The global economy is a complex network of interconnected markets, trade flows, and financial systems shaping the world's economic landscape. This infographic breaks down key factors like GDP growth, trade balances, and investment trends to visualize how different regions contribute to global prosperity. Understanding these economic indicators helps businesses, policymakers, and investors make informed decisions in a rapidly changing environment.
Key Drivers of the Global Economy
The global economy is shaped by several key drivers that influence growth, trade, and investment patterns worldwide. Major factors include technological innovation, international trade dynamics, and geopolitical stability. Understanding these drivers helps businesses and policymakers anticipate economic trends and make informed decisions.
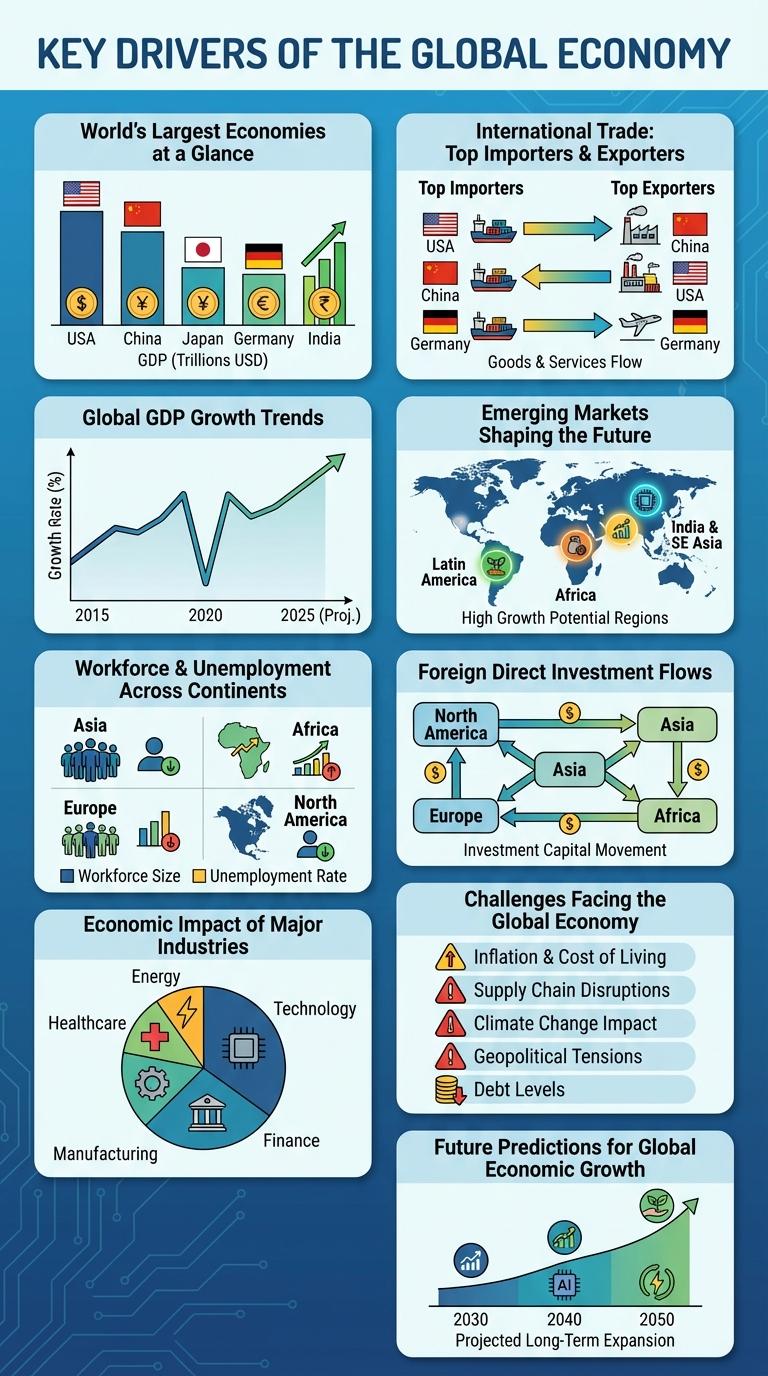
World's Largest Economies at a Glance
The global economy is defined by the economic output of its largest nations, which drive international trade and investment. Understanding the scale of these economies offers insights into global market dynamics and development trends.
