Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral infection primarily affecting young children and causing distinctive sores and rashes. It spreads easily through close contact, respiratory droplets, and contaminated surfaces, making hygiene crucial for prevention. Recognizing symptoms early can help contain outbreaks and ensure timely treatment to reduce discomfort.
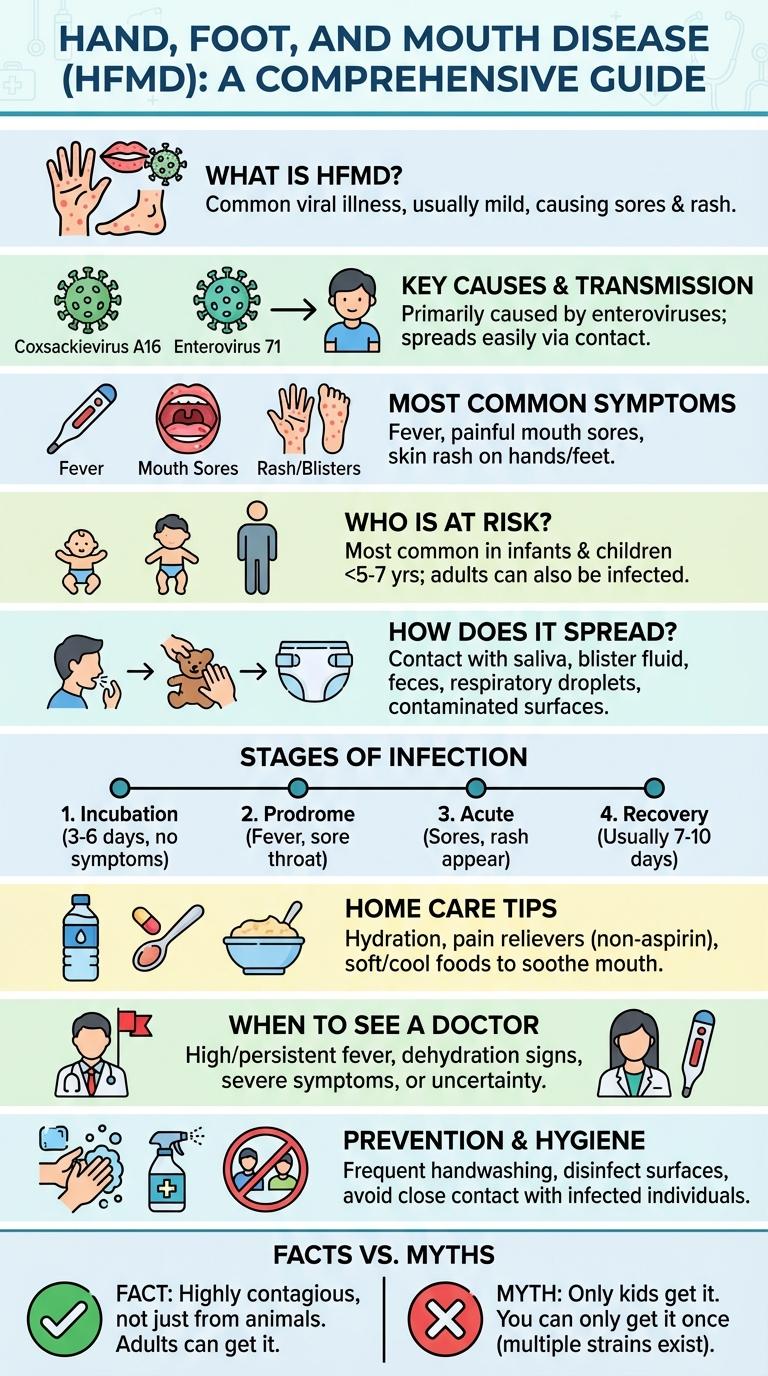
What Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness primarily affecting young children. It is characterized by fever, sores in the mouth, and a rash on the hands and feet.
HFMD is caused by viruses from the Enterovirus genus, most commonly the coxsackievirus. The disease spreads through close personal contact, respiratory droplets, and contact with contaminated surfaces. Symptoms usually appear within 3 to 7 days after exposure and resolve on their own within 7 to 10 days.
Key Causes and Transmission
What causes Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
HFMD is primarily caused by coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71. These viruses belong to the enterovirus family and are highly contagious among children.
How is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease transmitted?
The disease spreads through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, such as saliva, mucus, or blister fluid. Transmission also occurs via contaminated surfaces and close person-to-person contact, especially in childcare settings.
| Key Causes | Transmission Methods |
|---|---|
| Coxsackievirus A16 | Direct contact with saliva |
| Enterovirus 71 | Contact with nasal secretions |
| Other enteroviruses | Touching contaminated surfaces |
| High viral shedding in early infection | Close contact with infected persons |
| Common in children under 5 | Shared toys and utensils |
Most Common Symptoms
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection primarily affecting young children. It spreads through direct contact with nasal secretions, saliva, blister fluid, or feces of an infected person.
Most common symptoms include fever, sore throat, and painful red blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. These symptoms typically appear 3-7 days after exposure to the virus, often lasting 7 to 10 days.
Who Is at Risk?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease primarily affects infants and children under 5 years old due to their developing immune systems. It is highly contagious among children in daycare centers and schools where close contact facilitates virus spread. Adults with weakened immunity or close contact with infected individuals also face potential risk.
How Does It Spread?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection common in young children. It primarily spreads through close contact and contaminated surfaces.
- Direct Contact - The virus spreads through saliva, nasal secretions, or fluid from blisters when an infected person touches or coughs near others.
- Contaminated Surfaces - Touching objects or surfaces contaminated with the virus can lead to infection when hands touch the mouth, eyes, or nose.
- Fecal-Oral Route - The virus is present in stool, and inadequate handwashing after diaper changes or bathroom use facilitates transmission.
Preventive measures like proper hygiene and disinfecting surfaces reduce the spread of HFMD significantly.
Stages of Infection
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) progresses through distinct stages, beginning with an incubation period lasting 3 to 6 days after exposure to the virus. Initial symptoms include fever, sore throat, and malaise, followed by the appearance of red spots and sores on the hands, feet, mouth, and sometimes buttocks. The infection typically resolves within 7 to 10 days as the rash and symptoms gradually fade.
Home Care Tips
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection common in young children. It causes sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
To ease symptoms at home, ensure the child drinks plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. Offer soft, cool foods to prevent mouth pain while eating.
Keep the affected areas clean and dry to prevent secondary infections. Encourage frequent handwashing to reduce the spread of the virus within the household.
When to See a Doctor
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that mostly affects young children. Knowing when to see a doctor is crucial for proper care and to prevent complications.
- High Fever Lasting More Than 3 Days - Persistent fever may indicate complications requiring medical evaluation.
- Severe Mouth Pain or Difficulty Swallowing - Intense pain can lead to dehydration and needs professional attention.
- Signs of Dehydration - Symptoms like dry mouth, lethargy, or reduced urine output necessitate immediate medical care.
Prevention and Hygiene
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) spreads easily through direct contact with infected surfaces. Maintaining strict hygiene practices significantly reduces the risk of transmission.
Effective prevention focuses on regular sanitation and personal cleanliness to protect children and adults.
- Frequent Handwashing - Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after diaper changes and before meals.
- Disinfect Surfaces - Clean toys, doorknobs, and frequently touched objects regularly with disinfectants.
- Avoid Close Contact - Keep infected individuals separated from healthy children to limit exposure.
