Rice is a staple food for over half of the world's population, playing a crucial role in global nutrition and culture. This infographic highlights key facts about rice cultivation, consumption patterns, and its environmental impact. Understanding these aspects helps promote sustainable practices and food security worldwide.
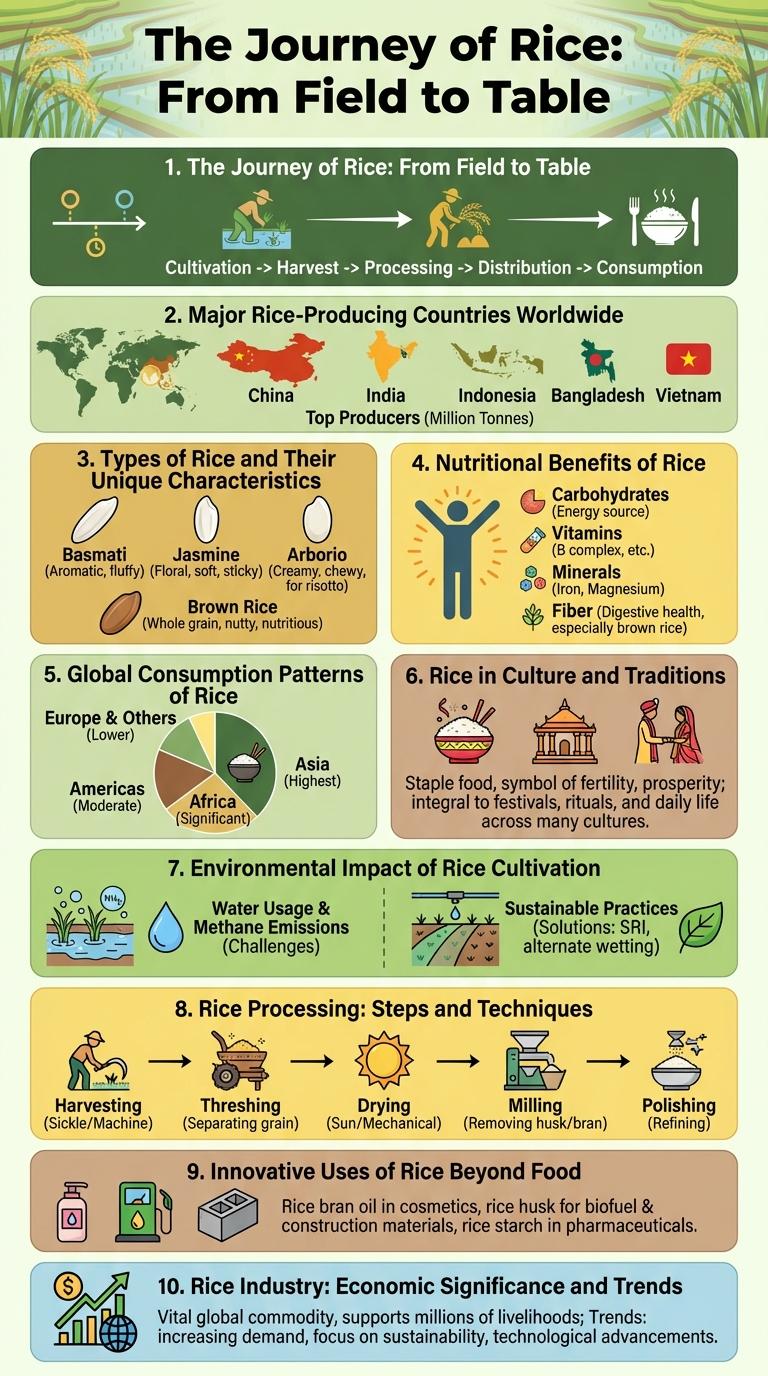
The Journey of Rice: From Field to Table
Rice is a staple food for over half of the world's population, beginning its journey in vast paddies and ending on dining tables globally. Understanding its path highlights the intricate process from cultivation to consumption.
- Planting and Growth - Rice seeds are sown in flooded fields, where they germinate and grow into mature plants over several months.
- Harvesting - Once mature, rice stalks are cut and gathered, often using mechanized harvesters or manual labor.
- Processing - The harvested rice undergoes threshing, drying, milling, and polishing to produce edible white or brown rice.
