Nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas, serving as the foundation of language and communication. This infographic breaks down the different types of nouns, including proper, common, abstract, and collective nouns, highlighting their unique roles. Understanding nouns enhances clarity and precision in both writing and speech.
What Are Nouns?
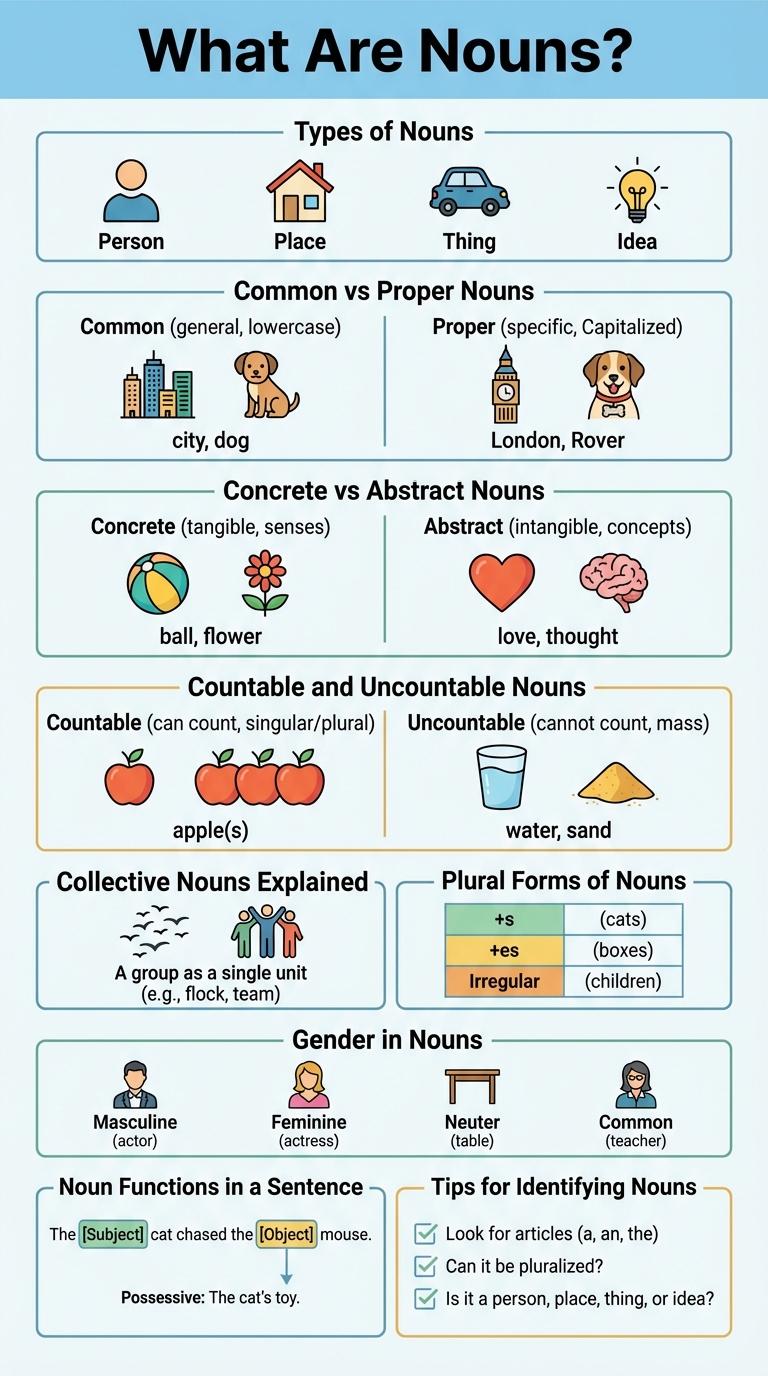
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They serve as the subject or object in a sentence.
Common nouns refer to general items, such as "city" or "car." Proper nouns specify names, like "Paris" or "Toyota." Abstract nouns represent intangible concepts, including "freedom" and "happiness."
Types of Nouns
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. Understanding the different types of nouns helps improve grammar and writing clarity.
Common nouns name general items like "city" or "dog," while proper nouns specify unique names such as "London" or "Max." Concrete nouns represent physical objects, whereas abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts like "freedom" or "happiness."
Collective nouns describe groups, for example, "team" or "flock." Countable nouns can be quantified, such as "books," and uncountable nouns represent substances or concepts that cannot be counted, like "water" or "knowledge."
Common vs Proper Nouns
| Type of Noun | Definition & Examples |
|---|---|
| Common Nouns | General names for people, places, or things. Examples: dog, city, teacher |
| Proper Nouns | Specific names for unique entities, always capitalized. Examples: London, Sarah, Amazon |
| Usage | Common nouns are generic; proper nouns identify particular individuals or locations. |
| Capitalization | Common nouns are lowercase unless starting a sentence; proper nouns are always capitalized. |
| Examples in Sentences | Common: The teacher spoke loudly. Proper: Mrs. Smith spoke loudly. |
Concrete vs Abstract Nouns
Nouns are fundamental parts of speech that name people, places, things, or ideas. They are categorized into concrete and abstract nouns based on their physical presence and perceptibility.
- Concrete Nouns - Refer to tangible objects that can be perceived through the senses, such as "apple," "dog," or "house."
- Abstract Nouns - Represent intangible concepts, emotions, or qualities like "freedom," "love," or "intelligence."
- Usage in Language - Concrete nouns often appear in descriptive writing, while abstract nouns are common in philosophical or emotional contexts.
Distinguishing between concrete and abstract nouns enhances clarity and precision in communication.
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They are categorized into countable and uncountable nouns based on whether they can be counted.
Countable nouns refer to items that can be counted individually, while uncountable nouns represent substances or concepts that cannot be separated into distinct units.
- Countable Nouns - These nouns have singular and plural forms, such as "apple" and "apples."
- Uncountable Nouns - These nouns do not usually have a plural form, examples include "water" and "information."
- Usage in Sentences - Countable nouns use numbers and articles like "a" or "an," while uncountable nouns use quantifiers like "some" or "much."
Collective Nouns Explained
Collective nouns refer to words that represent a group of individuals or things as a single entity. Examples include "team," "flock," and "family," illustrating how one word can denote multiple members.
Understanding collective nouns helps improve both comprehension and communication skills. They play a crucial role in grammar by clarifying whether the focus is on the group as a whole or its individual members.
Plural Forms of Nouns
Nouns change form to indicate more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Understanding plural forms is essential for proper grammar and communication.
Plural forms of nouns follow specific rules and exceptions in English.
- Regular Plurals - Most nouns form plurals by adding -s or -es to the singular form.
- Irregular Plurals - Some nouns have unique plural forms that change the word entirely.
- Uncountable Nouns - Certain nouns do not have plural forms because they represent substances or concepts.
Gender in Nouns
What is gender in nouns? Gender in nouns refers to the classification of words based on masculine, feminine, and neuter forms. This classification helps in understanding language structure and agreement in grammar.
Noun Functions in a Sentence
Nouns serve as the subject, object, or complement within a sentence, providing essential information about who or what is involved. They can function as the subject performing the action, the direct or indirect object receiving the action, or as a predicate nominative renaming the subject. Understanding noun functions enhances sentence clarity and effective communication.
