Justice is a fundamental principle that ensures fairness, equality, and accountability within society. Infographics visually represent the complex concepts of justice by breaking down legal systems, rights, and processes into easily understandable elements. Clear and concise graphics help raise awareness about the importance of justice in maintaining social order and protecting human rights.
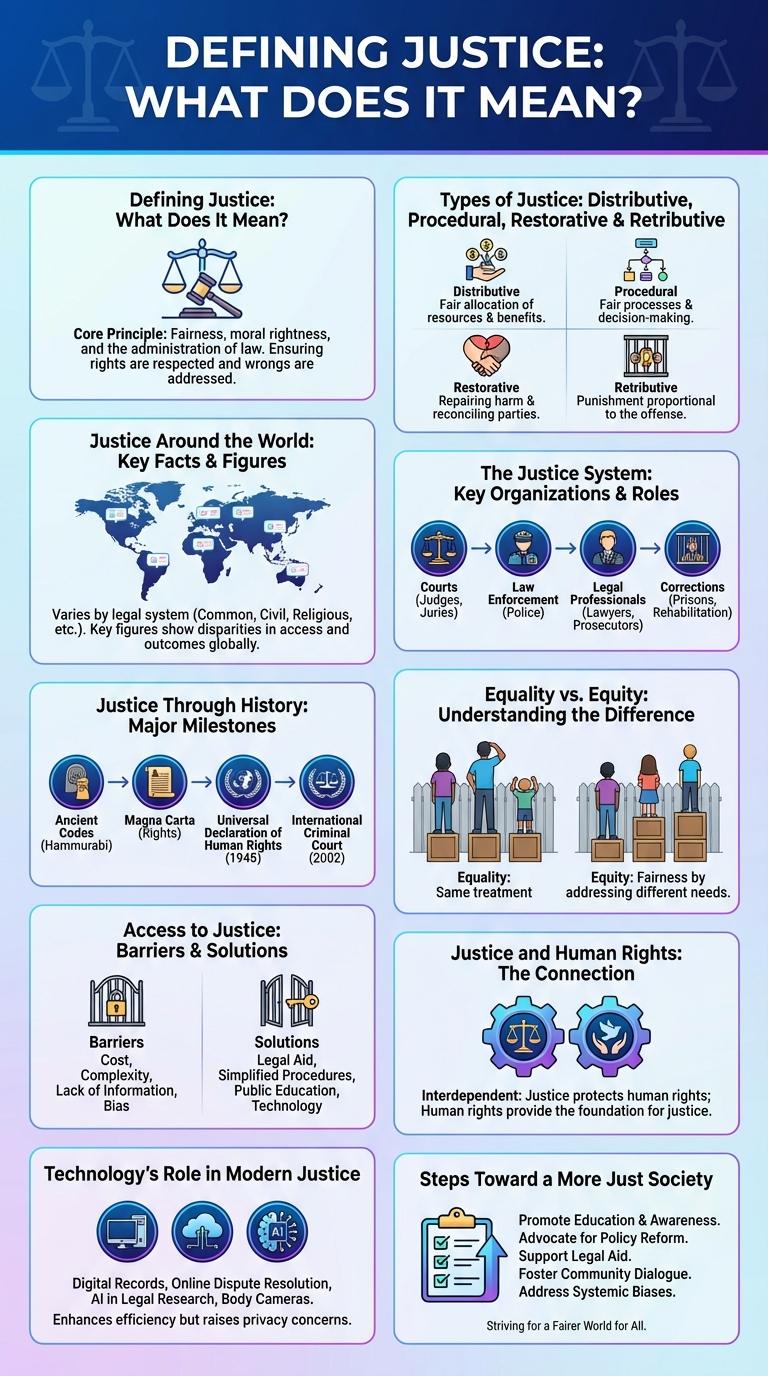
Defining Justice: What Does It Mean?
