Verbals are verb forms that function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, enriching sentence variety and complexity. This infographic clarifies the three types of verbals: gerunds, participles, and infinitives, highlighting their unique roles and examples. Understanding verbals enhances writing skills by allowing more precise and dynamic expression.
What Are Verbals?
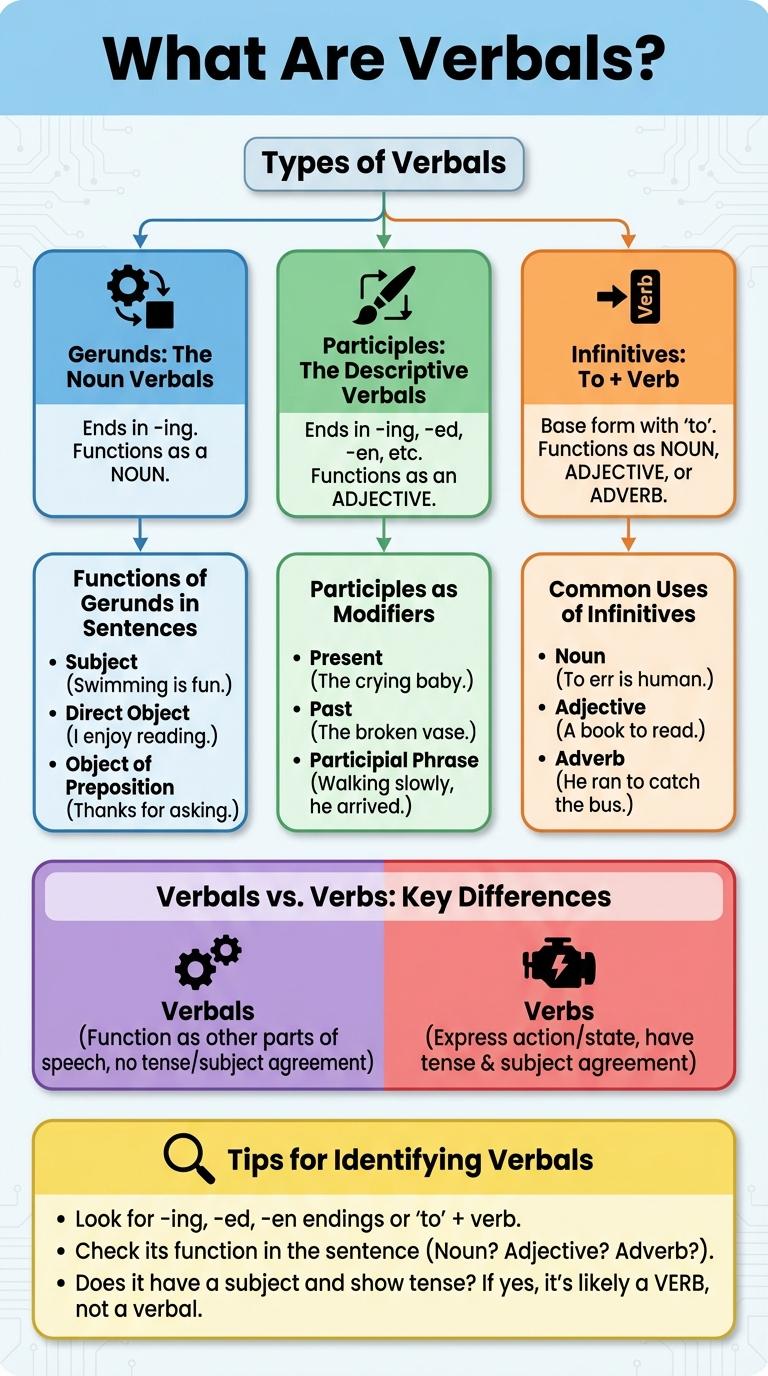
Verbals are verb forms that function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs instead of verbs. They include gerunds, participles, and infinitives. Each type of verbal serves a unique grammatical role within a sentence.
Types of Verbals
Verbals are verb forms that function as different parts of speech, rather than as the main verb. They include participles, gerunds, and infinitives, each serving unique grammatical roles.
Understanding the types of verbals helps improve sentence variety and clarity in writing.
- Participles - Verbals that act as adjectives, modifying nouns or pronouns in a sentence.
- Gerunds - Verbals ending in -ing that function as nouns within the sentence structure.
- Infinitives - The base form of a verb preceded by "to" that can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs.
Gerunds: The Noun Verbals
Gerunds function as noun verbals formed by adding -ing to a verb root. They perform typical noun roles such as subject, object, or complement in sentences.
- Subject - Gerunds can act as the subject of a sentence, e.g., "Swimming is healthy."
- Object - Gerunds serve as objects, e.g., "She enjoys reading."
- Complement - Gerunds function as subject complements, e.g., "His favorite activity is jogging."
Gerunds combine verbal meaning with noun functions, making them versatile components in English grammar.
Participles: The Descriptive Verbals
Participles are verbals that function as adjectives, providing descriptions to nouns or pronouns. They can appear in present or past forms, conveying ongoing or completed actions related to the noun they modify.
Present participles end in -ing and describe active or simultaneous actions. Past participles often end in -ed, -en, or irregular forms, describing completed actions or states.
Infinitives: To + Verb
Infinitives are verbals formed by combining "to" with the base form of a verb. They function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences.
Understanding infinitives improves sentence variety and clarity in English writing and speaking.
- Basic Form - An infinitive always begins with "to" followed by the base verb, e.g., to run, to eat.
- Noun Use - Infinitives can act as the subject or object of a sentence, such as "To learn is important."
- Adjective and Adverb Use - They modify nouns or verbs, for example, "He has a book to read" (adjective) and "She works hard to succeed" (adverb).
Functions of Gerunds in Sentences
| Function of Gerunds | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject of the Sentence | Swimming is a great form of exercise. |
| Direct Object | She enjoys reading books. |
| Object of a Preposition | They talked about traveling last summer. |
| Predicate Noun (Complement) | His favorite hobby is painting. |
| Appositive | Her passion, dancing, is evident. |
Participles as Modifiers
Participles are verb forms used as modifiers to describe nouns or pronouns. They often end in -ing (present participles) or -ed (past participles) but can have irregular forms.
Present participles express ongoing actions, such as "running water" or "a barking dog." Past participles often indicate completed actions or states, like "broken window" or "cooked meal." Both types function as adjectives within sentences, adding detailed description without needing a full clause.
Common Uses of Infinitives
What are the common uses of infinitives in English? Infinitives often express purpose, such as in "I want to learn." They also function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs within sentences.
Verbals vs. Verbs: Key Differences
Verbals are verb forms that function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, rather than as the main verbs of a sentence. Verbs express actions or states of being and serve as the predicate of a clause. Understanding the differences between verbals and verbs helps clarify sentence structure and improve grammar usage.
