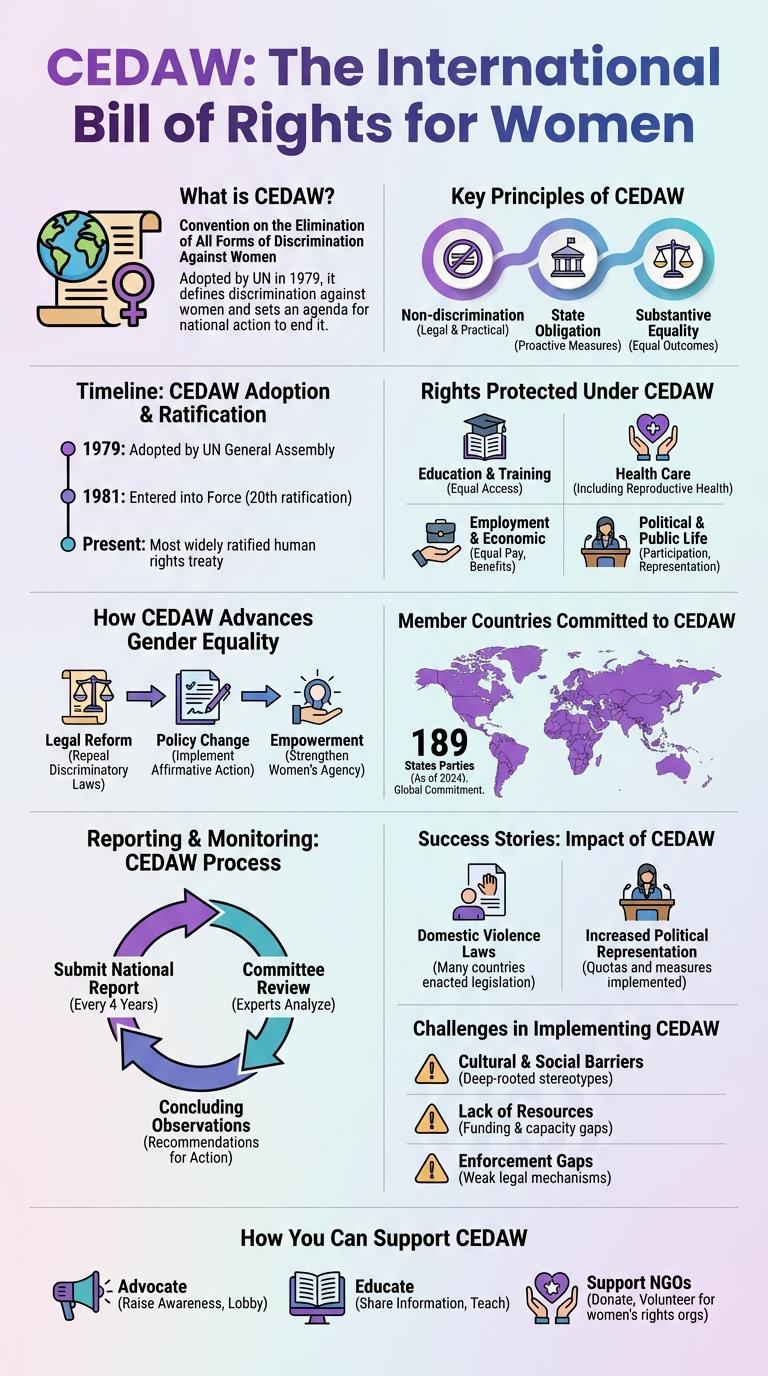
The infographic provides a clear visual overview of CEDAW, highlighting its role as the international treaty dedicated to eliminating discrimination against women. Key provisions and the impact of CEDAW on promoting gender equality worldwide are showcased through engaging graphics. Essential statistics and country compliance data emphasize the ongoing global efforts to implement its principles effectively.
What is CEDAW?
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted by the United Nations in 1979. It serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting women's rights and gender equality worldwide.
