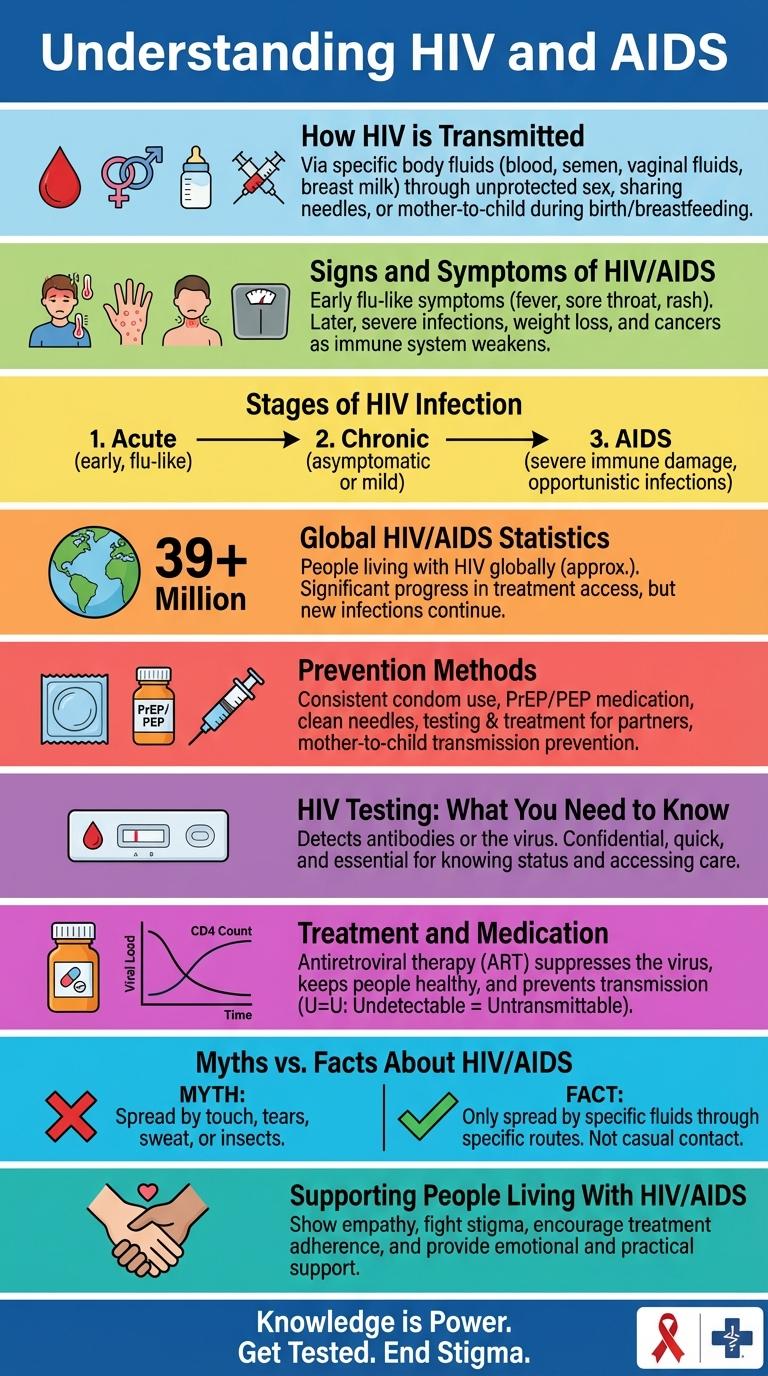
HIV and AIDS remain critical global health challenges, impacting millions of lives worldwide. Understanding the differences between HIV infection and AIDS progression is essential for effective prevention and treatment. This infographic presents key facts, statistics, and prevention strategies to raise awareness and promote informed action against the virus.
Understanding HIV and AIDS
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the body's immune system. AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is the advanced stage of HIV infection characterized by a severely weakened immune system.
Understanding the difference between HIV and AIDS is essential for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
- HIV Transmission - The virus spreads through contact with infected bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- Immune System Impact - HIV targets and destroys CD4 cells, which weakens the immune system over time.
