Batas serve as a significant cultural garment symbolizing tradition and identity in various communities. This infographic visually explores the history, styles, and cultural significance of batas, highlighting its role in everyday wear and special occasions. Understanding these aspects provides a deeper appreciation for the garment's enduring relevance and diversity.
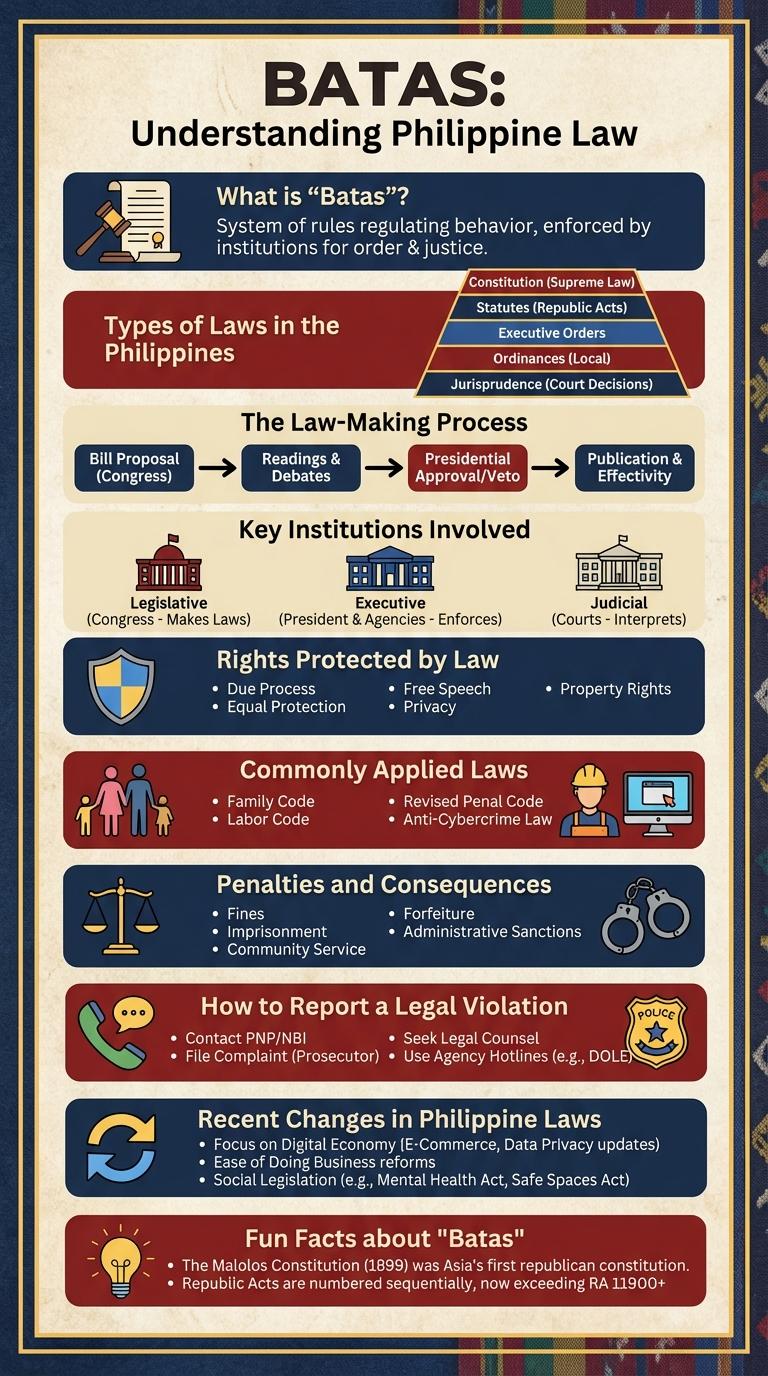
What is "Batas"?
"Batas" is a Filipino term meaning "law" or "rule." It refers to the set of guidelines or regulations governing behavior within a society.
