The justice system plays a crucial role in maintaining social order by ensuring laws are fairly applied and rights are protected. Infographics can effectively simplify complex legal processes, making information accessible and comprehensible to the public. Visual representation highlights key components like courts, law enforcement, and corrections, enhancing awareness and transparency.
Understanding the Justice System
What is the justice system and why is it important? The justice system is a framework of laws and institutions designed to ensure fairness and accountability in society. It protects individual rights and maintains social order.
How are laws created and enforced? Laws are created by legislative bodies such as parliaments or congresses and enforced by police and judicial authorities. Courts interpret these laws to resolve disputes and administer justice.
What roles do the different branches of the justice system play? The justice system typically includes the police, courts, and correctional institutions. Police enforce laws, courts adjudicate cases, and corrections manage penalties and rehabilitation.
How does the court process work? Cases begin with an investigation and arrest followed by arraignment, trial, and sentencing if the defendant is found guilty. Legal representation and evidence are critical throughout this process.
What is the goal of the justice system? The justice system aims to balance punishment, rehabilitation, and deterrence while upholding human rights and equality before the law. It strives to promote public trust and social stability.
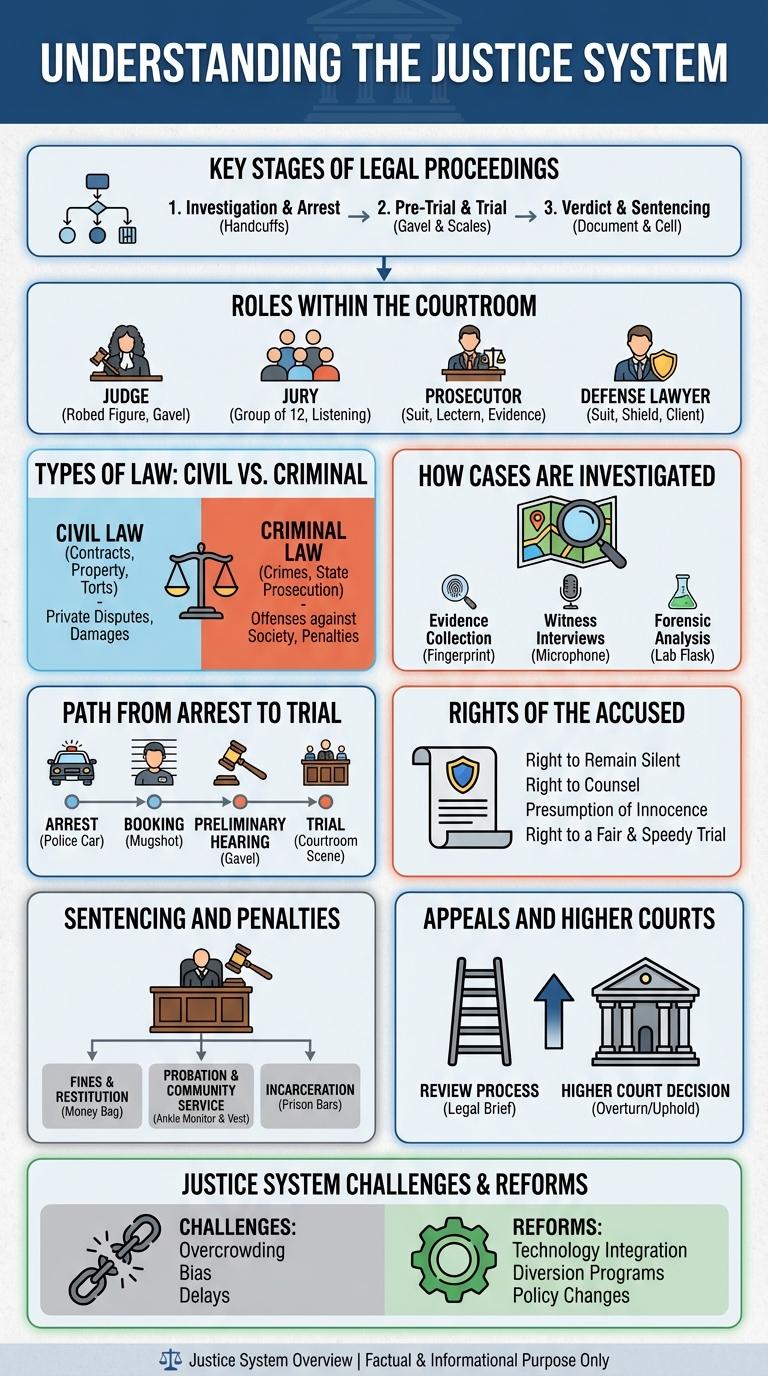
Key Stages of Legal Proceedings
The justice system operates through structured phases to ensure fair and lawful resolution of disputes. Each stage plays a crucial role in upholding legal standards and protecting rights.