- United States - Holds the position as the world's largest economy with a GDP exceeding $25 trillion, driven by technology, finance, and services sectors.
- China - The second-largest economy, rapidly expanding with a GDP over $18 trillion, particularly strong in manufacturing and exports.
- Japan - The third-largest economy, with a GDP around $5 trillion, known for its automotive and electronics industries.
The top economies collectively shape global economic policy and investment flows with significant influence on worldwide economic stability and growth.
International Trade: Top Importers & Exporters
| Top Exporting Countries (2023) | Export Value (Trillions USD) |
|---|---|
| China | 3.6 |
| United States | 1.8 |
| Germany | 1.5 |
| Netherlands | 0.9 |
| Japan | 0.8 |
| Top Importing Countries (2023) | Import Value (Trillions USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | 3.2 |
| China | 2.4 |
| Germany | 1.2 |
| Japan | 0.9 |
| United Kingdom | 0.8 |
The data highlights China and the United States as leading forces in global trade. China holds the largest share in exports with $3.6 trillion, driven by manufacturing and electronics. The United States leads imports at $3.2 trillion, reflecting its consumer market scale. Germany ranks highly in both categories, underpinned by its automotive and industrial sectors. These figures underscore the interdependent nature of the global economy and the critical role of international trade flows.
Global GDP Growth Trends
Global GDP growth has shown varied trends over the past decade, influenced by geopolitical events, technological advancements, and shifts in trade policies. Emerging markets have generally experienced faster growth compared to developed economies.
In recent years, the global economy faced disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a sharp contraction followed by a strong recovery phase. Advanced economies are now focusing on sustainable growth and digital transformation to foster resilience.
Emerging Markets Shaping the Future
Emerging markets are playing a crucial role in shaping the future of the global economy. These economies exhibit rapid growth, expanding trade networks, and increasing innovation capabilities.
Countries such as China, India, Brazil, and Indonesia are driving global economic shifts by attracting significant foreign investment and developing advanced manufacturing sectors. Growth rates in emerging markets often outpace those in developed economies, contributing to a realignment of global economic power. Rising consumer demand and digital transformation in these regions are creating new opportunities for businesses worldwide.
Workforce & Unemployment Across Continents
The global economy's workforce distribution reveals significant disparities in employment rates across continents. Unemployment trends highlight economic challenges unique to each region, shaping labor market dynamics worldwide.
- Asia commands the largest workforce - Housing over 60% of the global labor pool, Asia drives major economic growth through diverse industries.
- Africa faces the highest youth unemployment - Youth unemployment rates exceed 30% in many African countries, impacting social and economic development.
- Europe maintains low unemployment rates - With extensive social safety nets, Europe often experiences unemployment rates below 8%, stabilizing its labor markets.
- North America shows steady employment growth - Technological advancements and service sector expansion foster consistent job creation across the continent.
- South America confronts fluctuating unemployment - Economic volatility and political instability contribute to variable labor market conditions throughout the region.
Foreign Direct Investment Flows
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows represent cross-border investments where an investor acquires a lasting interest in a foreign enterprise. In 2023, global FDI inflows were estimated at $1.58 trillion, reflecting recovery post-pandemic and shifting economic dynamics. Key sectors attracting FDI include technology, renewable energy, and manufacturing, driven by emerging markets and developed nations alike.
Economic Impact of Major Industries
How do major industries shape the global economy? The economic impact of key industries drives GDP growth, employment, and innovation worldwide. Understanding these industries helps identify trends and investment opportunities.
| Industry | Economic Contribution |
|---|---|
| Technology | Accounts for over $5 trillion in global revenue, fueling digital transformation and productivity gains. |
| Energy | Generates approximately 4% of global GDP, with ongoing shifts toward renewable sources. |
| Manufacturing | Contributes 16% of global GDP, supporting supply chains and export markets. |
| Healthcare | Represents 10% of global GDP, driven by aging populations and medical innovation. |
| Finance | Encompasses around 8% of global GDP, facilitating capital flow and investment. |
Challenges Facing the Global Economy
The global economy is currently grappling with several critical challenges that threaten sustainable growth. Rising inflation and supply chain disruptions are intensifying financial pressures worldwide.
Geopolitical tensions and energy market volatility contribute to economic uncertainty across major regions. Structural changes, including labor market shifts and technological transformation, further complicate recovery efforts.
