An infographic about education visually presents key data and trends to enhance understanding and engagement. It highlights important statistics, learning outcomes, and educational resources in a clear, concise format. Such visuals help educators, students, and policymakers make informed decisions by simplifying complex information.
The Evolution of Education Through the Ages
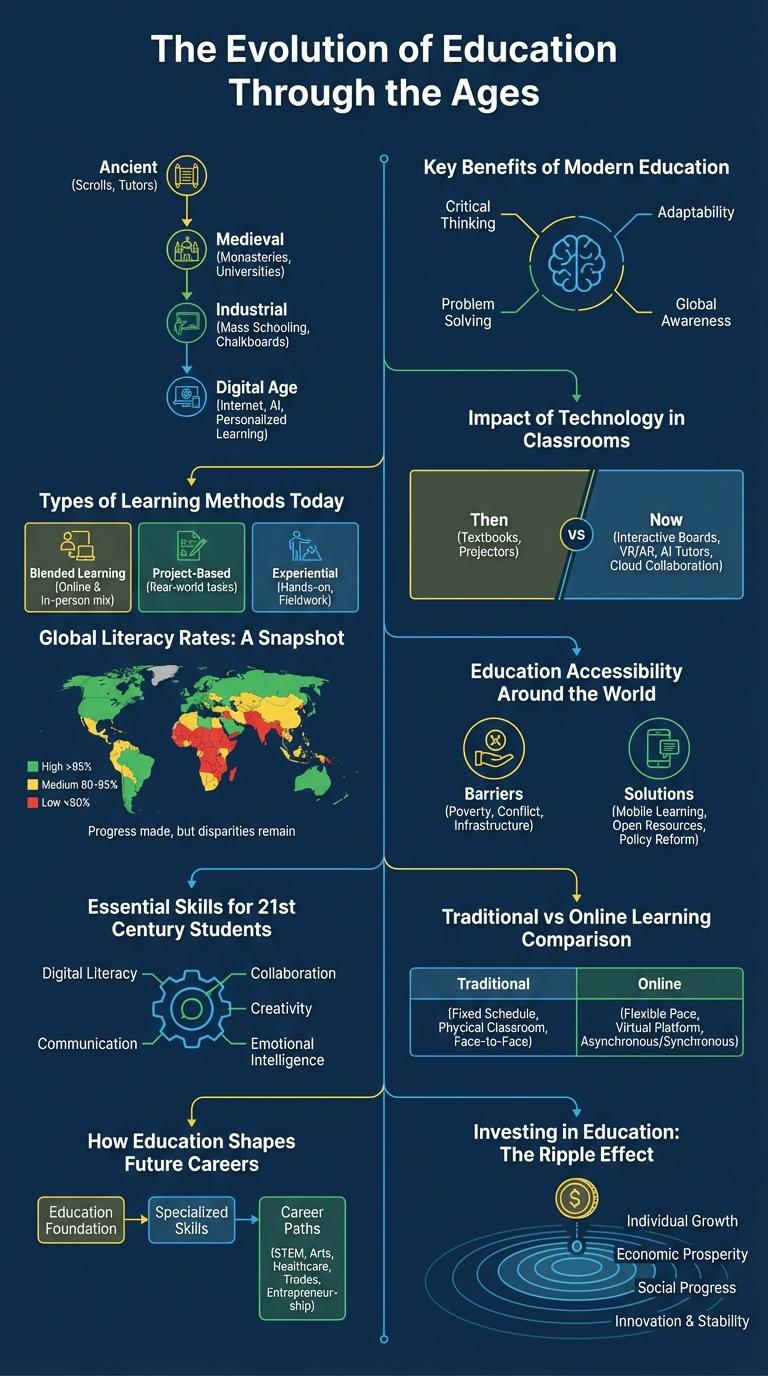
The Evolution of Education Through the Ages showcases the transformation of learning methods and environments. This infographic highlights key milestones that shaped modern education systems.
- Ancient Education - Early education was informal, focusing on oral traditions and practical skills within communities.
- Medieval Period - Education became institutionalized with the rise of universities and religious schools.
- Modern Education - The introduction of compulsory schooling and technological advancements transformed access and delivery of education.