- Investigation - Law enforcement collects evidence to determine if a crime has occurred.
- Charging - Prosecutors formally accuse a suspect based on gathered evidence.
- Trial - Both parties present arguments and evidence before a judge or jury.
- Sentencing - Judges impose penalties if the accused is found guilty.
- Appeals - Defendants can challenge verdicts or sentences in higher courts.
Understanding these key stages clarifies how justice is systematically pursued and maintained.
Roles Within the Courtroom
The justice system relies on key roles within the courtroom to ensure fair trials and legal proceedings. Judges preside over cases, interpret laws, and make rulings to maintain courtroom order. Attorneys represent the prosecution and defense, advocating for their clients, while jurors evaluate evidence to deliver impartial verdicts.
Types of Law: Civil vs. Criminal
The justice system encompasses various types of law, primarily civil and criminal law, each serving distinct functions in society. Understanding their differences is essential for grasping how legal disputes and offenses are managed.
Civil law deals with disputes between individuals or organizations, while criminal law addresses actions considered offenses against the state or society.
- Civil Law - Governs disputes such as contracts, property, and family matters, focusing on compensation or specific performance.
- Criminal Law - Involves prosecution by the government against individuals or entities accused of crimes, aiming at punishment or rehabilitation.
- Burden of Proof - Civil cases require a "preponderance of evidence," whereas criminal cases demand proof "beyond a reasonable doubt."
How Cases Are Investigated
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Incident Report | Initial complaint or report is filed by victim or witness to law enforcement. |
| Preliminary Investigation | Officers gather evidence, interview witnesses, and document the scene. |
| Case Assignment | Investigation is assigned to detectives or specialized units based on case type. |
| Evidence Analysis | Collected evidence is analyzed by forensic experts to support the investigation. |
| Report & Review | Investigators compile findings into reports for prosecutors to determine charges. |
Path from Arrest to Trial
The justice system follows a structured path from arrest to trial, ensuring legal procedures are upheld. Each step serves a vital role in protecting rights and determining guilt or innocence.
- Arrest - Law enforcement takes custody of a suspect based on probable cause of a crime.
- Booking - Officials record the suspect's personal information, fingerprints, and charges.
- Initial Appearance - The accused is informed of charges and bail conditions before a judge.
- Preliminary Hearing - A judge evaluates whether sufficient evidence exists to proceed to trial.
- Trial - Both prosecution and defense present evidence and arguments for a verdict.
Rights of the Accused
The justice system guarantees fundamental rights to individuals accused of crimes, ensuring fair treatment and due process. These rights protect against wrongful convictions and uphold the principle of innocent until proven guilty.
The right to remain silent prevents self-incrimination during legal proceedings. Accused individuals have the right to legal counsel for defense and representation. Fair trial guarantees unbiased judgment and the opportunity to confront witnesses.
Sentencing and Penalties
The justice system employs a structured sentencing framework designed to ensure fairness and proportionality in penalizing crimes. Sentencing options range from fines and probation to imprisonment and capital punishment, depending on the severity of the offense. Penalties aim to deter criminal behavior, rehabilitate offenders, and protect society.
Appeals and Higher Courts
Appeals and Higher Courts play a crucial role in ensuring the fairness and accuracy of judicial decisions within the justice system. These courts review cases from lower courts to determine if legal errors were made that could have affected the outcome.
The appellate process involves submitting legal briefs and, sometimes, oral arguments to higher judges who evaluate the application of law rather than re-examining factual evidence. Higher courts, including appellate courts and supreme courts, set legal precedents that guide lower courts and shape future rulings.
