An infographic about IP visually breaks down the complex concept of Internet Protocol, highlighting its role in addressing and routing data across networks. It simplifies technical terms like IPv4, IPv6, and subnet masks to enhance understanding for diverse audiences. Such visuals improve retention and offer quick reference points for networking fundamentals.
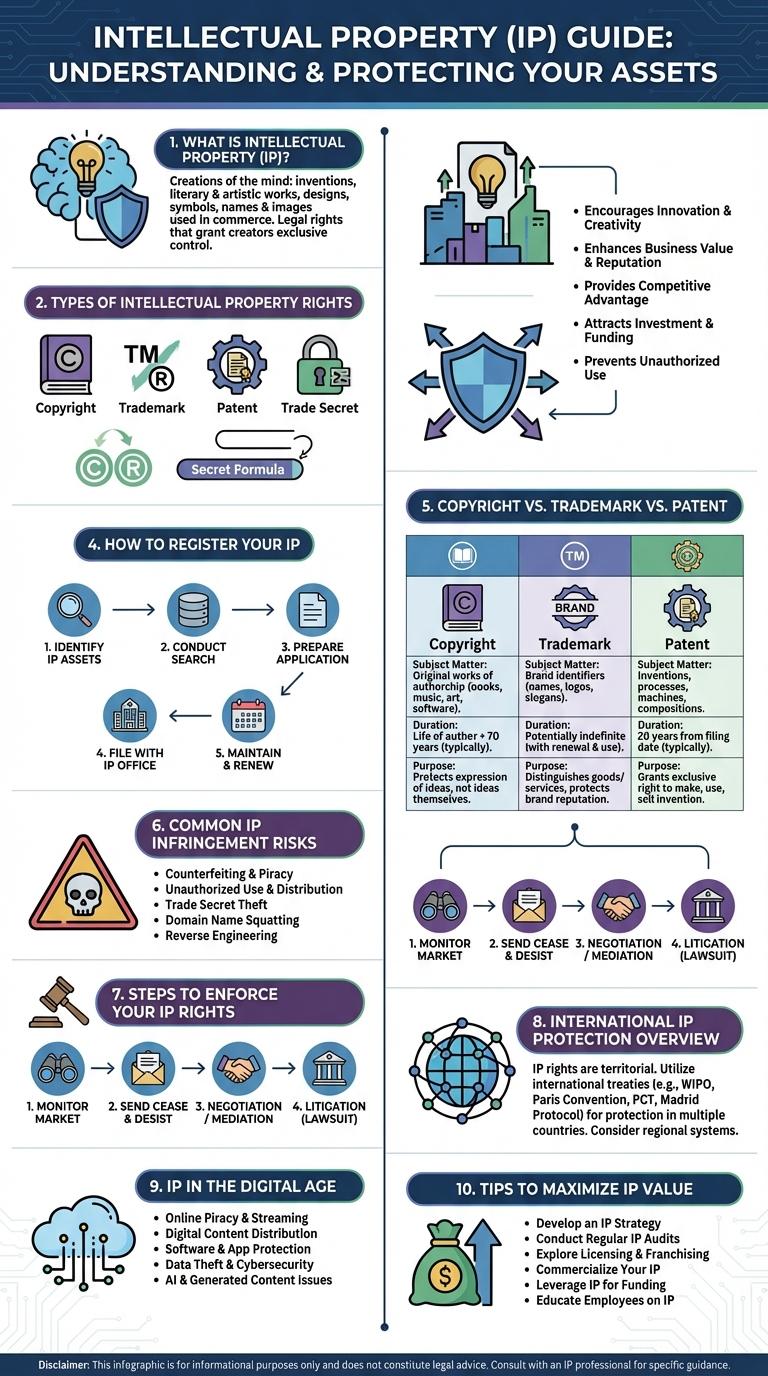
What is Intellectual Property (IP)?