Key Benefits of Modern Education
What are the key benefits of modern education? Modern education integrates technology and innovative teaching methods to enhance learning experiences. It prepares students for a dynamic and interconnected world.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalized Learning | Adapts to individual student needs and learning styles, improving engagement and outcomes. |
| Critical Thinking | Encourages analytical skills essential for problem-solving in diverse situations. |
| Technology Integration | Uses digital tools that enhance interactive learning and accessibility. |
| Global Awareness | Promotes understanding of cultural diversity and global issues. |
| Career Preparedness | Equips students with relevant skills for the evolving job market. |
Types of Learning Methods Today
Education today embraces diverse learning methods tailored to different needs and environments. Understanding these types enhances teaching effectiveness and student engagement.
- Traditional Classroom Learning - Structured, teacher-led instruction in a physical setting promoting direct interaction.
- Online Learning - Digital platforms providing flexible, self-paced education accessible from anywhere.
- Blended Learning - Combines face-to-face and online methods for a balanced educational experience.
- Experiential Learning - Hands-on activities that foster practical skills through real-world experiences.
- Self-Directed Learning - Learners independently manage their education based on personal goals and resources.
Choosing the right learning method can significantly improve educational outcomes for students and educators alike.
Impact of Technology in Classrooms
| Technology Feature | Impact on Education |
|---|---|
| Interactive Whiteboards | Enhance student engagement by allowing real-time collaboration and multimedia presentations. |
| Online Learning Platforms | Provide flexible access to resources, enabling personalized learning paths and remote education. |
| Educational Apps and Games | Improve retention through gamified lessons that make learning enjoyable and interactive. |
| Virtual Reality (VR) Tools | Offer immersive experiences that deepen understanding of complex subjects like science and history. |
| Cloud-Based Collaboration | Facilitate teamwork and project management among students and teachers across different locations. |
Global Literacy Rates: A Snapshot
Understanding global literacy rates provides insight into educational access worldwide. These rates reveal disparities and progress across different regions and populations.
- Global Literacy Rate - Approximately 86% of adults worldwide are literate as of recent data.
- Regional Variations - Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia have the lowest literacy rates, often below 65%.
- Gender Gap - Women represent two-thirds of the world's illiterate population, highlighting persistent gender disparities.
- Youth Literacy - Youth literacy rates tend to be higher, reflecting improvements in education access.
- Impact of Literacy - Higher literacy correlates with improved economic growth and health outcomes in communities.
Education Accessibility Around the World
Education accessibility varies significantly across different regions worldwide, with disparities in enrollment rates, infrastructure, and resource availability. Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of South Asia face the greatest challenges due to poverty, gender inequality, and insufficient educational facilities. Efforts by governments and international organizations aim to improve access through policy reforms, technology integration, and increased funding.
| Region | Primary School Enrollment Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| North America | 95 |
| Europe | 97 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 65 |
| South Asia | 75 |
| Latin America | 90 |
Essential Skills for 21st Century Students
Education in the 21st century demands a diverse set of essential skills for student success. These skills prepare learners for a rapidly changing global environment.
Critical thinking enables students to analyze information effectively and solve complex problems. Communication skills foster collaboration and clear expression of ideas across diverse platforms. Digital literacy ensures students can navigate and utilize technology to enhance learning and productivity.
Traditional vs Online Learning Comparison
Traditional learning involves face-to-face interaction in a physical classroom, emphasizing direct communication and structured schedules. Online learning offers flexibility, enabling students to access materials and participate in classes from any location with internet access.
Students in traditional classrooms benefit from immediate feedback and social engagement, supporting collaborative skills and motivation. Online learning provides self-paced study options and a wide range of digital resources, catering to diverse learning styles and schedules.
How Education Shapes Future Careers
Education lays the foundation for future career success by equipping individuals with essential knowledge and skills. It fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability, which are crucial in today's dynamic job market. A strong educational background increases employability and opens pathways to diverse professional opportunities.
| Education Level | Career Impact |
|---|---|
| High School | Basic qualifications, entry-level jobs |
| Associate Degree | Technical skills, higher earning potential |
| Bachelor's Degree | Access to professional roles |
| Master's Degree | Specialized knowledge, leadership positions |
| Doctorate | Expert roles, academia, research |
