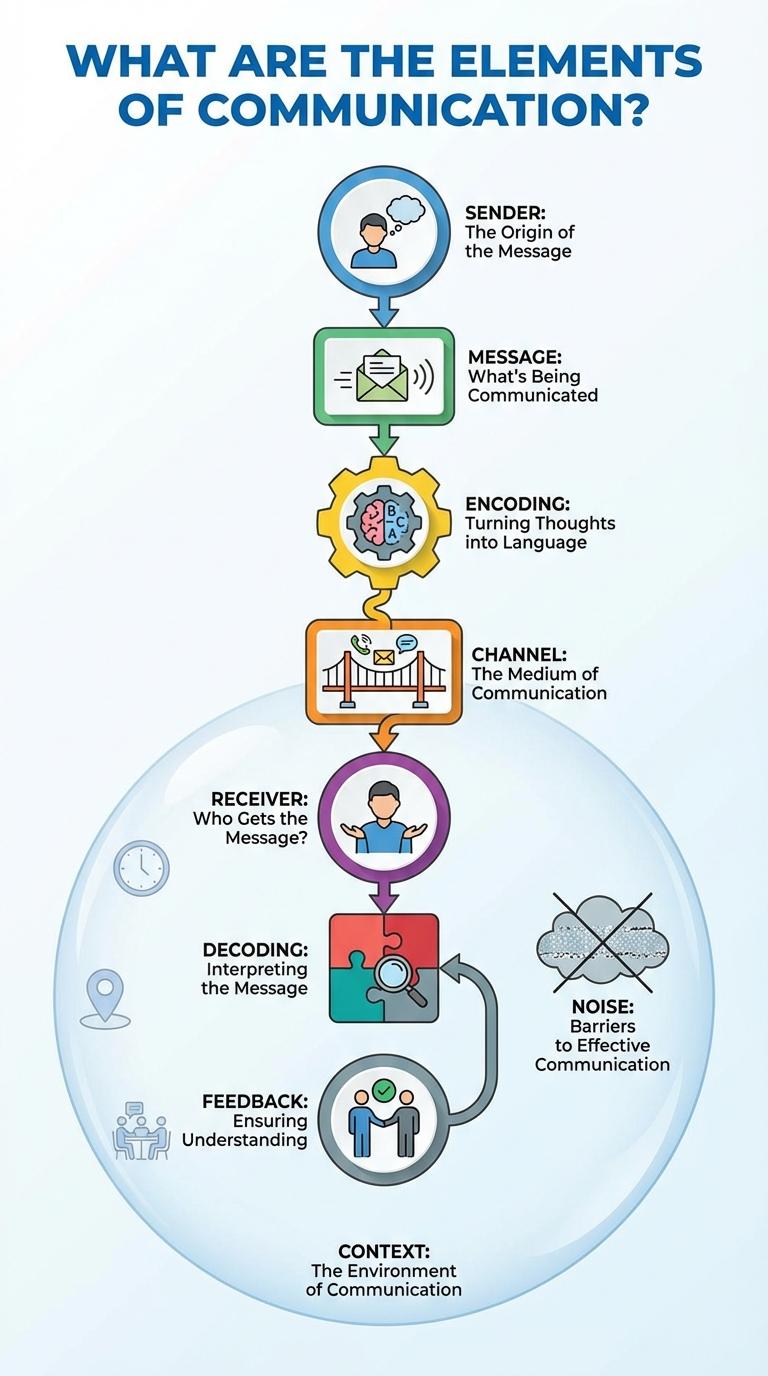
Effective communication relies on several key elements that work together to convey messages clearly and accurately. These components include the sender, message, medium, receiver, and feedback, all essential for successful information exchange. Understanding each element enhances interpersonal skills and helps avoid misunderstandings.
What Are the Elements of Communication?
Communication involves several key elements that work together to convey messages effectively. Understanding these components helps improve clarity and reduce misunderstandings in various contexts.
The primary elements of communication include the sender, who initiates the message, and the receiver, who interprets it. The message itself is the information or content being shared, while the medium refers to the channel used to transmit the message, such as speech, writing, or digital platforms. Feedback is the response from the receiver, confirming whether the message was understood as intended.
Sender: The Origin of the Message
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Sender | The originator of the message who encodes and transmits information to the receiver. |
| Role | Initiates communication by crafting and delivering the message. |
| Functions | Encodes the message using appropriate symbols, language, or signals to ensure clarity and understanding. |
| Importance | Sets the tone, purpose, and context for the entire communication process. |
| Characteristics | Clarity, intent, audience awareness, and encoding skills directly impact message effectiveness. |
Message: What's Being Communicated
The message is the core element of communication, representing the information or idea being conveyed. It encompasses the content, tone, and intent behind the communication. Effective messages are clear, concise, and tailored to the audience's needs and context.
Encoding: Turning Thoughts into Language
Encoding is the process of converting thoughts into verbal or non-verbal symbols that can be understood by others. It plays a crucial role in effective communication by shaping how messages are prepared and delivered.
- Idea Formation - The communicator formulates the message based on thoughts and emotions to be shared.
- Selection of Symbols - Appropriate language, gestures, or signs are chosen to represent the message clearly.
- Message Construction - Symbols are organized logically to encode the intended meaning before transmission.
Channel: The Medium of Communication
The channel is the medium through which a message travels from the sender to the receiver. Common communication channels include face-to-face conversations, emails, phone calls, and social media platforms. Choosing the appropriate channel affects message clarity, speed, and effectiveness.
Receiver: Who Gets the Message?
Who exactly is the receiver in the communication process?
The receiver is the individual or group who interprets and understands the message sent by the sender. Effective communication depends on the receiver accurately decoding the intended information.
Decoding: Interpreting the Message
Decoding is the process where the receiver interprets and makes sense of the message sent by the sender. This involves understanding the symbols, language, and context of the communication.
Effective decoding depends on the receiver's knowledge, experience, and current state of mind. Misinterpretation can occur if the message is unclear or if there is noise interfering with the communication.
Feedback: Ensuring Understanding
Feedback is a vital element in the communication process that ensures messages are correctly understood. It involves the receiver responding to the sender, confirming comprehension or indicating the need for clarification.
- Active Listening - Engages the receiver in fully concentrating on the message to provide meaningful feedback.
- Clarification - Helps resolve misunderstandings by asking questions and confirming details.
- Nonverbal Cues - Includes gestures and facial expressions that signal understanding or confusion.
Effective feedback closes the communication loop, enhancing accuracy and mutual understanding.
Noise: Barriers to Effective Communication
Noise refers to any interference that disrupts the clarity or accuracy of communication between sender and receiver. It creates barriers that hinder effective message transmission and understanding.
- Physical Noise - External sounds or environmental factors that distract participants during communication.
- Psychological Noise - Internal mental states such as stress or prejudice that distort message perception.
- Semantic Noise - Misinterpretations caused by ambiguous or complex language used in the message.