- Distribution - Processed rice is packaged and transported to markets, ensuring availability worldwide.
- Consumption - Rice is prepared in countless culinary styles reflecting cultural diversity and nutrition.
The journey of rice from field to table exemplifies agricultural innovation and global food supply chains.
Major Rice-Producing Countries Worldwide
Rice is a staple food for more than half of the world's population, with its production concentrated in specific regions. The major rice-producing countries contribute significantly to global food security and economy.
China leads as the largest producer, followed by India, both accounting for over half of the world's rice output. Other key producers include Indonesia, Bangladesh, and Vietnam, which play vital roles in sustaining regional and global demand.
Types of Rice and Their Unique Characteristics
Rice is a staple food with diverse types including Basmati, Jasmine, Arborio, and Brown rice, each offering unique textures and flavors. Basmati rice is known for its long grains and aromatic fragrance, ideal for Indian and Middle Eastern dishes. Jasmine rice offers a soft, sticky texture with a floral aroma, while Arborio is creamy and perfect for risottos; Brown rice retains its bran layer, providing higher fiber content and a nuttier taste.
Nutritional Benefits of Rice
What are the nutritional benefits of rice? Rice is a rich source of carbohydrates, providing essential energy for the body. It also contains important nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber that support overall health.
How does rice contribute to a balanced diet? Rice offers low fat content and is gluten-free, making it suitable for various dietary needs. Brown rice, in particular, contains antioxidants and higher fiber levels, promoting digestive health.
Which vitamins and minerals are found in rice? Rice contains B vitamins such as thiamine, niacin, and riboflavin, which aid metabolism and brain function. It also provides minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese, essential for bone health and enzyme function.
Is rice beneficial for energy and weight management? The complex carbohydrates in rice provide sustained energy release, preventing spikes in blood sugar. Brown rice's fiber content supports satiety, helping to manage hunger and weight.
Can rice play a role in heart health? Regular consumption of whole grain rice is linked to reduced cholesterol levels and lower risk of heart disease. It helps maintain healthy blood pressure due to its potassium content.
Global Consumption Patterns of Rice
Rice is a staple food for over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia. Its consumption patterns vary significantly across different regions, reflecting cultural, economic, and dietary preferences.
- Asia dominates rice consumption - Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are the largest rice consumers due to their high population and rice-based diets.
- Rice consumption per capita varies globally - Southeast Asia and South Asia exhibit the highest per capita rice intake compared to Western countries.
- Emerging markets show growing rice demand - Africa and Latin America are increasing rice consumption as dietary habits evolve with urbanization.
Rice in Culture and Traditions
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Symbolism | Rice symbolizes prosperity, fertility, and life in many cultures around the world. |
| Rituals | Used in ceremonies like weddings, harvest festivals, and religious offerings. |
| Culinary Traditions | Staple food in Asian, African, and Latin American cuisines, varying from sticky rice to biryani dishes. |
| Festivals | Events such as Japan's rice planting festivals and India's Pongal celebrate rice cultivation and harvest. |
| Art and Language | Rice appears in folklore, proverbs, and traditional arts, reflecting cultural identity. |
Environmental Impact of Rice Cultivation
Rice cultivation plays a significant role in global food supply but has notable environmental impacts. Understanding these effects is critical for developing sustainable agricultural practices.
- Water Usage - Rice farming consumes approximately 2,500 liters of water per kilogram of produced rice, making it one of the most water-intensive crops.
- Methane Emissions - Flooded rice paddies are a major source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
- Soil Degradation - Continuous monoculture of rice can lead to soil nutrient depletion and increased vulnerability to erosion.
Rice Processing: Steps and Techniques
Rice processing involves multiple steps to transform harvested paddy into edible rice. Key stages include cleaning, hulling, milling, and polishing to ensure quality and safety.
Cleaning removes impurities like stones and dust, while hulling separates the husk from the grain. Milling further refines rice by removing bran layers, producing white or brown rice depending on the extent of milling.
Innovative Uses of Rice Beyond Food
Rice serves as a versatile raw material extending beyond culinary use into various innovative applications. Researchers develop biodegradable packaging and textiles from rice husks, promoting sustainability and reducing plastic waste. Furthermore, rice-derived biofuels and cosmetics showcase the crop's potential in energy and personal care industries, emphasizing its economic and environmental importance.
