Understanding the legal basis is essential for interpreting laws, regulations, and official guidelines accurately. This infographic visually breaks down key legal principles, sources of law, and their hierarchical structure to clarify complex legal frameworks. Clear insight into these foundations aids in better compliance and informed decision-making.
Understanding Legal Basis: An Overview
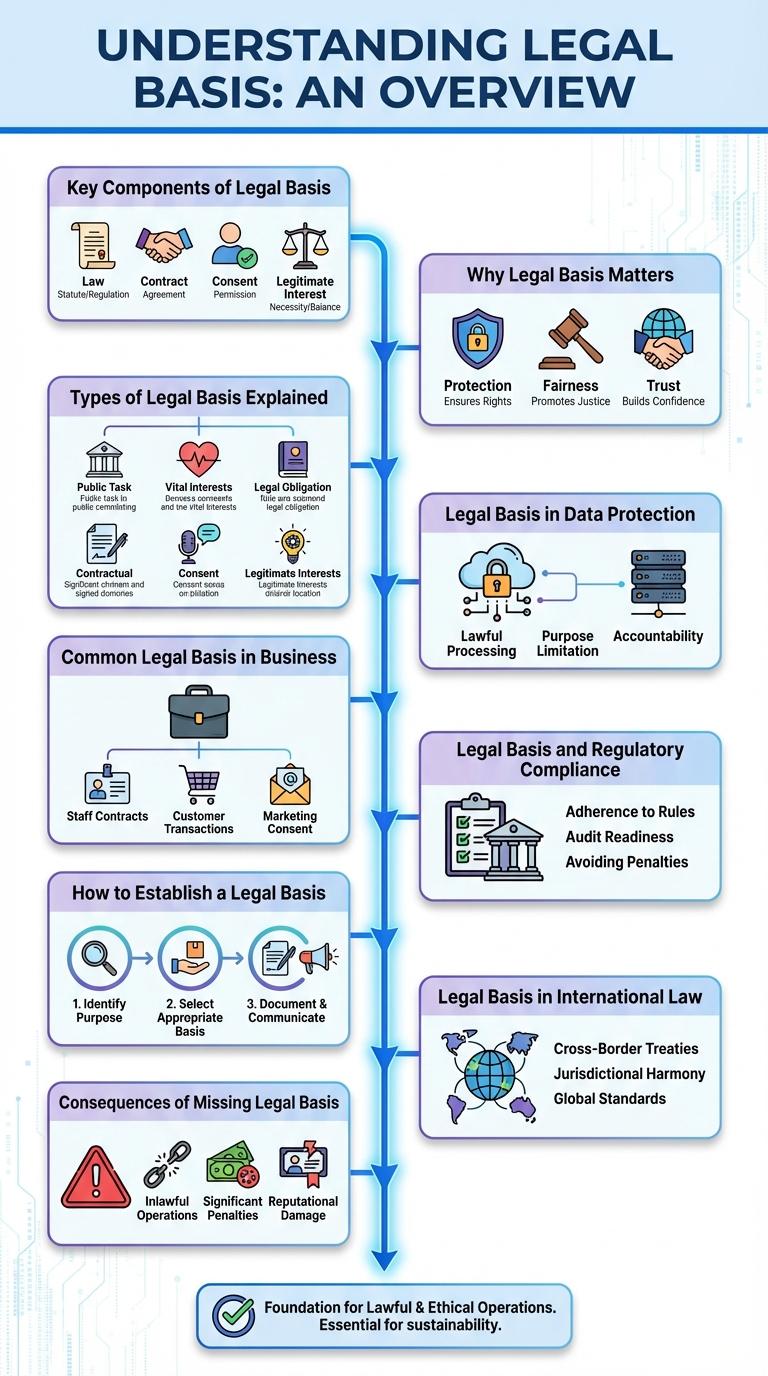
Understanding the legal basis is essential for interpreting laws and regulations accurately. Legal basis refers to the fundamental laws, statutes, or constitutional provisions that justify and empower governmental actions and policies. It provides the framework that ensures actions are lawful, legitimate, and consistent with established legal principles.
Key Components of Legal Basis
The legal basis provides the foundation for laws and regulations within a jurisdiction. It outlines the principles and authorities that govern legal actions and decisions.
- Statutory Laws - Laws enacted by legislative bodies that establish legal standards and requirements.
- Constitutional Provisions - Fundamental principles and rights outlined in a country's constitution that guide legal interpretation.
- Judicial Precedents - Previous court decisions that serve as authoritative guidelines for resolving similar legal issues.
Why Legal Basis Matters
Legal basis establishes the foundation for lawful actions and decisions within any organization or government. It ensures that all activities comply with established laws and regulations.
Understanding the legal basis minimizes risks of disputes and legal penalties. It promotes transparency, accountability, and trust among stakeholders and the public.
Types of Legal Basis Explained
What are the different types of legal basis in law? Legal basis refers to the foundation or authority behind a law, regulation, or legal action. Understanding each type helps clarify the scope and application of legal provisions.
| Type of Legal Basis | Description |
|---|---|
| Constitutional Basis | Derived from a country's constitution, this basis provides supreme authority for laws and government actions. |
| Statutory Basis | Established by legislation passed by a governing body, such as parliament or congress, providing specific rules or requirements. |
| Judicial Basis | Grounded in court decisions and legal precedents that interpret laws and establish binding principles. |
| Administrative Basis | Based on regulations and orders issued by government agencies under authority delegated by statutes. |
| Contractual Basis | Arising from agreements between parties, legally binding them to fulfill obligations as specified. |
Legal Basis in Data Protection
Legal basis in data protection refers to the lawful grounds on which personal data is processed according to regulations like the GDPR. Key legal bases include consent, contractual necessity, compliance with legal obligations, vital interests, public tasks, and legitimate interests. Proper identification of the legal basis ensures transparency, accountability, and compliance in data handling practices.
Common Legal Basis in Business
| Legal Basis | Description |
|---|---|
| Contracts Law | Governs agreements between businesses and individuals, ensuring enforceability of commercial deals. |
| Corporate Law | Regulates company formation, governance, and compliance with statutory requirements. |
| Labor Law | Defines employee rights, employer obligations, and workplace standards. |
| Intellectual Property Law | Protects creations of the mind including trademarks, patents, and copyrights. |
| Tax Law | Outlines tax obligations for businesses, including income tax, VAT, and payroll taxes. |
Legal Basis and Regulatory Compliance
Legal basis establishes the foundation for lawful actions and decisions within organizations. Regulatory compliance ensures adherence to laws and standards governing business operations.
- Statutory Law - Laws enacted by legislative bodies that organizations must follow to maintain legal operations.
- Contractual Agreements - Binding agreements that define rights and obligations between parties under legal frameworks.
- Regulatory Requirements - Rules imposed by governmental agencies to enforce standards and protect public interests.
How to Establish a Legal Basis
Establishing a legal basis involves identifying the formal authority or law that permits an action or process. This foundation ensures that activities comply with established legal frameworks and uphold the rule of law.
Begin by reviewing relevant statutes, regulations, or contracts applicable to the specific context. Verify that the legal provisions explicitly authorize the intended action or decision. Documenting the legal basis supports transparency and accountability in all legal and administrative procedures.
Legal Basis in International Law
Legal basis in international law establishes the framework for state interactions and the resolution of disputes. It comprises treaties, customary international law, and general principles accepted by the international community.
Sources such as the United Nations Charter and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties provide authoritative guidance. International courts and tribunals rely on these legal foundations to ensure compliance and enforce accountability.
