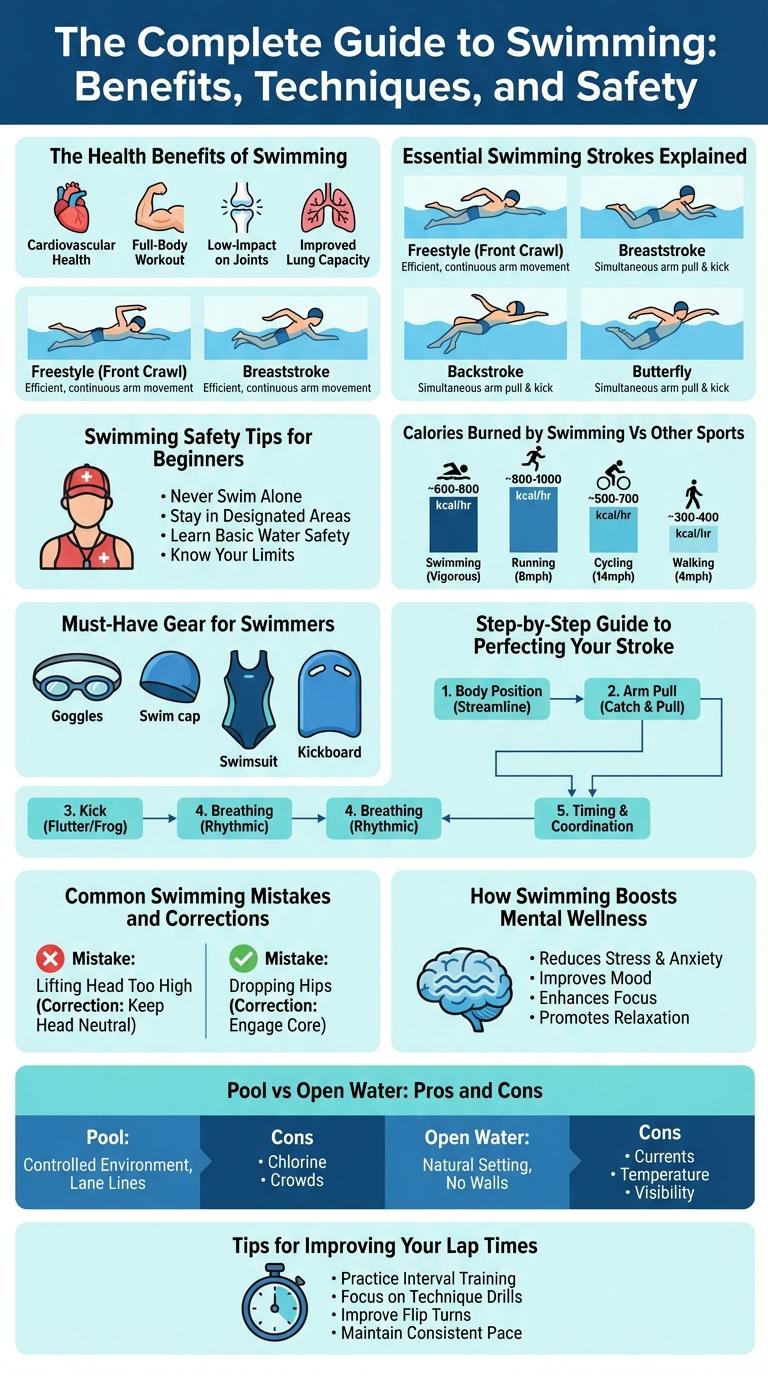
An infographic about swimming visually highlights key statistics, techniques, and health benefits of the sport. It presents data on stroke types, calorie burn rates, and safety tips in an engaging, easy-to-understand format. Clear visuals and concise facts help swimmers of all levels improve performance and stay informed.
The Health Benefits of Swimming
Swimming is a full-body workout that supports cardiovascular health and muscle strength. It is an accessible exercise suitable for all ages and fitness levels.