Batas serves as a framework to maintain order and ensure justice among citizens.
- Definition - Batas are legally binding rules established by authorities or governing bodies.
- Purpose - Batas aims to regulate conduct and protect the rights of individuals.
- Scope - Batas applies to various areas such as criminal, civil, and administrative matters.
Types of Laws in the Philippines
The Philippines has a comprehensive legal system comprising various types of laws that govern different aspects of society. These laws ensure order, protect rights, and promote justice throughout the country.
Types of laws in the Philippines include statutory laws, which are enacted by the legislative branch, and constitutional laws, which are derived from the Philippine Constitution. Administrative laws regulate government agencies, while criminal laws address offenses and prescribe penalties.
| Type of Law | Description |
| Constitutional Law | Fundamental laws derived from the 1987 Philippine Constitution. |
| Statutory Law | Legislation enacted by Congress, such as Republic Acts and Codes. |
| Administrative Law | Rules and regulations implemented by government agencies. |
| Criminal Law | Laws defining crimes and penalties, like the Revised Penal Code. |
| Civil Law | Governs private rights and obligations, including contracts and family law. |
The Law-Making Process
The law-making process begins with the introduction of a bill in either the House of Representatives or the Senate. The bill undergoes committee evaluation, debates, and multiple readings before a vote is taken. Once approved by both chambers, the bill is sent to the President for signing into law or veto.
Key Institutions Involved
Batas is a regulatory framework that involves several key institutions to ensure compliance and enforcement. These institutions work collaboratively to implement policies, monitor activities, and address violations effectively.
- Legislative Bodies - Create and amend laws related to batas to provide a legal foundation.
- Regulatory Agencies - Oversee the enforcement and adherence to batas within relevant sectors.
- Judicial Institutions - Interpret batas-related laws and adjudicate disputes or violations.
The combined efforts of these institutions maintain the integrity and effectiveness of batas implementation.
Rights Protected by Law
Batas laws ensure the protection of fundamental human rights including freedom of speech, right to privacy, and equal treatment under the law. These rights form the core principles that safeguard individuals from discrimination and abuse.
Legal frameworks establish clear guidelines for upholding civil liberties in various contexts such as employment, education, and public services. Enforcement mechanisms guarantee that violations are addressed promptly, reinforcing citizens' trust in the justice system.
Commonly Applied Laws
Batas refer to laws that regulate social behavior within a community or country. Commonly applied laws ensure order and justice by setting clear rules for citizens.
These laws include criminal law, civil law, labor law, family law, and environmental law. Criminal law addresses offenses against the state or individuals, imposing penalties like imprisonment. Civil law manages disputes between private parties involving contracts, property, and personal rights.
Penalties and Consequences
| Penalty | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Monetary Fines | Financial burden varying by violation severity, enforced by regulatory bodies |
| Imprisonment | Loss of freedom for set periods due to serious offenses or repeated violations |
| License Suspension | Temporary or permanent revocation of permits or licenses required for certain activities |
| Community Service | Mandated hours of unpaid work contributing to public welfare |
| Criminal Record | Permanent documentation affecting future employment and legal status |
How to Report a Legal Violation
How do you report a legal violation effectively? Identify the specific law that has been broken and gather all relevant evidence. Submit a formal complaint to the appropriate authorities, such as the police or legal oversight bodies, to initiate the investigation process.
Recent Changes in Philippine Laws
The Philippine legal landscape has experienced significant updates aimed at enhancing governance and public welfare. Recent changes in laws reflect the government's commitment to transparency, social justice, and economic progress.
- Data Privacy Act Amendments - Enhanced provisions strengthen personal data protection and impose stricter penalties for violations.
- Community-Based Monitoring System Act - Institutionalizes community data gathering to improve public service delivery and development planning.
- Sustainable Forest Management Act Update - Introduces stricter regulations to promote biodiversity conservation and combat illegal logging.
