outcomes - Criminal law outcomes may include imprisonment or fines, civil law results typically involve monetary damages or specific performance orders.
Stages of a Legal Case
Understanding the stages of a legal case helps clarify the judicial process. The key phases include investigation, trial, and judgment. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring justice is served efficiently and fairly.
Roles in the Legal System
The legal system is composed of various key roles that ensure justice is served and laws are upheld. Each role has distinct responsibilities that contribute to the functioning of courts and legal processes.
Judges interpret and apply the law, overseeing court proceedings and making rulings. Lawyers represent clients, providing legal advice and advocating on their behalf in court.
Rights and Responsibilities
Understanding your legal rights and responsibilities is essential for navigating everyday situations confidently. Rights protect individuals' freedoms and guarantees under the law, while responsibilities require adherence to laws and ethical conduct. Balancing both ensures justice, fairness, and social order within communities.
Landmark Legal Cases
| Landmark Legal Case | Significance |
|---|---|
| Marbury v. Madison (1803) | Established judicial review, empowering courts to declare laws unconstitutional |
| Brown v. Board of Education (1954) | Declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional, advancing civil rights |
| Roe v. Wade (1973) | Recognized a woman's constitutional right to abortion under privacy rights |
| Miranda v. Arizona (1966) | Established Miranda rights, requiring police to inform suspects of their rights |
| United States v. Nixon (1974) | Limited presidential privilege, enforcing rule of law during Watergate scandal |
