Visual representations in literature highlight key themes, historical periods, and influential authors, making complex information more accessible and engaging. Infographics distill vast amounts of literary data into concise, visually appealing formats that enhance comprehension and retention. This approach transforms literary analysis into an interactive experience, appealing to both students and enthusiasts.
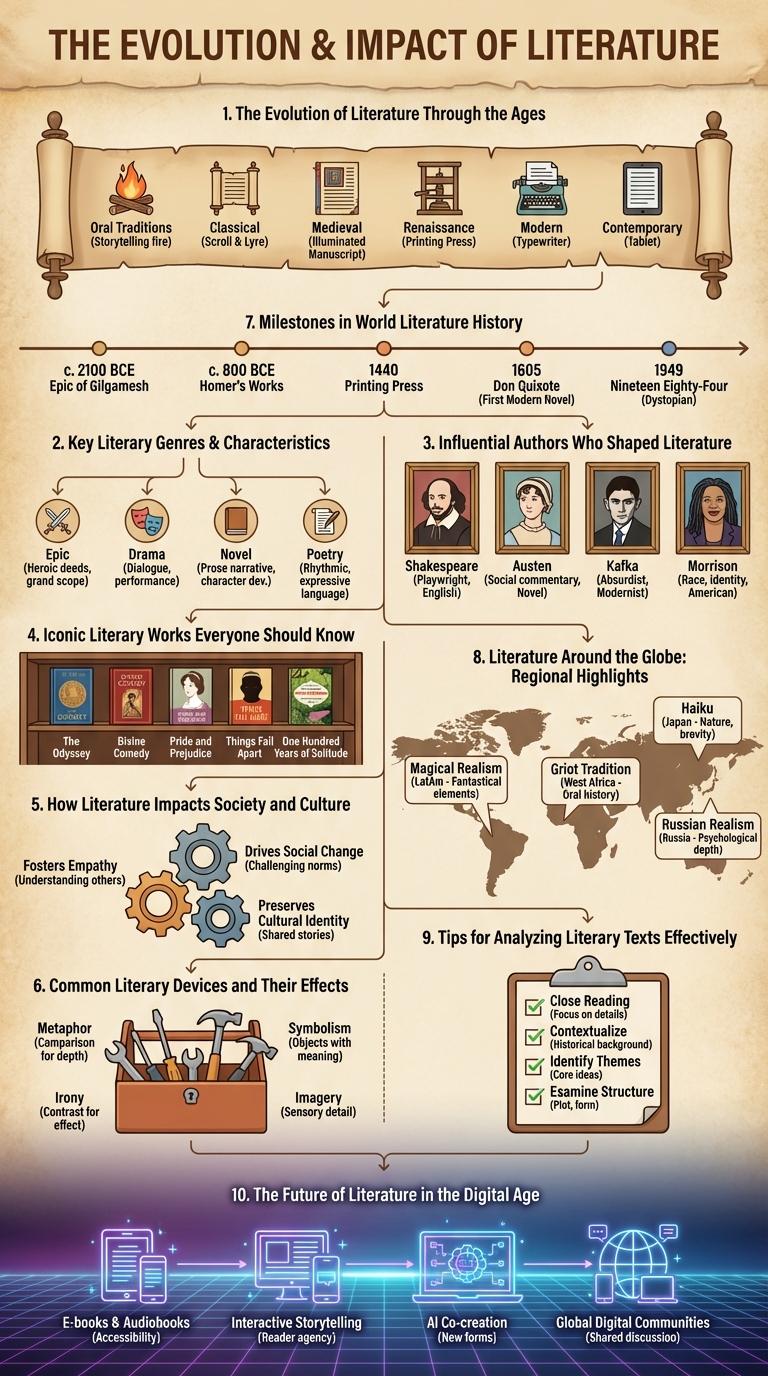
The Evolution of Literature Through the Ages
The evolution of literature traces the transformation of human expression from ancient oral traditions to modern digital narratives. Key periods include Ancient Literature, Medieval Literature, the Renaissance, and Contemporary Literature, each reflecting societal changes and technological advancements. Literary forms and themes continuously adapt, highlighting cultural shifts and the enduring human quest for meaning.
