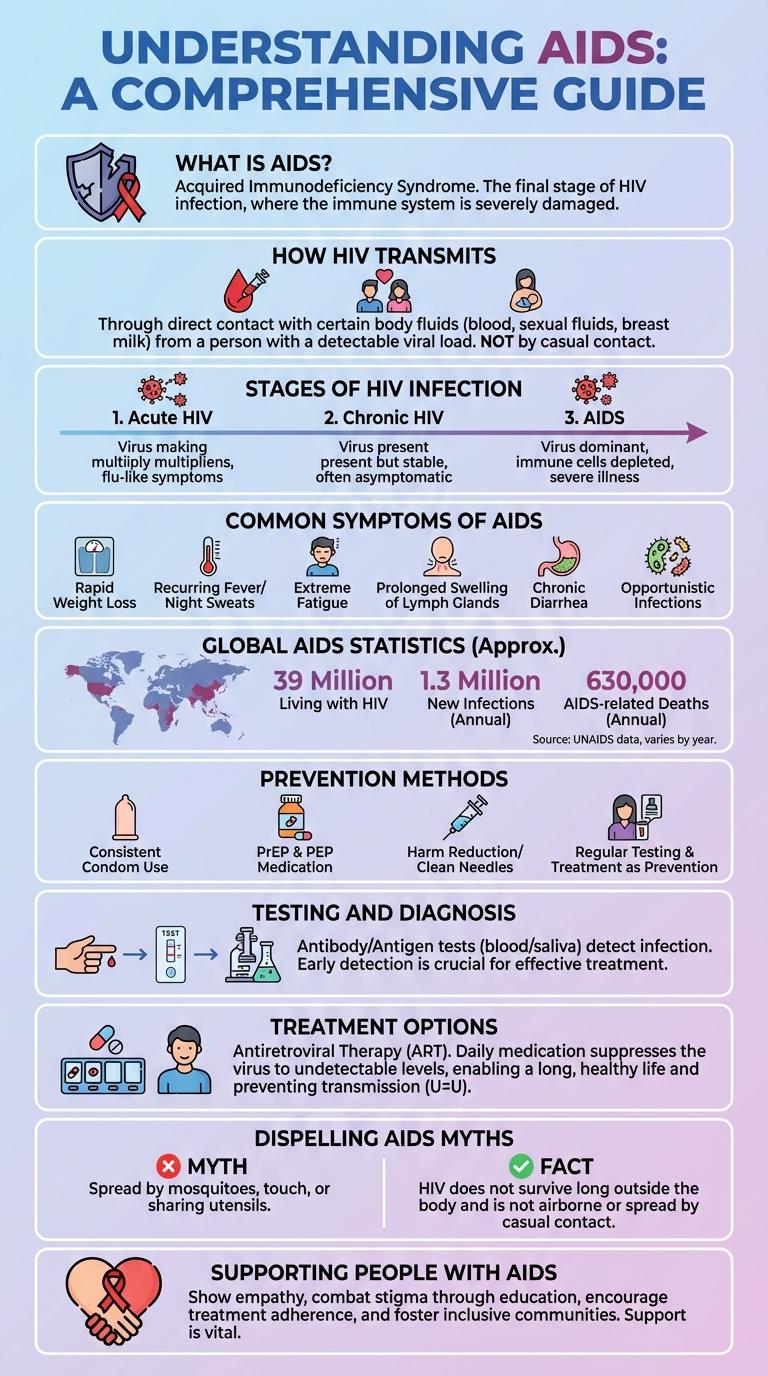
A comprehensive infographic about AIDS presents crucial facts and statistics that enhance public understanding of this global health issue. It highlights transmission methods, prevention strategies, and current treatment options to promote awareness and reduce stigma. Clear visuals and concise data help communicate the ongoing impact of AIDS worldwide.
What is AIDS?
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, a condition caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). It severely weakens the immune system, making the body vulnerable to infections and certain cancers.
- Caused by HIV - HIV attacks vital immune cells, leading to a gradual decline in immune function.
- Late stage of HIV infection - AIDS manifests when the immune system is critically damaged and opportunistic infections occur.
- Life-threatening condition - Without treatment, AIDS significantly reduces lifespan due to weakened defense against diseases.
How HIV Transmits
HIV primarily transmits through direct contact with certain body fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, rectal fluids, and breast milk. The virus cannot be spread through casual contact such as hugging or sharing utensils.
Common transmission routes include unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles or syringes, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. Understanding these transmission methods is crucial for effective prevention and reducing the spread of HIV.
Stages of HIV Infection
HIV infection progresses through three main stages: Acute Infection, Clinical Latency, and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). The Acute Infection stage occurs within 2-4 weeks after exposure, characterized by flu-like symptoms and high viral replication. Clinical Latency can last several years with minimal symptoms, while AIDS is the advanced stage where the immune system is severely damaged, leading to opportunistic infections.
Common Symptoms of AIDS
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is caused by the HIV virus, which attacks the immune system. Common symptoms include persistent fever, swollen lymph nodes, and extreme fatigue. Early detection of these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention and managing the disease effectively.
Global AIDS Statistics
Global AIDS statistics reveal the ongoing impact of HIV/AIDS worldwide. Millions of people live with the virus, while new infections and AIDS-related deaths persist in many regions.
As of 2023, approximately 38 million people are living with HIV globally. Around 1.5 million new HIV infections occur each year, with about 650,000 AIDS-related deaths annually. Sub-Saharan Africa remains the most affected region, accounting for nearly 60% of all HIV cases.
Prevention Methods
AIDS prevention focuses on reducing the transmission of HIV through education and safe practices. Key methods include consistent condom use, regular testing, and avoiding sharing needles.
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a medication that significantly lowers HIV risk for high-exposure individuals. Comprehensive awareness campaigns play a critical role in promoting these prevention strategies worldwide.
Testing and Diagnosis
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Types of HIV Tests | Antibody tests, Antigen/Antibody tests, Nucleic Acid Tests (NAT) |
| Window Period | Time between infection and detectable antibodies ranges from 10 days to 3 months |
| Testing Locations | Clinics, hospitals, community centers, home testing kits |
| Importance of Early Diagnosis | Enables early treatment, reduces transmission risk, improves health outcomes |
| Recommended Testing Frequency | At least once for all adults, every 3-6 months for high-risk groups |
Treatment Options
Effective management of AIDS relies heavily on antiretroviral therapy (ART), which suppresses HIV replication and improves immune function. Early and consistent treatment significantly enhances quality of life and reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) - Combines multiple drugs to reduce HIV viral load and prevent disease progression.
- Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) - Preventative medication for high-risk individuals to reduce HIV infection chances.
- Opportunistic Infection Management - Uses targeted treatments to control infections common in immunocompromised patients.
Dispelling AIDS Myths
Can you get AIDS from casual contact?
AIDS cannot be transmitted through hugging, shaking hands, or sharing utensils. The virus spreads primarily through blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Does AIDS only affect certain groups of people?
AIDS can affect anyone regardless of age, gender, race, or sexual orientation. It is not limited to any specific group or community.
Is there a cure for AIDS?
Currently, there is no cure for AIDS, but antiretroviral therapy (ART) helps manage the disease effectively. ART reduces the viral load and improves quality of life for people living with HIV/AIDS.
Can mosquitoes transmit the AIDS virus?
Mosquitoes and other insects do not transmit HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV cannot survive or reproduce inside insects.
Does using a condom guarantee 100% prevention of AIDS?
Condoms significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission when used correctly and consistently. While highly effective, no prevention method is 100% foolproof, so combining methods is recommended.
