Effective assessment tools are critical for measuring learning outcomes and guiding instructional improvements. Infographics simplify complex data by visually representing key metrics and trends, enhancing comprehension and retention. Utilizing infographic formats in assessment reporting fosters clearer communication between educators, students, and stakeholders.
What Is Assessment?
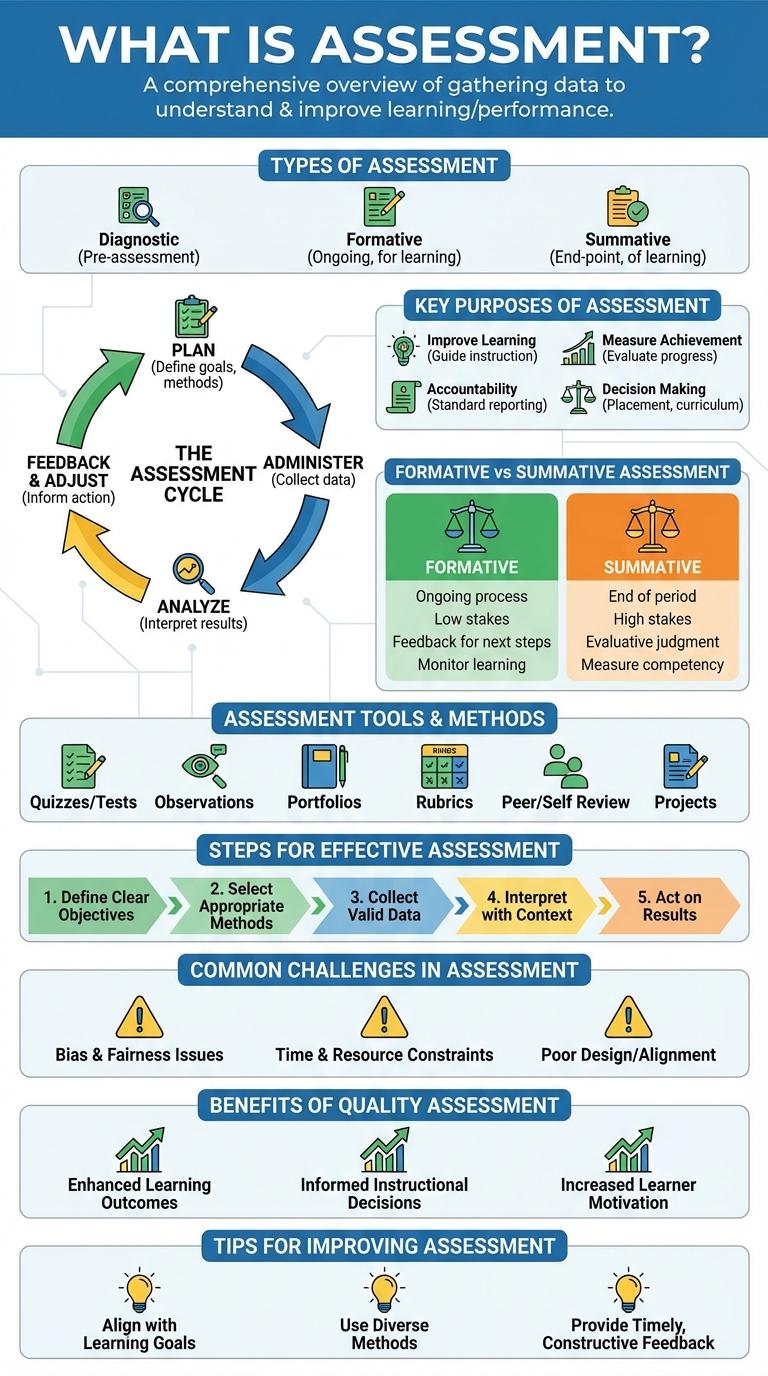
Assessment is a systematic process used to evaluate knowledge, skills, attitudes, or beliefs. It provides valuable information to guide learning, development, and decision-making.
Assessments can be formative, supporting ongoing improvement, or summative, measuring overall achievement. They employ various methods such as tests, observations, and self-assessments to capture a comprehensive understanding.
Types of Assessment
Assessment plays a crucial role in measuring learning progress and understanding student abilities. Various types of assessment include formative, summative, diagnostic, and performance-based methods. Each type serves distinct purposes, such as providing ongoing feedback, evaluating final outcomes, identifying learning gaps, and assessing practical skills.
The Assessment Cycle
The Assessment Cycle is a structured process used to evaluate and improve learning outcomes. It ensures continuous feedback and enhancement in educational settings.
The cycle begins with setting clear learning objectives, which guide what needs to be assessed. Next, data is collected through various assessment methods like tests, quizzes, or observations. Finally, the results are analyzed to inform teaching strategies and support student development.
Key Purposes of Assessment
Assessment plays a vital role in educational and organizational contexts to measure knowledge, skills, and performance. It provides insights that guide decision-making, improve learning, and ensure accountability.
- Measurement of Learning Outcomes - Assessment evaluates the extent to which learners have achieved specified knowledge and skill objectives.
- Feedback for Improvement - Assessment offers detailed information that helps learners and educators identify strengths and areas needing development.
- Decision-Making and Accountability - Assessment data supports informed decisions regarding curriculum design, student placement, and policy formation.
Formative vs Summative Assessment
What are the key differences between formative and summative assessment? Formative assessment provides ongoing feedback to improve student learning, while summative assessment evaluates overall learning at the end of an instructional period. Formative assessments include quizzes and peer reviews, whereas summative assessments involve final exams and projects.
Assessment Tools & Methods
| Assessment Tools | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|
| Rubrics | Formative Assessment |
| Surveys | Summative Assessment |
| Quizzes | Self-Assessment |
| Portfolios | Peer Assessment |
| Checklists | Performance-Based Assessment |
Steps for Effective Assessment
Effective assessment is a crucial part of measuring learning outcomes and guiding instructional decisions. It involves a series of structured steps to ensure accurate and meaningful evaluation.
- Define Objectives - Clearly outline what knowledge or skills the assessment aims to measure.
- Choose Assessment Methods - Select appropriate tools such as quizzes, projects, or observations based on the objectives.
- Collect Data - Gather evidence of learning through careful administration of the chosen assessments.
- Analyze Results - Interpret the data to understand learner performance and identify gaps.
- Provide Feedback - Deliver constructive feedback to support learner improvement and inform future instruction.
Following these steps ensures assessment processes are effective, reliable, and aligned with educational goals.
Common Challenges in Assessment
Assessment plays a critical role in measuring student learning, but educators often face obstacles that impact its effectiveness. Understanding these common challenges helps improve assessment design and implementation.
- Subjectivity in Grading - Personal biases can influence the fairness and consistency of assessment results.
- Time Constraints - Limited time for preparing and grading assessments reduces their quality and depth.
- Misalignment with Learning Objectives - Assessments that do not match curriculum goals fail to accurately measure student understanding.
Benefits of Quality Assessment
Quality assessment enhances learning outcomes by providing clear benchmarks and actionable feedback. It supports informed decision-making for educators and institutions, ensuring teaching strategies meet student needs effectively. Consistent assessment promotes accountability and continuous improvement across educational programs.
