BPP infographics visually break down complex information into clear, digestible segments, enhancing comprehension and retention. They use engaging graphics and concise text to illustrate key concepts related to BPP's services and educational resources. This approach makes learning more accessible and efficient for students and professionals alike.
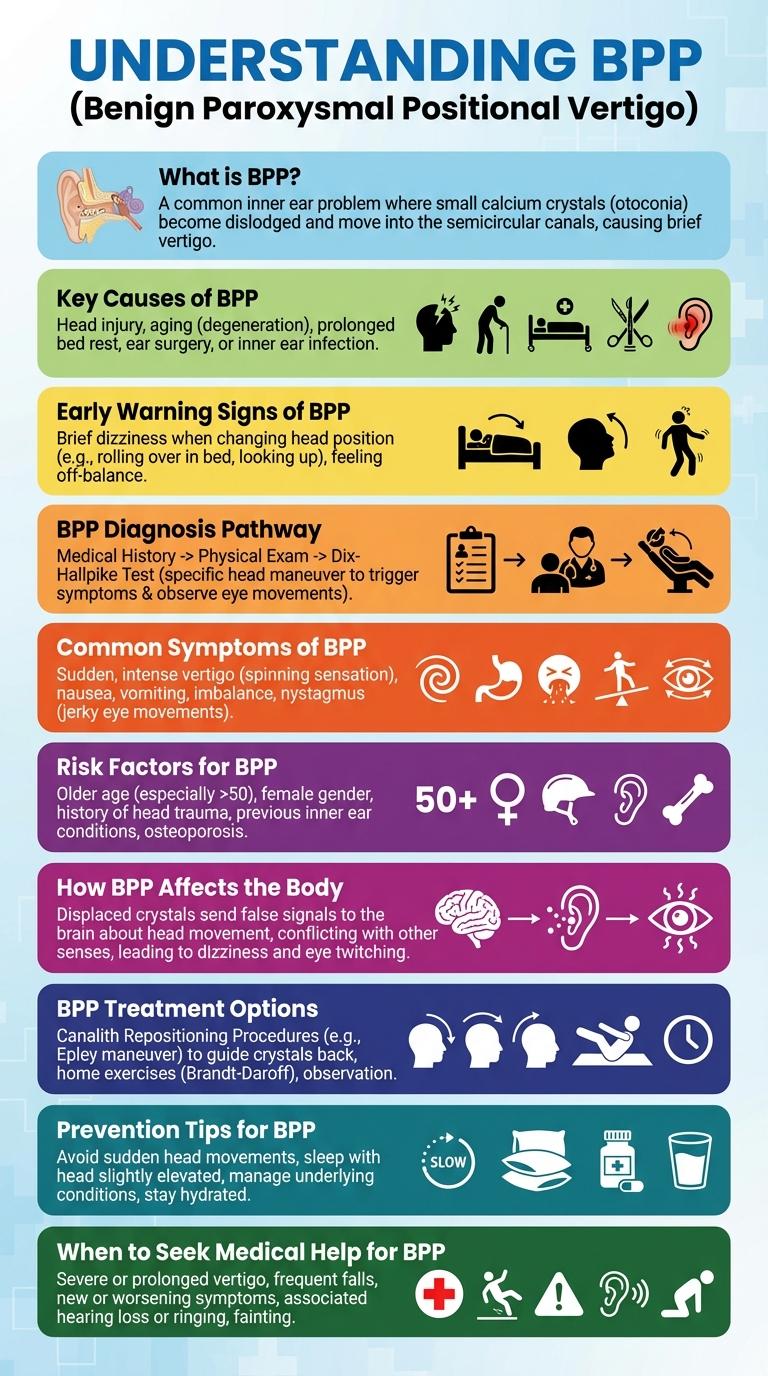
What is BPP?
BPP stands for Binder of Protoporphyrin IX, a protein involved in heme biosynthesis. It plays a critical role in transporting protoporphyrin IX within cells.
BPP ensures proper heme production, essential for oxygen transport and cellular respiration. Deficiencies or malfunctions in BPP can lead to metabolic disorders.
Key Causes of BPP
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is a common inner ear disorder that causes brief episodes of dizziness. It results from dislodged calcium crystals within the semicircular canals of the inner ear.
- Canalithiasis - Free-floating otoconia disrupt the fluid movement in the semicircular canals, leading to vertigo.
- Head Trauma - Physical injury to the head can dislodge otoliths, triggering BPPV symptoms.
- Degeneration of Inner Ear Structures - Age-related changes cause detachment of otoconia from the utricle, causing imbalance.
Early Warning Signs of BPP
Early identification of Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is crucial for effective intervention. Recognizing early warning signs can guide timely support and treatment.
- Emotional Instability - Intense mood swings and difficulty managing emotions often indicate emerging BPD symptoms.
- Fear of Abandonment - Persistent anxiety about being rejected or left alone is a common early warning sign.
- Impulsive Behaviors - Engaging in risky activities without considering consequences reflects underlying emotional distress linked to BPD.
Noticing these signs early enables individuals to seek professional help and improve long-term outcomes.
BPP Diagnosis Pathway
The BPP Diagnosis Pathway is a structured approach used in medical settings to accurately identify BPP (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo). This pathway emphasizes a series of diagnostic tests and clinical assessments to confirm the condition.
Diagnosis begins with a detailed patient history and symptom evaluation. Next, specific positional tests like the Dix-Hallpike maneuver are performed to detect abnormal eye movements. Accurate diagnosis allows for targeted treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing symptoms effectively.
Common Symptoms of BPP
BPP, or Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, is a common inner ear disorder causing brief episodes of dizziness. Recognizing the common symptoms helps in timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Dizziness - Sudden sensation of spinning or moving, often triggered by head position changes.
- Loss of Balance - Difficulty maintaining stability while standing or walking.
- Nausea - Feeling queasy or sick, often accompanying vertigo episodes.
- Nystagmus - Involuntary eye movements occurring during vertigo attacks.
- Lightheadedness - A sense of faintness or wooziness without actual spinning sensation.
Risk Factors for BPP
What are the primary risk factors for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)? BPPV risk factors include age-related degeneration of the inner ear and head injuries. Other contributors involve prolonged bed rest and certain vestibular disorders.
How BPP Affects the Body
Blood pH plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's overall function by regulating the acid-base balance. The body constantly adjusts to keep blood pH within the narrow range of 7.35 to 7.45.
When blood pH deviates from this range, it can affect enzyme activity, oxygen delivery, and cellular metabolism. BPP disturbances may lead to conditions like acidosis or alkalosis, impacting organ systems and overall health.
BPP Treatment Options
BPP (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) is treated through various effective methods aimed at repositioning inner ear crystals. The Epley maneuver is a common technique used to alleviate dizziness by guiding particles to their correct location. For persistent cases, vestibular rehabilitation therapy and medication may be recommended to manage symptoms and improve balance.
Prevention Tips for BPP
| Prevention Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintain Good Oral Hygiene | Brush teeth twice daily and floss regularly to reduce bacterial buildup that can cause BPP (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo). |
| Manage Head and Neck Injuries | Avoid sudden head movements and use protective gear during physical activities to prevent dislodging ear crystals. |
| Perform Balance Exercises | Engage in balance and vestibular rehabilitation exercises to improve inner ear function and reduce BPP episodes. |
| Sleep with Head Elevated | Use pillows to elevate the head during sleep to prevent displacement of otoliths in the inner ear. |
| Seek Early Treatment | Consult a healthcare professional promptly at onset of vertigo symptoms to prevent worsening of BPP. |
