Fake news spreads misinformation rapidly, distorting public perception and undermining trust in reliable sources. Visualizing the impact and common tactics of fake news helps audiences identify and resist deceptive content. Awareness through engaging infographics empowers critical thinking and promotes media literacy.
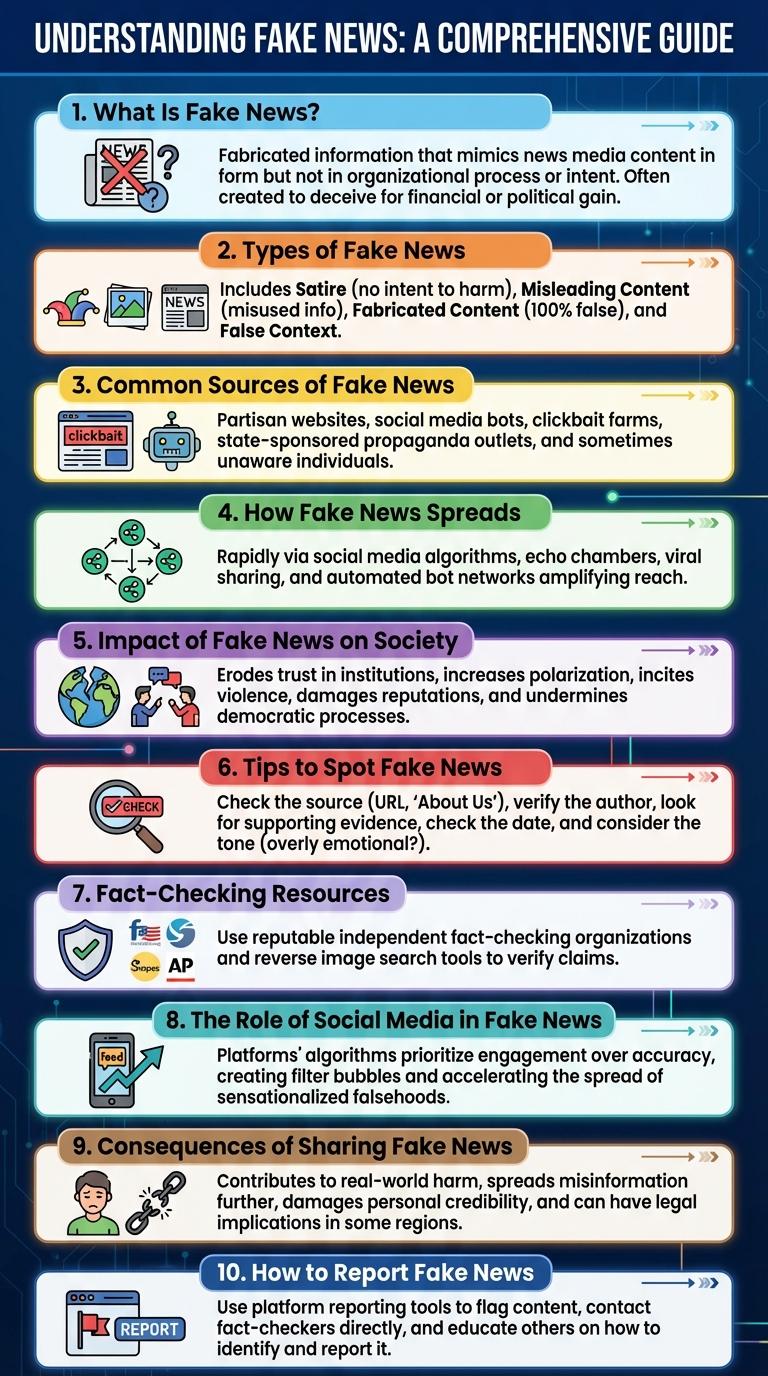
What Is Fake News?
Fake news refers to false or misleading information presented as news. It is designed to deceive readers and manipulate public opinion.
Often created to generate clicks or advance political agendas, fake news spreads rapidly on social media platforms. Recognizing fake news requires critical evaluation of sources and content.
Types of Fake News
Fake news spreads misinformation that can mislead and manipulate public opinion. Understanding the different types of fake news helps in identifying and combating it effectively.
Types of fake news include fabricated content, where stories are entirely made up with no factual basis. Misleading content distorts facts to create false impressions. Satire or parody presents exaggerated or humorous stories that can be mistaken for real news.
Common Sources of Fake News
Fake news spreads rapidly through various common sources, often misleading large audiences. Understanding these sources helps in identifying and avoiding misinformation effectively.
- Social Media Platforms - Rapid sharing and weak content verification make social media a primary channel for fake news circulation.
- Unverified News Websites - Websites lacking editorial standards often publish sensational or false stories to attract clicks.
- Messaging Apps - Encrypted, private chats on messaging apps facilitate the unchecked spread of rumors and false information.
- Political Propaganda - Fake news is used strategically by political groups to influence public opinion and discredit opponents.
- Sensationalist Blogs - Blogs focusing on exaggerated or fabricated stories aim to entertain or provoke strong emotional responses.
Recognizing these common sources is essential to critically evaluate news and prevent the spread of fake information.
How Fake News Spreads
Fake news spreads rapidly through social media platforms where sensational content captures user attention and encourages sharing without verification. Bots and automated accounts amplify misinformation by increasing its visibility and reach across networks. Emotional responses often drive users to engage with and propagate fake news, making it difficult to control its dissemination.
Impact of Fake News on Society
Fake news significantly disrupts social harmony and undermines public trust in reliable information. Its widespread circulation fuels misinformation, leading to harmful consequences across communities.
- Erosion of Trust - Fake news diminishes confidence in media and authoritative sources, confusing public perception.
- Polarization - False information intensifies social and political divisions by promoting biased narratives.
- Public Health Risks - Misinformation about health issues can result in dangerous behaviors and increased disease spread.
Tips to Spot Fake News
Fake news spreads misinformation that can mislead and confuse readers. Common signs include sensational headlines, lack of credible sources, and poor grammar. Always verify information through trusted news outlets before sharing.
Fact-Checking Resources
| Fact-Checking Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Snopes | Established website that debunks myths, rumors, and misinformation with detailed analysis. |
| PolitiFact | Focuses on political claims using a Truth-O-Meter rating to verify accuracy. |
| FactCheck.org | Nonprofit that monitors factual accuracy of statements by public figures and media. |
| AP Fact Check | Associated Press's service providing verified information on current news stories. |
| Media Bias/Fact Check | Assesses media sources for bias and factual reliability, helping users identify trustworthy outlets. |
The Role of Social Media in Fake News
Social media platforms serve as primary channels for the rapid spread of fake news, leveraging algorithms that prioritize engaging content over factual accuracy. These platforms enable users to share misinformation widely, often without verification.
Fake news on social media can influence public opinion and polarize communities by spreading biased or false narratives. The anonymity and speed of social media contribute to the challenge of tracking and combating fake news effectively.
Consequences of Sharing Fake News
Sharing fake news can lead to widespread misinformation and damage public trust. Understanding the consequences helps promote responsible information sharing.
Fake news consequences affect individuals, communities, and society at large.
- Erosion of Trust - Fake news undermines confidence in reliable news sources and institutions.
- Social Division - False information can create misunderstandings and increase polarization within communities.
- Harm to Public Health - Misinformation about health topics can lead to dangerous behaviors and poor decision-making.
- Damage to Reputations - Individuals or organizations targeted by fake news may suffer unjust harm to their credibility.
- Legal and Economic Impact - Sharing false information can result in legal consequences and economic losses for businesses and individuals.
