The Austronesian language family spans thousands of islands across Southeast Asia and the Pacific, connecting over 1,200 languages with shared linguistic roots. This infographic highlights key features such as geographic distribution, linguistic diversity, and cultural significance. Exploring these elements reveals the vast influence of Austronesian languages on global communication and heritage.
Origins of the Austronesian Peoples
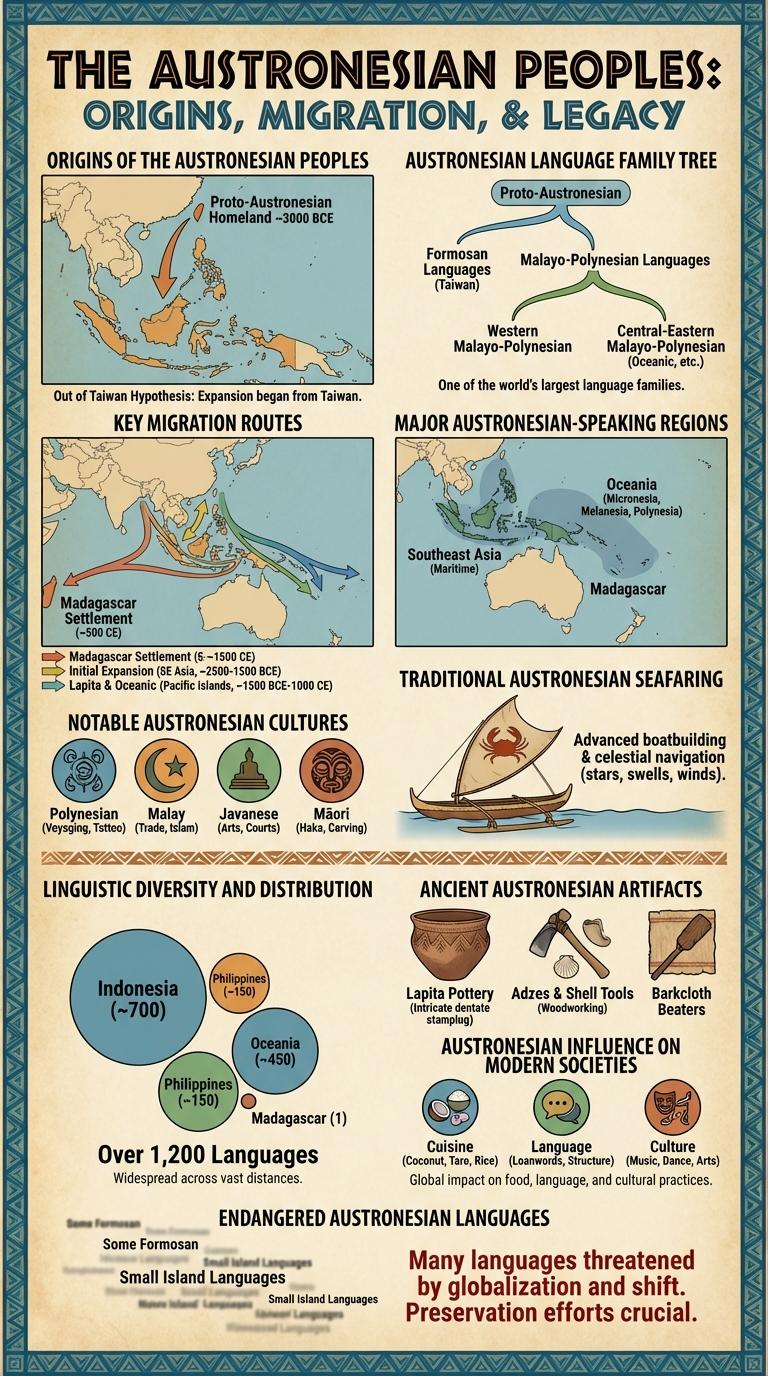
Where did the Austronesian peoples originate? The Austronesian peoples trace their origins to Taiwan around 3000 BCE. They later expanded across the islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, forming one of the largest language families in the world.
Austronesian Language Family Tree
The Austronesian language family is one of the largest language families in the world, encompassing over 1,200 languages spoken across Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, and parts of Madagascar. It is characterized by a widespread geographic distribution and significant linguistic diversity.