- Definition - CEDAW is often described as the international bill of rights for women, aiming to eliminate discrimination in all forms.
- Purpose - It obliges countries to implement measures to ensure equal rights for women in political, social, economic, and cultural fields.
- Scope - The treaty addresses issues including education, employment, health, and legal protections to empower women globally.
Key Principles of CEDAW
| Key Principles | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-Discrimination | Guarantees equal rights and opportunities for women in political, economic, social, and cultural spheres without any discrimination. |
| Equality Between Men and Women | Establishes legal and practical equality in all areas of life including family, work, and public life. |
| State Obligation | Requires governments to take appropriate measures to eliminate discrimination against women and promote gender equality. |
| Intersectionality | Recognizes multiple and overlapping forms of discrimination faced by women due to race, ethnicity, disability, or other status. |
| Accountability and Monitoring | Mandates regular reporting and review processes to monitor implementation and progress in achieving gender equality. |
Timeline: CEDAW Adoption & Ratification
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on December 18, 1979. Countries began ratifying CEDAW soon after its adoption, with many key nations joining in the early 1980s. Ratification signifies a commitment to eliminating discrimination against women and promoting gender equality globally.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1979 | CEDAW adopted by UN General Assembly |
| 1981 | CEDAW entered into force |
| 1995 | Beijing Declaration reinforced CEDAW goals |
| 2000 | Most UN member states ratified CEDAW |
| 2020+ | Ongoing ratification and implementation efforts |
Rights Protected Under CEDAW
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is a vital international treaty aimed at promoting gender equality. It protects women's rights in various social, political, and economic areas worldwide.
CEDAW ensures equal access to education, employment, and healthcare for women. It safeguards women's rights to participate in political and public life. The treaty also addresses discrimination against women in marriage and family relations.
How CEDAW Advances Gender Equality
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is a landmark international treaty dedicated to promoting women's rights globally. It establishes legal standards to combat gender discrimination and ensure equal opportunities for women in all spheres of life.
CEDAW advances gender equality by obligating countries to implement policies that eliminate discrimination in education, employment, and healthcare. The treaty promotes women's political participation, access to justice, and protection from gender-based violence, driving systemic change and empowerment.
Member Countries Committed to CEDAW
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) has been ratified by 189 member countries worldwide, demonstrating a global commitment to gender equality. These countries pledge to implement measures that eliminate discrimination against women in political, economic, social, and cultural fields. Non-member states and those with reservations are actively engaged in dialogues to align with the standards set by CEDAW.
Reporting & Monitoring: CEDAW Process
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) ensures member states submit regular reports on measures taken to uphold women's rights. The CEDAW Committee monitors these reports to evaluate progress and recommend actions for compliance.
- Initial Report Submission - States parties submit an initial report within one year of ratifying the convention, outlining legal and practical measures taken.
- Periodic Reporting - Every four years, states provide updated reports detailing their progress and challenges in implementing CEDAW standards.
- Committee Review and Recommendations - The CEDAW Committee examines reports, engages in constructive dialogue, and issues concluding observations with recommendations for improvement.
Success Stories: Impact of CEDAW
CEDAW, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, has driven significant progress in gender equality worldwide. Its enforcement has empowered women through legal reforms and social changes.
- Legal Reforms - CEDAW prompted over 180 countries to revise laws discriminating against women, enhancing protections and rights.
- Increased Women's Participation - Political and economic participation of women surged due to policies inspired by CEDAW commitments.
- Reduction in Gender-Based Violence - Countries adopting CEDAW guidelines reported measurable declines in domestic violence and trafficking.
These successes illustrate CEDAW's critical role in advancing global gender equality and women's empowerment.
Challenges in Implementing CEDAW
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) aims to promote gender equality globally. Despite its adoption by many countries, challenges persist in fully implementing its provisions.
Common obstacles include cultural resistance, lack of political will, and insufficient resources. These factors hinder the effective enforcement of laws designed to protect women's rights under CEDAW.
