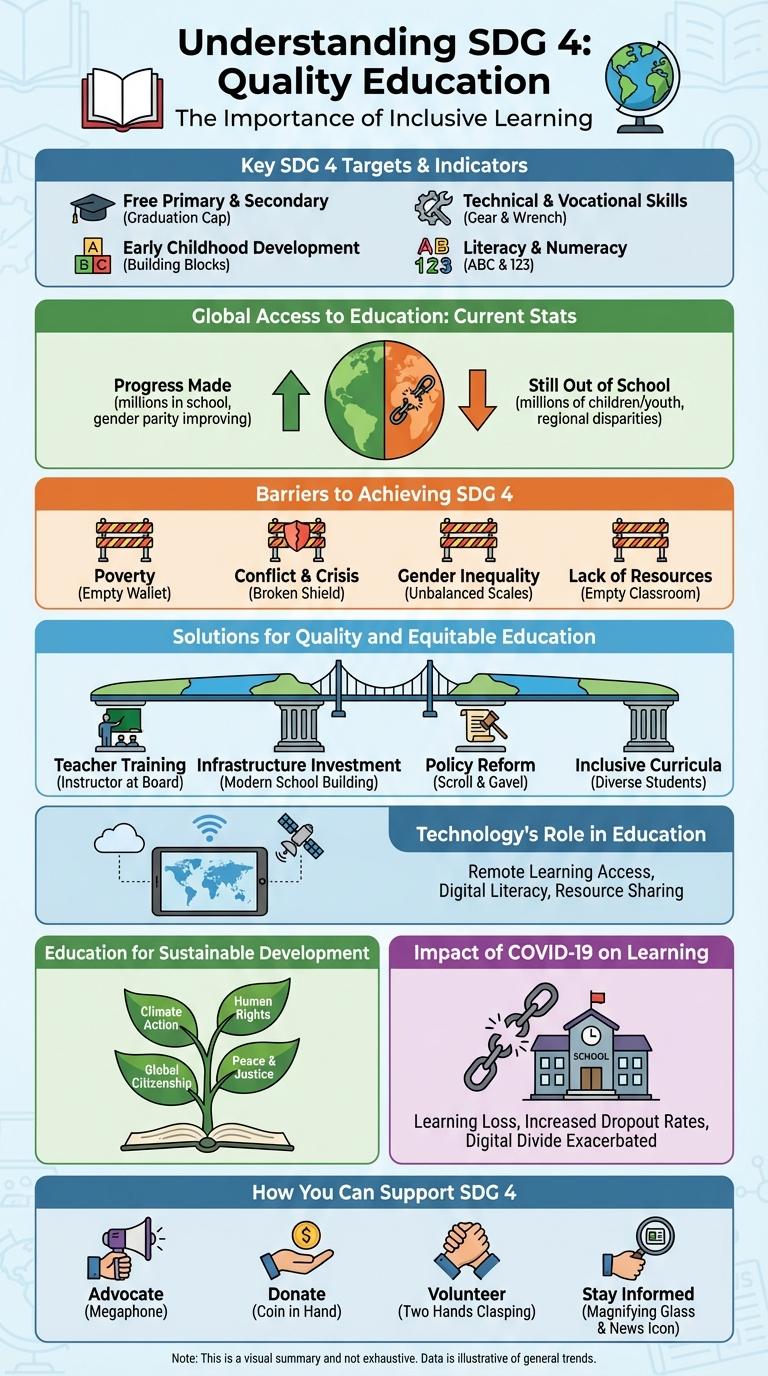
SDG 4 focuses on ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities for all. This infographic highlights key targets, progress indicators, and challenges faced worldwide in achieving universal access to education. Visualizing these data points reveals the critical steps needed to advance global learning outcomes and reduce disparities.
Understanding SDG 4: Quality Education
SDG 4 aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all. It promotes lifelong learning opportunities to improve knowledge and skills worldwide.
- Access to Education - SDG 4 focuses on eliminating barriers to education, ensuring all children and adults can attend school.
- Quality Learning - The goal emphasizes skills development for employment, citizenship, and sustainable development.