- AIDS Diagnosis - AIDS is diagnosed when the CD4 cell count drops below 200 cells/mm3 or when certain opportunistic infections occur.
How HIV is Transmitted
HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, primarily spreads through the exchange of certain body fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, rectal fluids, and breast milk. It attacks the immune system, leading to AIDS if untreated.
Transmission occurs mostly via unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. Sharing needles or syringes, receiving contaminated blood transfusions, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding are other common ways HIV spreads. Using protection and proper medical precautions significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Signs and Symptoms of HIV/AIDS
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) attacks the immune system, leading to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) if untreated. Early detection through signs and symptoms supports timely medical intervention and reduces transmission.
Recognizing common HIV/AIDS symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and care management.
- Fever and Night Sweats - Persistent high fever and excessive sweating often indicate the body's response to HIV infection.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes - Enlarged lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpits, or groin, reflect immune system activity fighting the virus.
- Unexplained Weight Loss - Significant weight loss without dieting or increased exercise can signal disease progression toward AIDS.
Stages of HIV Infection
HIV infection progresses through distinct stages that impact the immune system over time. Understanding these stages is crucial for effective treatment and management.
The initial stage, Acute HIV Infection, occurs 2 to 4 weeks after exposure and features flu-like symptoms. The virus multiplies rapidly, causing a high viral load and increased infectiousness.
The Chronic HIV Infection or Clinical Latency stage can last several years with limited symptoms. During this phase, the virus remains active but reproduces at lower levels, gradually weakening the immune system.
AIDS, the final stage, happens when the immune system is severely damaged, and the CD4 cell count drops below 200 cells/mm3. Opportunistic infections and cancers become common, making treatment essential for survival.
Global HIV/AIDS Statistics
Over 38 million people worldwide live with HIV as of 2023, according to UNAIDS. Approximately 1.5 million new HIV infections occur annually, with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for nearly 60% of cases. Global access to antiretroviral therapy has increased, with 28 million people receiving treatment, improving life expectancy and reducing transmission rates.
Prevention Methods
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) attacks the immune system, while AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is the advanced stage of HIV infection. Effective prevention methods are crucial to reduce transmission and protect public health.
Using condoms consistently during sexual intercourse significantly lowers the risk of HIV transmission. Regular testing, antiretroviral therapy (ART), and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) also play vital roles in preventing HIV infection.
HIV Testing: What You Need to Know
| HIV Testing | Key Facts |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect HIV infection early to start timely treatment and prevent transmission |
| Types of Tests | Antibody tests, Antigen/antibody combination tests, Nucleic acid tests (NAT) |
| Testing Window Period | Typically 10 to 33 days after exposure depending on test type |
| Where to Get Tested | Clinics, hospitals, community centers, home testing kits |
| Importance of Testing | Early diagnosis enables effective antiretroviral treatment and reduces transmission risk |
Treatment and Medication
HIV treatment focuses on antiretroviral therapy (ART) to control the virus and prevent progression to AIDS. Early and consistent medication improves life expectancy and reduces transmission risk.
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) - ART suppresses HIV replication, maintaining low viral load and preserving immune function.
- Medication Adherence - Consistent intake of prescribed medications is critical for treatment efficacy and resistance prevention.
- Drug Regimens - Common regimens combine multiple drugs targeting different stages of the HIV lifecycle.
Effective treatment transforms HIV from a fatal diagnosis into a manageable chronic condition.
Myths vs. Facts About HIV/AIDS
Can HIV be transmitted through casual contact? HIV cannot be spread by hugging, shaking hands, or sharing dishes. It requires specific transmission routes such as blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child.
Is AIDS the same as HIV? HIV is the virus that causes AIDS, which is the final stage of HIV infection. Not everyone with HIV develops AIDS with proper treatment.
Can a person with HIV look healthy? Many people with HIV appear completely healthy for years. Regular treatment helps maintain health and prevent symptoms.
Does HIV only affect certain groups of people? HIV can affect anyone regardless of age, gender, or sexual orientation. It is a global health issue requiring awareness and prevention for all.
Is there a cure for HIV/AIDS? Currently, there is no cure for HIV, but antiretroviral therapy can control the virus effectively. Early diagnosis and treatment improve quality of life and reduce transmission risk.
