Modal verbs express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability in English, playing a crucial role in sentence construction. Understanding their functions and nuances enhances clarity and precision in communication. This infographic visually breaks down the common modal verbs and their key uses for efficient learning.
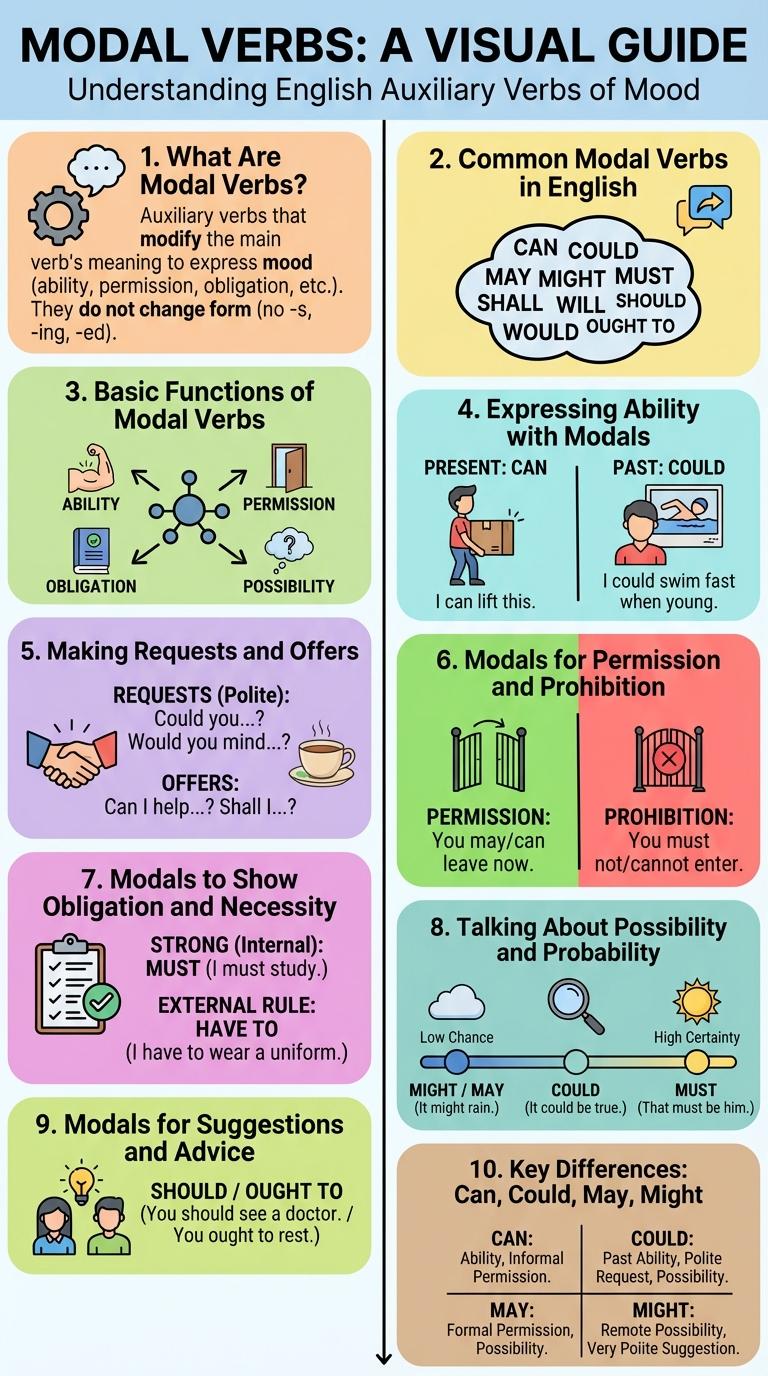
What Are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must.
They modify the meaning of main verbs without changing their form. Modal verbs are essential for indicating mood and tone in English communication.
Common Modal Verbs in English
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability. They help modify the main verb to convey different meanings in English sentences.
Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
- Can - Expresses ability or possibility.
- Must - Indicates obligation or strong necessity.
- May - Shows permission or a possibility.
- Should - Suggests advice or expectation.
- Will - Denotes future intention or willingness.
Basic Functions of Modal Verbs
| Modal Verb | Basic Function |
|---|---|
| Can | Expresses ability or possibility |
| May | Indicates permission or probability |
| Must | Shows obligation or strong necessity |
| Should | Gives advice or suggests recommendations |
| Will | Expresses future intention or certainty |
Expressing Ability with Modals
Modal verbs are essential tools in English to express ability, possibility, and permission. The primary modals used to convey ability are "can" and "could."
"Can" indicates present or general ability, while "could" refers to past ability or polite requests. These modals clarify what someone is able to do in different contexts.
Making Requests and Offers
Modal verbs like "can," "could," and "will" are essential for making polite requests and offers. Using "can" or "could" softens the request, making it more courteous, while "will" is often used to offer assistance. Mastering these modals enhances effective communication in everyday situations.
Modals for Permission and Prohibition
Modal verbs express different levels of permission and prohibition in English. They help speakers clarify what is allowed or forbidden in various situations.
Modals for permission include "can," "may," and "might," often used to ask or give consent. For example, "Can I leave early?" requests permission politely. Prohibition modals like "must not" and "cannot" indicate rules or bans, such as "You must not smoke here."
Modals to Show Obligation and Necessity
Modal verbs such as "must," "have to," and "need to" express obligation and necessity in English. "Must" indicates a strong obligation often imposed by the speaker or rules. "Have to" conveys external obligations, while "need to" highlights essential actions required to achieve a goal.
Talking About Possibility and Probability
Modal verbs express degrees of possibility and probability, helping speakers convey uncertainty or likelihood. Understanding these verbs enhances clarity in communication and improves English proficiency.
- Can - Indicates general possibility or ability in the present or future.
- May - Suggests a moderate degree of possibility, often used in formal contexts.
- Might - Expresses a lower probability or more uncertainty than "may".
- Could - Implies that something is possible, often in hypothetical or tentative situations.
- Must - Indicates a high probability or logical conclusion based on evidence.
Modals for Suggestions and Advice
How can modal verbs improve your suggestions and advice?
Modal verbs like "should," "ought to," and "could" are essential tools for offering clear and polite suggestions. They help express advice with varying degrees of certainty and politeness.
| Modal Verb | Example Usage |
|---|---|
| Should | You should try the new restaurant downtown. |
| Ought to | She ought to see a doctor soon. |
| Could | You could join the gym to improve your fitness. |
| Had better | You had better finish your homework before going out. |
| Might | You might want to consider taking a break. |