Key Literary Genres and Their Characteristics
Literature encompasses a variety of genres, each with distinct characteristics that engage readers differently. Key literary genres include fiction, nonfiction, poetry, drama, and fantasy, catering to diverse tastes and purposes. Understanding these genres helps readers appreciate the unique styles, themes, and structures that define literary works.
| Genre | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Fiction | Imaginary narratives, plot-driven, character development |
| Nonfiction | Factual writing, informative, real events and people |
| Poetry | Expressive language, rhythm, often uses meter and rhyme |
| Drama | Scripted performance, dialogue-focused, staged presentation |
| Fantasy | Imaginative worlds, magical elements, heroic quests |
Influential Authors Who Shaped Literature
Who are the most influential authors that shaped literature throughout history?
These writers introduced groundbreaking themes and styles that transformed narrative art. Their works continue to inspire readers and shape literary traditions globally.
| Author | Contribution |
|---|---|
| William Shakespeare | Revolutionized drama and poetry with complex characters and timeless themes. |
| Jane Austen | Pioneered social commentary through novels focusing on manners and relationships. |
| James Joyce | Advanced modernist literature with stream-of-consciousness technique. |
| Leo Tolstoy | Explored deep philosophical and ethical questions in epic narratives. |
| Toni Morrison | Highlighted African American experiences and identity in powerful storytelling. |
Iconic Literary Works Everyone Should Know
Iconic literary works have shaped cultures and influenced generations worldwide. These masterpieces continue to inspire readers with timeless themes and unforgettable characters.
Exploring essential literary classics enhances understanding of human nature and society.
- To Kill a Mockingbird - Harper Lee's novel addresses racial injustice through the eyes of a child in the American South.
- 1984 - George Orwell's dystopian tale warns of totalitarianism and loss of individual freedom.
- Pride and Prejudice - Jane Austen explores social class and romantic misunderstandings in 19th-century England.
How Literature Impacts Society and Culture
Literature serves as a mirror reflecting societal values, beliefs, and challenges, shaping cultural identities across generations. It captures the essence of human experience, fostering empathy and understanding among diverse communities.
Through storytelling, literature preserves history and sparks critical thinking, influencing social change and cultural evolution. Its impact extends beyond entertainment, driving education and inspiring movements worldwide.
Common Literary Devices and Their Effects
Literature uses various literary devices to enhance storytelling and convey deeper meanings. These devices help readers connect with the text emotionally and intellectually.
- Metaphor - A figure of speech that compares two unrelated things to highlight a shared quality.
- Foreshadowing - A technique that hints at future events, building suspense and anticipation.
- Irony - A contrast between expectations and reality, often revealing deeper truths or humor.
- Alliteration - The repetition of initial consonant sounds to create rhythm and mood.
- Symbolism - Using symbols to represent ideas or concepts beyond the literal meaning.
Understanding these literary devices enriches the reading experience and interpretation of texts.
Milestones in World Literature History
World literature has evolved through significant milestones that shaped cultural narratives and artistic expression. Key historical moments highlight the development of storytelling, poetry, and prose across civilizations.
- The Epic of Gilgamesh - The earliest known literary work from ancient Mesopotamia, marking the beginning of written storytelling.
- Homer's Iliad and Odyssey - Foundation of Western literature with epic poems that influenced narrative structure and themes.
- Shakespearean Plays - Revolutionized English literature through innovative use of language and exploration of human nature.
Literature Around the Globe: Regional Highlights
Literature around the globe reflects diverse cultural narratives and historical contexts, shaping unique regional identities. Each area offers distinctive storytelling traditions that influence global literary landscapes.
In Asia, classical epics and modern novels coexist, showcasing a fusion of ancient wisdom and contemporary issues. African literature often addresses themes of colonialism and resilience, rich with oral storytelling heritage.
Tips for Analyzing Literary Texts Effectively
Analyzing literary texts requires a deep understanding of themes, characters, and stylistic devices. Focusing on key elements enhances comprehension and critical thinking.
Identify the main themes and how they develop throughout the text. Examine character motivations and relationships to uncover underlying messages. Pay attention to literary devices such as symbolism, imagery, and tone to enrich interpretation.