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Justice is the principle of fairness and moral rightness within a society. |
| Types | Distributive Justice, Procedural Justice, Retributive Justice, Restorative Justice |
| Core Elements | Equality, Fairness, Accountability, Rights Protection |
| Purpose | To ensure equitable treatment and maintain social order by upholding laws and ethical standards. |
| Philosophical Roots | Rooted in theories by Aristotle, John Rawls, and others focusing on fairness and social contract. |
Types of Justice: Distributive, Procedural, Restorative & Retributive
Justice manifests in various forms that address fairness and accountability within society. Distributive justice concerns the equitable allocation of resources, while procedural justice emphasizes fairness in the processes that resolve disputes. Restorative justice focuses on repairing harm through reconciliation, and retributive justice centers on appropriate punishment for wrongdoing.
Justice Around the World: Key Facts & Figures
What defines justice across different countries worldwide? Justice systems vary globally, reflecting cultural, legal, and social norms. Understanding these differences highlights how nations address fairness and law enforcement.
| Country | Justice System Type |
|---|---|
| United States | Common Law with Jury Trials |
| Germany | Civil Law with Inquisitorial Courts |
| Japan | Mixed System with Emphasis on Mediation |
| Saudi Arabia | Sharia Law-based Courts |
How effectively do countries deliver justice on a global scale? World Justice Project reports rank countries using metrics like civil justice, criminal justice, and fundamental rights. Scandinavian countries show high scores due to transparency and accessibility.
| Region | Justice Performance Score |
|---|---|
| Nordic Countries | 85-90% |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 35-45% |
| Latin America | 50-60% |
| Europe (excluding Nordic) | 70-80% |
The Justice System: Key Organizations & Roles
The justice system ensures fairness and law enforcement through a network of organizations and defined roles. Understanding these key components helps clarify how justice is administered in society.
- Law Enforcement Agencies - Responsible for investigating crimes, maintaining public order, and apprehending suspects.
- Court System - Interprets laws, conducts trials, and adjudicates disputes between parties.
- Prosecutors - Represent the state by presenting evidence to prove the guilt of the accused in criminal cases.
- Defense Attorneys - Provide legal representation and defend individuals accused of crimes.
- Correctional Institutions - Manage the rehabilitation and incarceration of convicted offenders.
Justice Through History: Major Milestones
Justice has evolved through centuries, shaping societies and legal systems worldwide. Key historical milestones reflect the ongoing quest for fairness and equality.
The Code of Hammurabi established one of the first known legal frameworks in ancient Mesopotamia around 1754 BCE. The Magna Carta of 1215 marked a significant step toward limiting royal power and protecting individual rights in England.
The establishment of the U.S. Constitution in 1787 laid a foundation for modern democratic justice principles. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted in 1948, set global standards for human dignity and legal fairness.
Equality vs. Equity: Understanding the Difference
Justice ensures fair treatment, but understanding the difference between equality and equity is essential for true fairness. Equality means providing the same resources or opportunities to everyone, while equity involves distributing resources based on individual needs to achieve equal outcomes. Recognizing these concepts helps create a more inclusive and just society.
Access to Justice: Barriers & Solutions
Access to justice ensures that all individuals can seek and obtain remedies through fair legal systems. Barriers such as high costs, complex procedures, and lack of awareness prevent many from accessing legal support.
Financial constraints limit the ability to hire legal representation, while complicated legal language discourages non-experts from pursuing their rights. Remote locations often lack nearby legal services, creating geographical hurdles. Solutions include legal aid programs, simplified procedures, and digital platforms providing remote access to justice resources.
Justice and Human Rights: The Connection
Justice serves as the foundation for upholding human rights globally. Protecting human rights ensures fairness and dignity for all individuals within a society.
- Equality Before the Law - Justice guarantees that every person receives equal treatment without discrimination or bias.
- Protection of Fundamental Rights - Justice enforces laws that safeguard freedoms such as speech, privacy, and assembly.
- Accountability and Redress - Justice systems provide mechanisms for addressing violations and delivering fair remedies to victims.
Technology's Role in Modern Justice
Technology has transformed modern justice by enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of legal processes. Digital tools enable faster case management, evidence analysis, and legal research.
Artificial intelligence aids in predicting case outcomes and identifying legal precedents. Blockchain ensures transparency and security in handling court records and contracts.
