Food safety is essential for preventing foodborne illnesses and ensuring public health. Proper handling, storage, and preparation methods minimize contamination risks and protect consumers. Infographics provide a clear, visual guide to best practices in food safety, making complex information easy to understand and apply.
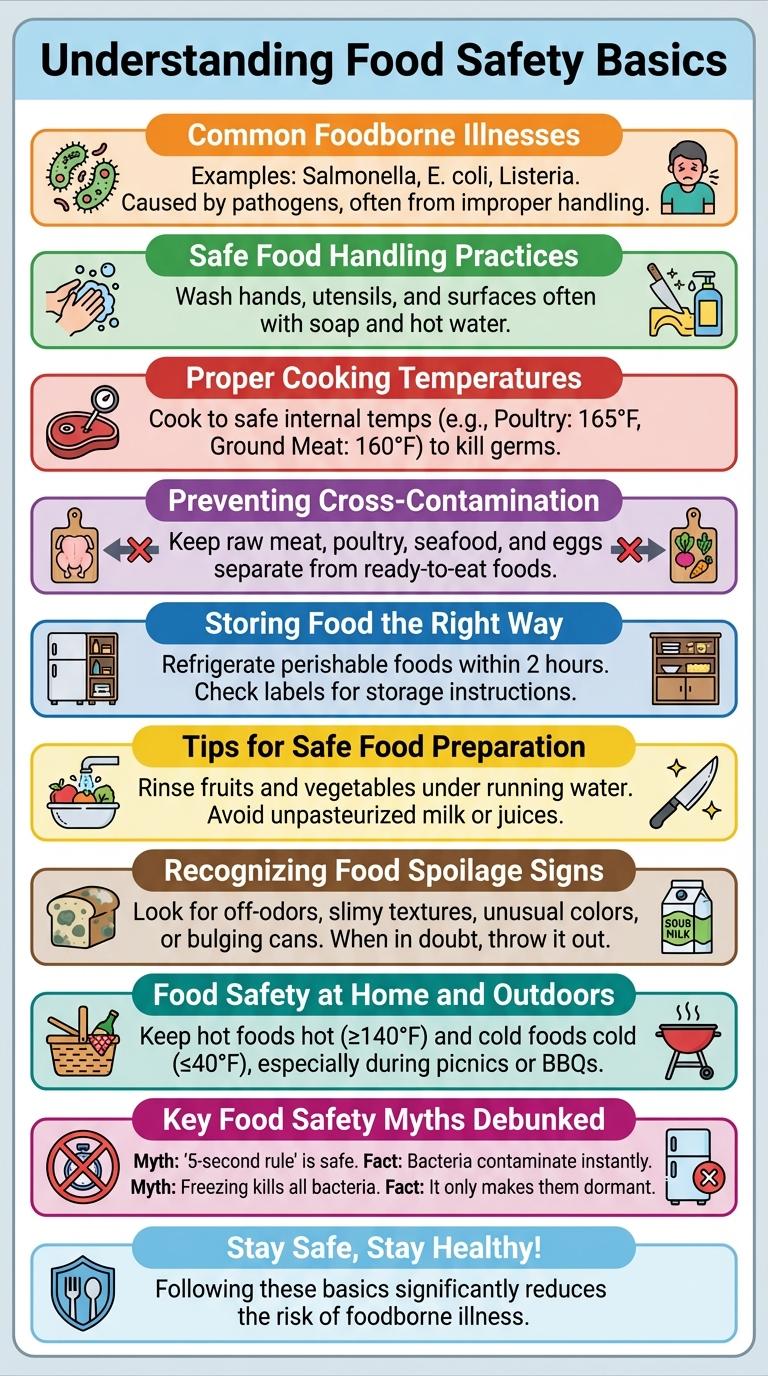
Understanding Food Safety Basics
Food safety involves handling, preparing, and storing food to prevent foodborne illnesses. Understanding the basics includes recognizing proper cooking temperatures, avoiding cross-contamination, and keeping food at safe storage temperatures. Following these practices reduces the risk of harmful bacteria and ensures food remains safe to consume.
Common Foodborne Illnesses
Food safety is crucial to prevent foodborne illnesses, which affect millions worldwide each year. Understanding common foodborne pathogens helps in minimizing risks and ensuring safe food consumption.
The most common foodborne illnesses include Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria, Norovirus, and Campylobacter. Salmonella often comes from undercooked poultry and eggs, while E. coli is linked to contaminated beef and unpasteurized products. Proper cooking, hygiene, and food storage can significantly reduce these risks.
Safe Food Handling Practices
Food safety is essential to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure healthy eating. Proper food handling practices reduce contamination risks and protect consumers.
- Wash Hands Thoroughly - Clean hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before handling food to eliminate harmful bacteria.
- Separate Raw and Cooked Foods - Use different cutting boards and utensils to avoid cross-contamination between raw and cooked items.
- Cook Foods to Safe Temperatures - Ensure meats, poultry, and seafood reach recommended internal temperatures to kill pathogens.
Following safe food handling guidelines safeguards health and enhances food quality.
Proper Cooking Temperatures
Proper cooking temperatures are essential to eliminate harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. Different types of food require specific internal temperatures to ensure safety.
Using a food thermometer helps confirm that meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs reach the recommended temperature. This practice reduces the risk of contamination and keeps food safe to eat.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
Preventing cross-contamination is essential for maintaining food safety and avoiding foodborne illnesses. Proper handling and storage techniques reduce the risk of harmful bacteria transferring between foods.
Implement these key steps to ensure safe food preparation and storage.
- Separate Raw and Cooked Foods - Use different cutting boards and utensils to avoid bacteria transfer from raw meat to ready-to-eat foods.
- Wash Hands Thoroughly - Clean hands with soap and warm water before and after handling food to prevent contamination.
- Store Foods Properly - Keep raw meats on lower shelves and sealed containers to prevent drips onto other foods in the refrigerator.
Storing Food the Right Way
Proper food storage is essential to prevent contamination and extend the shelf life of perishable items. Keep raw meats separate from ready-to-eat foods to avoid cross-contamination.
Store foods at safe temperatures: refrigerate below 40degF (4degC) and freeze below 0degF (-18degC). Use airtight containers to maintain freshness and reduce exposure to bacteria and moisture.
Tips for Safe Food Preparation
Safe food preparation reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses by preventing cross-contamination and ensuring proper cooking temperatures. Always wash hands and surfaces thoroughly before handling food. Use a food thermometer to verify that meats reach the recommended internal temperatures for safety.
Recognizing Food Spoilage Signs
How can you recognize food spoilage easily? Identifying spoiled food is crucial to avoid health risks. Look for changes in color, texture, and odor as primary spoilage indicators.
Food Safety at Home and Outdoors
Food safety is essential both at home and outdoors to prevent foodborne illnesses. Proper handling, cooking, and storage techniques ensure a safe eating experience everywhere.
- Clean Hands and Surfaces - Wash hands and sanitize surfaces before handling food to eliminate harmful bacteria.
- Proper Cooking Temperatures - Cook meats and perishables to recommended internal temperatures to kill pathogens.
- Safe Food Storage - Refrigerate perishable foods promptly and keep cold foods below 40degF (4degC) to slow bacterial growth.
