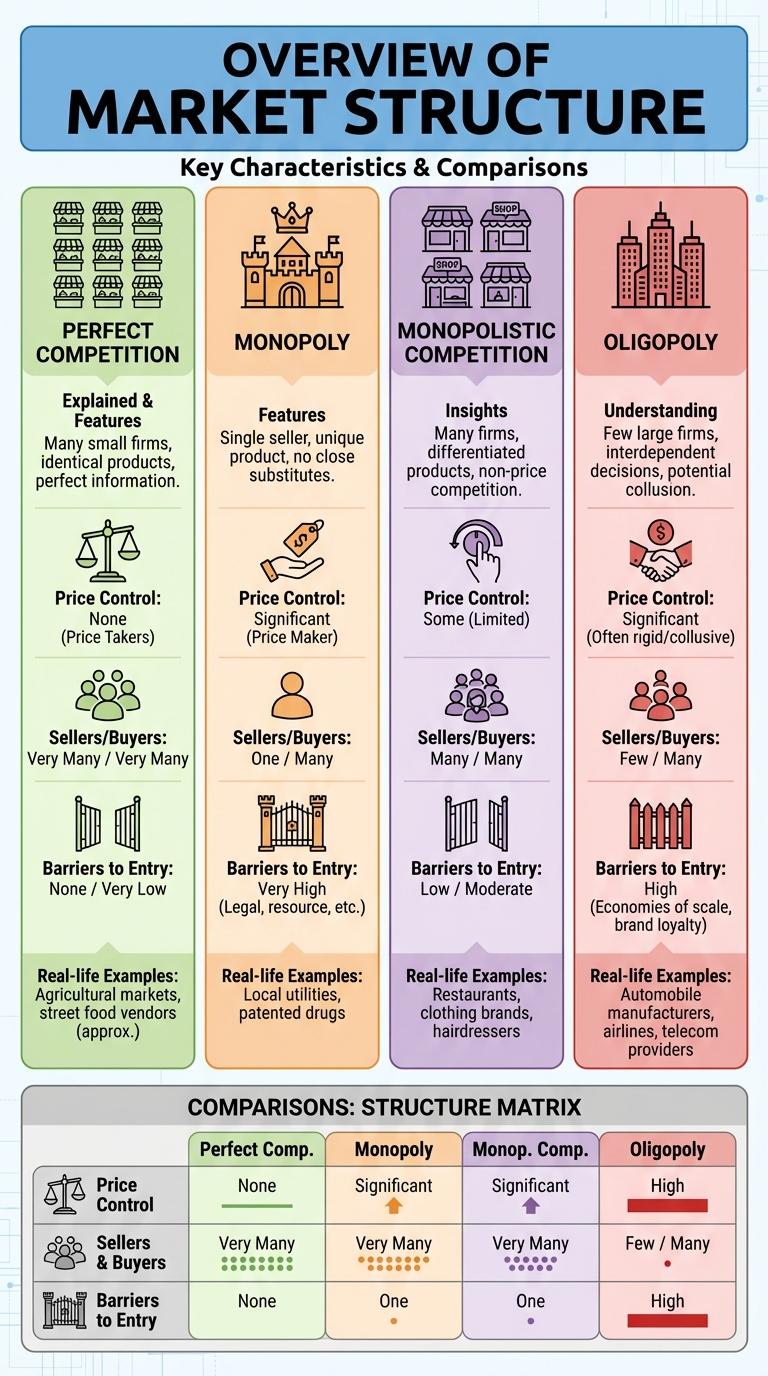
The infographic visually explains the key components and classifications of the market structure, detailing how different types of markets operate and interact with buyers and sellers. It covers concepts such as perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition, highlighting their unique features and competitive dynamics. Essential economic principles are presented clearly to enhance understanding of market behaviors and outcomes.
Overview of Market Structure
Market structure refers to the organizational and other characteristics of a market that influence the nature of competition and pricing. It determines how firms operate, the level of market power they hold, and how goods and services are distributed. Common types include perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly.
Key Characteristics of Market Structures
| Market Structure | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Perfect Competition | Many sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, perfect information |
| Monopoly | Single seller, unique product, high barriers to entry, price maker |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many sellers, differentiated products, some barriers to entry, some price control |
| Oligopoly | Few sellers, interdependent decision-making, barriers to entry, products may be homogeneous or differentiated |
Perfect Competition Explained
Perfect competition is a market structure characterized by many small firms selling identical products. Each firm is a price taker, unable to influence the market price due to the high level of competition.
In this structure, buyers and sellers have full information, ensuring transparency. The ease of entering and exiting the market maintains the competitive environment and drives efficiency.
Features of Monopoly
Monopoly represents a market structure dominated by a single seller controlling the entire supply of a product or service. This structure limits competition, granting significant market power to the monopolist.
- Single Seller - Only one firm supplies the entire market, eliminating competition.
- Unique Product - The product offered has no close substitutes available to consumers.
- Barriers to Entry - High obstacles prevent other firms from entering the market.
- Price Maker - The monopolist sets prices without competitive pressure.
- Restricted Output - Output levels are controlled to maximize profits rather than meet demand fully.
Monopolies influence market efficiency and consumer choice by restricting supply and controlling prices.
Monopolistic Competition Insights
Monopolistic competition is a market structure characterized by many firms offering differentiated products. It combines features of both perfect competition and monopoly, leading to unique competitive dynamics.
- Product Differentiation - Firms sell products that are similar but not identical, allowing for brand loyalty and consumer choice.
- Many Sellers - Numerous firms compete, each holding a small market share without dominating the market.
- Free Entry and Exit - New competitors can enter the market easily, while existing firms can leave without significant barriers.
Understanding Oligopoly
Oligopoly is a market structure characterized by a small number of firms dominating the industry, leading to limited competition. These firms hold significant market power, often influencing prices and output levels through strategic interactions. Understanding oligopoly helps in analyzing how companies maintain control and the impact on consumer choices.
Comparisons: Price Control in Each Structure
Price control varies significantly across different market structures, influencing both market efficiency and consumer welfare. Understanding these variations provides insight into how prices are regulated or left to market forces.
- Perfect Competition - Prices are determined by market supply and demand with no individual firm control, leading to efficient price regulation.
- Monopolistic Competition - Firms have limited price control due to product differentiation but face competition that restricts excessive pricing.
- Oligopoly - Price control is moderate, often influenced by collusion or price leadership among a few dominant firms to stabilize or increase prices.
- Monopoly - The sole supplier wields significant price control, often setting higher prices due to lack of competition and entry barriers.
- Government Intervention - Imposed price ceilings or floors can regulate prices in any market structure to protect consumers or producers.
Number of Sellers and Buyers
The estruktura ng pamilihan (market structure) is defined by the number of sellers and buyers participating in the market. This structure determines the level of competition and market control each participant holds.
Markets with many sellers and buyers, such as perfect competition, feature minimal individual influence on prices. In contrast, markets like monopoly have a single seller dominating buyers. Oligopoly markets have few sellers influencing a large number of buyers, impacting pricing and supply decisions.
Barriers to Entry Across Structures
Barriers to entry vary significantly across different market structures, influencing competition levels. Perfect competition features minimal barriers, allowing new firms to enter freely, while monopolies have high barriers that prevent new competitors.
In monopolistic competition, moderate barriers exist due to brand loyalty and product differentiation. Oligopolies present substantial barriers through economies of scale, legal restrictions, and control over essential resources, limiting new entrants.