- Equity and Inclusion - SDG 4 targets marginalized groups to reduce disparities in education access and outcomes.
The Importance of Inclusive Learning
SDG 4 aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all, promoting lifelong learning opportunities. Inclusive learning addresses barriers faced by marginalized groups, enabling equal access and participation.
Inclusive education supports children with disabilities, girls, and disadvantaged communities by adapting teaching methods and learning environments. It fosters diversity, reduces inequalities, and promotes social cohesion. Quality education builds skills necessary for employment and sustainable development.
Key SDG 4 Targets & Indicators
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. Key targets include universal primary and secondary education, equal access to affordable vocational training, and eliminating gender disparities in education. Indicators track metrics such as literacy rates, enrollment ratios, and completion rates across different education levels.
| Key SDG 4 Targets | Relevant Indicators |
|---|---|
| Universal primary and secondary education | Gross enrollment ratio, completion rate |
| Equal access to vocational & higher education | Participation rate in vocational training, tertiary education enrollment |
| Eliminate gender disparities | Gender parity index in enrollment |
| Increase literacy and numeracy | Adult literacy rate, youth literacy rate |
| Improve quality of education | Student-teacher ratio, learning outcomes assessments |
Global Access to Education: Current Stats
Global Access to Education remains a critical goal within Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), aiming to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all. Despite progress, approximately 258 million children and youth worldwide are still out of school.
Primary school completion rates have increased to 79%, yet disparities persist in low-income regions, where children face barriers such as poverty and conflict. Female literacy rates have improved, but gender gaps in education access continue to challenge global targets.
Barriers to Achieving SDG 4
What are the main barriers to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) on quality education? Access to quality education remains limited due to socioeconomic disparities and insufficient educational infrastructure in many regions. These challenges hinder inclusive and equitable learning opportunities for all children and adults worldwide.
| Barrier | Impact |
|---|---|
| Poverty and Inequality | Limits access to schooling and resources, especially for marginalized groups. |
| Lack of Qualified Teachers | Reduces teaching quality and learning outcomes in many countries. |
| Inadequate Infrastructure | Prevents safe and conducive learning environments, affecting attendance. |
| Gender Disparities | Results in unequal educational opportunities between boys and girls. |
| Conflict and Crisis | Disrupts schooling and limits access to education for displaced children. |
Solutions for Quality and Equitable Education
SDG 4 aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all, promoting lifelong learning opportunities. Solutions include investing in teacher training, integrating technology in classrooms, and developing inclusive curricula that address diverse learning needs. Strengthening education systems and increasing funding help reduce disparities and improve learning outcomes worldwide.
Technology's Role in Education
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing Sustainable Development Goal 4 (Quality Education) by enhancing access, engagement, and personalized learning experiences worldwide. Digital tools and platforms address educational disparities and support inclusive, equitable education for all.
- Access to Learning Resources - Online libraries, e-books, and educational apps provide students and teachers with vast learning materials anytime, anywhere.
- Interactive and Personalized Education - Adaptive learning technologies customize lessons based on individual student needs, improving comprehension and retention.
- Bridging Educational Gaps - Remote learning platforms connect underserved communities to quality education, reducing geographic and socioeconomic barriers.
Investing in education technology fosters lifelong learning opportunities and accelerates progress toward universal quality education.
Education for Sustainable Development
Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) empowers learners to build a sustainable future by acquiring knowledge, skills, and values. SDG 4 highlights the importance of inclusive, equitable quality education that promotes lifelong learning opportunities for all.
- Global Reach - Over 90% of countries have integrated ESD into national education policies to address sustainability challenges.
- Skill Development - ESD fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and active citizenship for sustainable development.
- Gender Equality - Equal access to education reduces gender disparities and promotes social inclusion worldwide.
Impact of COVID-19 on Learning
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted education for over 1.6 billion learners worldwide, causing unprecedented school closures. Remote learning challenges widened existing inequalities, impacting vulnerable and marginalized students the most.
Access to digital devices and stable internet became critical for continuing education during lockdowns. Many countries faced setbacks in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 4, which aims for inclusive and equitable quality education for all.