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Intellectual Property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, including inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, symbols, names, and images used in commerce. |
| Types of IP | Patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, and industrial designs. |
| Purpose | Protects creators' rights, encourages innovation, and promotes fair competition. |
| Legal Framework | Governed by national and international laws such as the TRIPS Agreement and WIPO treaties. |
| Importance | Drives economic growth by securing exclusive rights to use and commercialize intellectual assets. |
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual Property (IP) protects creations of the mind, ensuring creators can control and benefit from their innovations. The main types of Intellectual Property Rights include copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. Each type serves a unique purpose, safeguarding different forms of creative and intellectual work.
The Importance of Protecting IP
Why is protecting intellectual property essential for innovation? Safeguarding IP ensures creators retain exclusive rights to their inventions and creative works. This protection encourages investment in research and development, fostering continuous innovation and economic growth.
How to Register Your IP
Registering your intellectual property (IP) secures your legal rights to your creations, inventions, or brands. Begin by identifying the type of IP--patent, trademark, or copyright--and gather necessary documents. Submit your application to the appropriate government office, such as the USPTO for patents and trademarks or the Copyright Office for copyrights.
Copyright vs. Trademark vs. Patent
Intellectual Property (IP) protects creations of the mind, categorized mainly into copyright, trademark, and patent. Each type safeguards different aspects of innovation and brand identity.
Copyright protects original works such as literature, music, and art, granting exclusive rights to the creator to reproduce and distribute. It lasts for the creator's lifetime plus 70 years in most jurisdictions.
Trademark protects symbols, names, and slogans used to identify goods or services, helping consumers distinguish brands in the marketplace. Trademarks can be renewed indefinitely as long as they are in use.
Patent protects inventions and technological innovations, granting the inventor exclusive rights to use and commercialize the invention typically for 20 years. Patents require public disclosure of the invention in exchange for protection.
Common IP Infringement Risks
Intellectual Property (IP) infringement poses significant risks to businesses and creators, often resulting in legal and financial consequences. Understanding common IP infringement risks helps in implementing effective protection strategies.
- Unauthorized Use - Using copyrighted materials or trademarks without permission violates IP rights and can lead to lawsuits.
- Counterfeiting - Producing and selling fake goods under someone else's brand damages reputation and revenue.
- Patent Infringement - Copying patented inventions without licensing rights results in costly legal disputes.
Steps to Enforce Your IP Rights
Understanding how to enforce your intellectual property (IP) rights is crucial to protecting your creative and commercial assets. Effective enforcement helps prevent unauthorized use and maintains the value of your IP.
- Identify Infringement - Monitor the market regularly to detect any unauthorized use of your IP.
- Document Evidence - Collect and store proof of infringement such as samples, dates, and witness statements.
- Send Cease and Desist Letter - Notify the infringer formally to demand the stop of unauthorized activities.
- Seek Legal Advice - Consult IP attorneys to evaluate the strength of your case and options available.
- Initiate Legal Action - File lawsuits or complaints to enforce your rights through courts or relevant authorities.
Consistent enforcement protects your IP assets and promotes innovation and fair competition.
International IP Protection Overview
International intellectual property (IP) protection ensures creators and businesses safeguard their innovations and brands across multiple countries. It involves treaties and organizations that harmonize laws and enforcement globally, preventing infringement and counterfeit goods.
Key international agreements like the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) and the Madrid Protocol streamline patent and trademark registration worldwide. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) plays a central role in administering these treaties and facilitating cross-border IP dispute resolution.
IP in the Digital Age
Intellectual Property (IP) in the digital age faces evolving challenges and opportunities due to rapid technology growth. Digital platforms demand new strategies to protect creative works and innovations.
Effective IP management supports innovation, safeguards digital content, and fosters global collaboration in technology and creativity.
- Digital Content Protection - Digital rights management (DRM) systems help secure copyrights on music, videos, and software from unauthorized distribution.
- Patent Innovations - Patents protect technological inventions including software algorithms and digital tools essential in modern industries.
- Global IP Enforcement - International treaties and agreements streamline IP protection across borders to combat digital piracy and counterfeiting.