The family branches into several major groups, including Malayo-Polynesian, Formosan, and Oceanic languages. These branches further divide into numerous subgroups, reflecting the complex migration and settlement patterns of Austronesian-speaking peoples.
| Major Branch | Regions Spoken |
|---|---|
| Formosan | Taiwan |
| Malayo-Polynesian | Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia |
| Oceanic | Pacific Islands |
| Micronesian | Micronesia |
| Polynesian | Polynesia |
Key Migration Routes
The Austronesian people embarked on extensive maritime migrations originating from Taiwan around 3000 BCE. Their voyages spanned vast areas of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, shaping the cultural landscapes of many island communities.
Key migration routes extended through the Philippines, Indonesia, and into the Pacific Islands, reaching as far as Madagascar to the west and Easter Island to the east. These routes highlight significant seafaring skills and the diffusion of Austronesian languages and technologies.
Major Austronesian-speaking Regions
The Austronesian language family is one of the largest in the world, stretching across vast regions of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its speakers inhabit diverse islands and coastal areas, forming rich cultural and linguistic communities.
The major Austronesian-speaking regions highlight the expansive reach and diversity of these languages.
- Southeast Asia - Includes the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, and parts of Vietnam and Thailand, where thousands of Austronesian languages are spoken.
- Pacific Islands - Encompasses Polynesia, Micronesia, and Melanesia, featuring languages such as Maori, Hawaiian, and Fijian.
- Madagascar - An island nation off the southeast coast of Africa, where Malagasy, an Austronesian language, is the national language.
Notable Austronesian Cultures
The Austronesian peoples are known for their diverse and rich cultural heritage spread across islands in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. Their traditions, languages, and art forms reflect their deep connection with the ocean and nature.
Notable Austronesian cultures highlight unique contributions in navigation, craftsmanship, and social organization.
- Polynesian Navigation - Masterful use of stars and ocean currents enabled long-distance voyages across the Pacific Ocean.
- Javanese Court Traditions - Rich performing arts including wayang kulit shadow puppetry and gamelan orchestras.
- Filipino Baybayin Script - Ancient pre-colonial writing system used for communication and record-keeping.
- Maori Carving Arts - Intricate wood carvings symbolize tribal stories and ancestral heritage.
- Talaandig Weaving - Traditional textiles reflect symbolism and spiritual meanings in Mindanao, Philippines.
Traditional Austronesian Seafaring
Austronesian people are renowned for their exceptional seafaring skills, which enabled them to explore and settle vast areas of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Their maritime technology and navigation techniques are key to understanding ancient oceanic migration patterns.
The traditional Austronesian seafaring employed outrigger canoes and double-hulled vessels that provided stability in open waters. Skilled navigators relied on star paths, ocean swells, wind patterns, and bird flight to traverse thousands of miles without modern instruments. This mastery facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of languages across islands from Taiwan to Madagascar and Polynesia.
Linguistic Diversity and Distribution
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Language Family | Austronesian |
| Number of Languages | Over 1,200 |
| Geographic Distribution | Southeast Asia, Pacific Islands, Madagascar, Taiwan |
| Major Language Groups | Malayo-Polynesian, Formosan |
| Speakers | Approximately 386 million |
Ancient Austronesian Artifacts
Ancient Austronesian artifacts provide valuable insights into the rich cultural heritage of Austronesian-speaking peoples, who spread across Southeast Asia and the Pacific. These artifacts include intricately carved wooden tools, pottery adorned with geometric patterns, and shell jewelry, reflecting advanced craftsmanship and trade networks. Archaeological findings such as the Lapita pottery shards are key evidence of early Austronesian migration and maritime skills.
Austronesian Influence on Modern Societies
The Austronesian language family spans over 1,200 languages spoken across Southeast Asia, the Pacific, and parts of Madagascar. Its cultural and linguistic heritage significantly shapes modern societies in these regions.
- Maritime Technology - Austronesian seafaring innovations like the outrigger canoe facilitated vast oceanic exploration and trade, influencing modern naval engineering.
- Linguistic Impact - Austronesian languages contribute to national languages such as Indonesian, Filipino, and Malagasy, enriching cultural identity and communication.
- Agricultural Practices - Techniques such as wet-rice cultivation and unique crop varieties from Austronesian origins continue to support diverse farming systems globally.
Contemporary societies benefit from the Austronesian legacy through language, technology, and agriculture, highlighting their enduring global influence.