Regular swimming improves lung capacity and promotes joint flexibility.
- Enhances Cardiovascular Fitness - Swimming increases heart rate and promotes efficient blood circulation without stressing the joints.
- Builds Muscle Strength - The resistance of water strengthens muscles across the entire body on every stroke.
- Improves Mental Health - Swimming reduces stress and anxiety through rhythmic breathing and release of endorphins.
Essential Swimming Strokes Explained
Swimming involves various strokes that enhance speed, efficiency, and endurance in water. Understanding these essential strokes helps swimmers improve technique and performance.
- Freestyle - The fastest stroke, characterized by alternating arm movements and flutter kicks for speed.
- Backstroke - Performed on the back with alternating arm pulls and flutter kicks, promoting good posture.
- Breaststroke - Features simultaneous arm movements and frog-like kicks for a smooth, gliding motion.
Swimming Safety Tips for Beginners
Swimming is a fun and beneficial activity for all ages. Beginners should prioritize safety to enjoy the experience without risks.
Always swim in designated areas supervised by lifeguards. Use proper flotation devices if you are not a confident swimmer. Never swim alone and inform someone about your swimming plans.
Calories Burned by Swimming Vs Other Sports
| Activity | Calories Burned (30 minutes) |
|---|---|
| Swimming (Freestyle, Moderate) | 250-350 |
| Running (5 mph) | 240-355 |
| Cycling (12-14 mph) | 210-310 |
| Walking (4 mph) | 120-180 |
| Jump Rope | 300-430 |
Must-Have Gear for Swimmers
Swimming requires specific gear to enhance performance and safety. Essential items include a well-fitted swimsuit, a quality swim cap, and goggles designed for underwater clarity. Other important gear comprises earplugs, swim fins, and a kickboard for training purposes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Perfecting Your Stroke
Mastering swimming strokes enhances both efficiency and speed in the water. Perfecting your technique reduces fatigue and prevents injuries.
Begin with proper body alignment: keep your head in line with your spine and maintain a horizontal position. Focus on controlled breathing, timing each breath to your strokes.
Common Swimming Mistakes and Corrections
What are common mistakes swimmers make? Many swimmers struggle with improper breathing techniques and poor body positioning in the water.
How can these mistakes be corrected? Focusing on rhythmic breathing and maintaining a streamlined body posture improves efficiency and reduces fatigue.
Why is kicking technique important? Inefficient kicking wastes energy and slows forward movement in the pool.
What correction helps improve kicking? Engaging the hips and using flexible ankles promote stronger, more effective kicks.
How does arm movement affect swimming performance? Incorrect arm strokes can cause drag and reduce propulsion.
What should swimmers do to fix arm stroke errors? Emphasizing high elbow recovery and full arm extension increases speed and power.
How Swimming Boosts Mental Wellness
Swimming enhances mental wellness by reducing stress hormones and promoting the release of endorphins, which improve mood and reduce anxiety. The rhythmic nature of swimming supports mindfulness, helping swimmers achieve a meditative state that alleviates symptoms of depression. Consistent swimming routines increase brain function by improving circulation and oxygen flow, leading to better cognitive health and mental clarity.
Pool vs Open Water: Pros and Cons
Swimming offers diverse experiences depending on the environment, with pools and open water providing unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these differences helps swimmers choose the best setting for their goals.
- Pool Swimming - Controlled environment with consistent water temperature and clear visibility.
- Pool Swimming - Ideal for technique improvement and structured training sessions.
- Open Water Swimming - Natural surroundings offer varied conditions and enhance endurance skills.
- Open Water Swimming - Requires navigation and adaptability due to currents, waves, and weather.
- Open Water Swimming - Greater risk factors necessitate safety measures and experience.
Choosing between pool and open water depends on individual preferences, training needs, and safety considerations.
