Public finance infographics illustrate the management of government revenue, expenditure, and debt in a clear, visual format. They highlight key aspects like taxation, budgeting, and public spending to provide a quick understanding of fiscal policies. These visuals help analyze how governments allocate resources to maintain economic stability and fund public services.
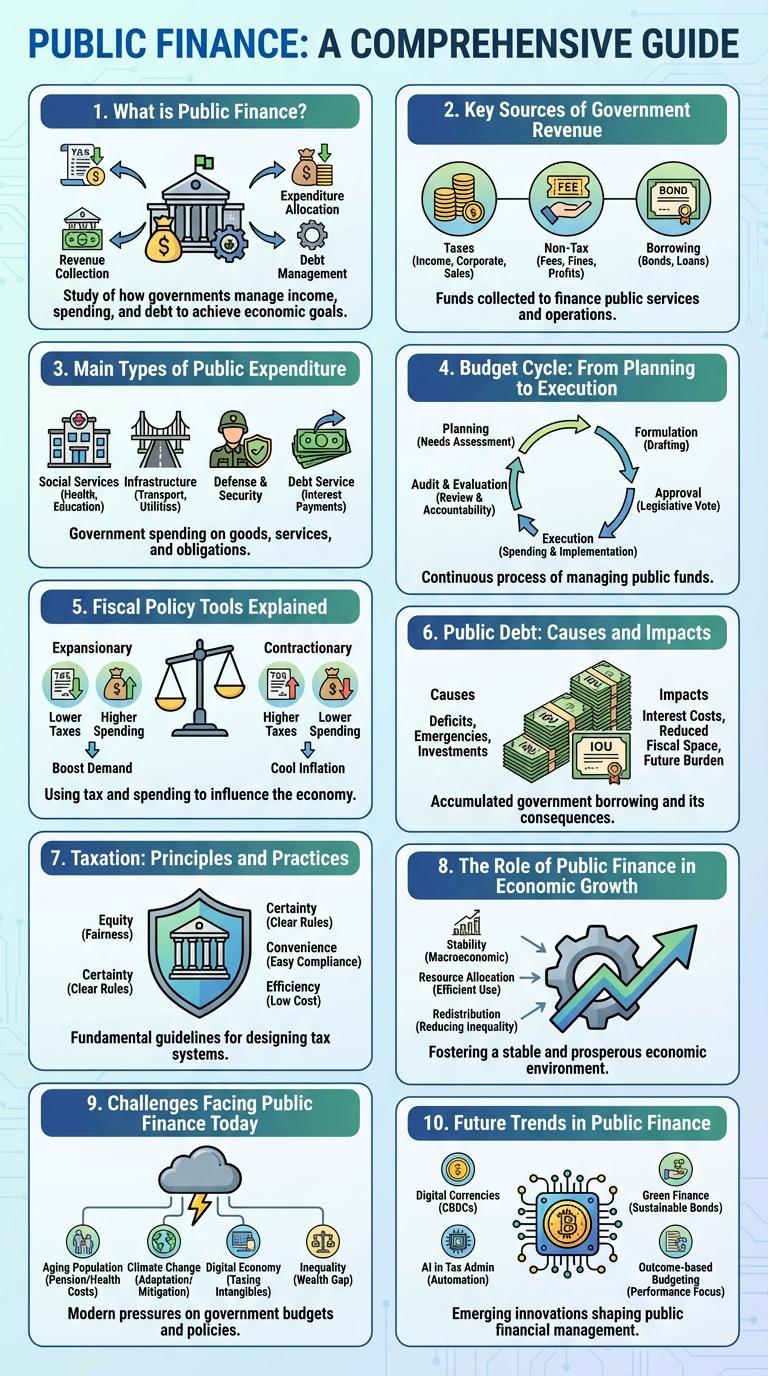
What is Public Finance?
Public finance is the study of how governments manage revenue, expenditures, and debt to influence the economy. It involves budgeting, taxation, government spending, and borrowing to provide public goods and services. The goal of public finance is to promote economic stability, growth, and equitable resource distribution.
Key Sources of Government Revenue
Public finance relies on diverse revenue streams to fund government operations and public services. Understanding key sources helps clarify fiscal policy and economic priorities.
- Taxation - The primary source of government revenue including income, corporate, and sales taxes collected from individuals and businesses.
- Fees and Charges - Revenue generated from government services such as licensing, permits, and user fees for public utilities and facilities.
- Grants and Transfers - Funds received from higher levels of government or international organizations, supporting specific programs or budget gaps.
Main Types of Public Expenditure
Public finance involves managing government revenue and expenditure to influence the economy and provide public services. Understanding the main types of public expenditure helps in analyzing government priorities and economic impact.
Public expenditure is broadly categorized into capital and current expenditure. Capital expenditure includes investments in infrastructure, education, and health that provide long-term benefits. Current expenditure covers salaries, subsidies, social security payments, and operational costs necessary for daily government functioning.
Budget Cycle: From Planning to Execution
The public finance budget cycle consists of several key phases vital for effective financial management. It begins with budget planning, where priorities and funding requirements are established based on government goals.
Next, the approval stage involves legislative review and authorization of budget allocations. The cycle continues with execution, where funds are disbursed and government programs are implemented according to the approved budget.
Fiscal Policy Tools Explained
What are the primary fiscal policy tools used by governments to manage the economy? Fiscal policy tools include government spending and taxation, which influence economic activity by adjusting aggregate demand.
How does government spending act as a fiscal policy tool? Increased government spending injects money into the economy, stimulating growth and reducing unemployment during recessions.
What role does taxation play in fiscal policy? Taxation controls disposable income, reducing inflationary pressures or funding public services depending on whether taxes are raised or lowered.
What is the impact of transfer payments in fiscal policy? Transfer payments like social security and unemployment benefits redistribute income and support aggregate demand during economic downturns.
How do automatic stabilizers function as a fiscal policy mechanism? Automatic stabilizers, such as progressive taxes and welfare programs, adjust government revenues and spending automatically to moderate economic fluctuations without new legislation.
Public Debt: Causes and Impacts
Public debt arises when a government borrows to cover budget deficits, finance infrastructure projects, or respond to economic crises. Common causes include excessive government spending, tax revenue shortfalls, and unexpected economic downturns.
High public debt can lead to increased interest payments, crowding out essential public investments. It may also affect a country's credit rating, raising borrowing costs and potentially slowing economic growth.
Taxation: Principles and Practices
Public finance is essential for government revenue, enabling the provision of public goods and services. Taxation remains the primary method of financing government activities and redistributing wealth.
- Equity Principle - Taxes should be fair, with taxpayers paying based on their ability to pay.
- Efficiency Principle - Tax systems should minimize economic distortions and encourage growth.
- Transparency Principle - Tax policies must be clear and understandable to maintain public trust.
Effective taxation supports sustainable public finance, promoting economic stability and social welfare.
The Role of Public Finance in Economic Growth
Public finance plays a crucial role in economic growth by allocating resources efficiently through government taxation and spending. It funds infrastructure, education, and healthcare, which are essential for enhancing productivity and development. Strategic public finance policies stimulate investment, create jobs, and promote long-term economic stability.
Challenges Facing Public Finance Today
Public finance faces numerous challenges in adapting to economic and social demands. Efficient management of resources is crucial for sustainable growth and public welfare.
- Rising Public Debt - Increasing government borrowing strains fiscal stability and limits future spending capacity.
- Revenue Shortfalls - Tax base erosion and economic slowdowns reduce essential government income.
- Healthcare and Social Welfare Costs - Aging populations drive higher expenditures, pressuring budgets and service delivery.
