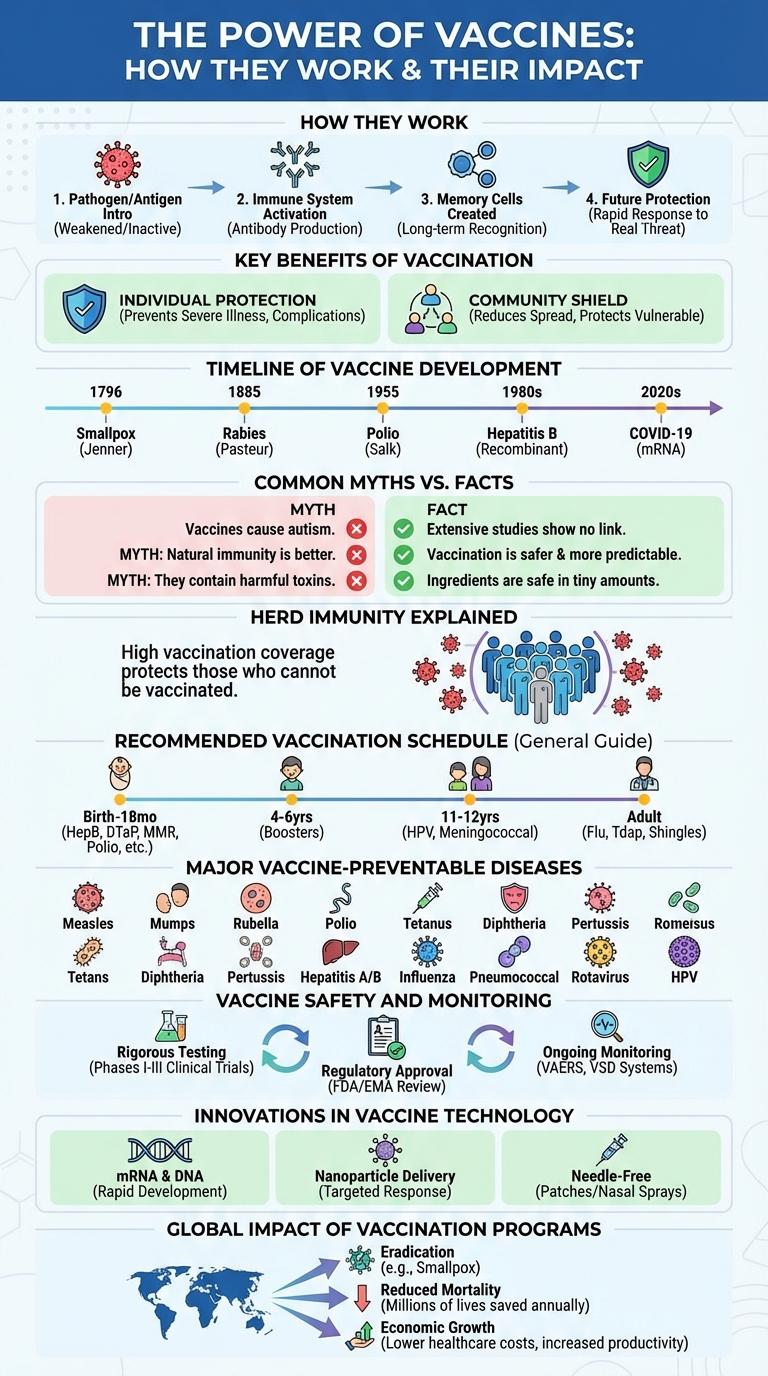
Vaccines play a crucial role in preventing infectious diseases and protecting public health worldwide. This infographic highlights key information about vaccine efficacy, safety, and the importance of immunization schedules. Understanding these facts helps promote informed decisions and encourages widespread vaccine acceptance.
The Power of Vaccines: How They Work
Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens without causing illness. They introduce a harmless component of a virus or bacteria, training the body to respond quickly upon future exposure.
This process builds immunity by creating memory cells that remember the pathogen. Effective vaccination reduces disease spread, protects vulnerable populations, and prevents outbreaks.
Key Benefits of Vaccination
Vaccination protects individuals from serious infectious diseases by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens. It reduces the spread of contagious illnesses, contributing to community-wide immunity and protecting vulnerable populations. Vaccines are proven to prevent outbreaks, decrease healthcare costs, and save millions of lives globally each year.
Timeline of Vaccine Development
The timeline of vaccine development highlights key milestones in medical history that have saved millions of lives. Vaccines have evolved from early smallpox prevention to advanced mRNA technology for modern diseases.
- 1796: Smallpox Vaccine - Edward Jenner developed the first successful vaccine using cowpox to prevent smallpox.
- 1885: Rabies Vaccine - Louis Pasteur created the first vaccine for rabies, marking progress in viral disease prevention.
- 1955: Polio Vaccine - Jonas Salk introduced the inactivated polio vaccine, drastically reducing polio cases worldwide.
- 1981: Hepatitis B Vaccine - The first vaccine to prevent a type of liver cancer caused by the hepatitis B virus was developed.
- 2020: mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines - Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna produced the first authorized mRNA vaccines to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
Common Myths vs. Facts about Vaccines
| Common Myths | Facts about Vaccines |
|---|---|
| Vaccines cause autism. | Extensive research confirms no link between vaccines and autism spectrum disorders. |
| Natural immunity is better than vaccine-acquired immunity. | Vaccines safely provide immunity without the risks of serious illness from natural infection. |
| Vaccines contain harmful toxins. | Vaccine ingredients are carefully tested for safety and used in minimal, non-toxic amounts. |
| Vaccines are unnecessary because diseases are rare. | Vaccination maintains herd immunity and prevents outbreaks of potentially deadly diseases. |
| Vaccines can overload the immune system. | The immune system can handle multiple vaccines safely as they contain only a tiny fraction of daily antigen exposure. |
Herd Immunity Explained
What is herd immunity and why is it important? Herd immunity occurs when a large portion of a community becomes immune to a contagious disease, significantly reducing its spread. This protection helps safeguard those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and immunocompromised individuals.
How do vaccines contribute to herd immunity? Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens without causing illness. Widespread vaccination increases the number of immune individuals, lowering the overall transmission of the disease.
What percentage of the population needs to be vaccinated for herd immunity? The required vaccination rate varies by disease but typically ranges from 70% to 95%. Diseases with higher contagiousness, like measles, require a larger percentage to prevent outbreaks.
What are the benefits of achieving herd immunity through vaccination? Herd immunity protects vulnerable groups, reduces the prevalence of the disease, and contributes to the eventual eradication of certain infectious diseases. It also decreases healthcare costs and limits economic disruption caused by outbreaks.
Which diseases have seen a decline due to herd immunity? Diseases such as polio, measles, and diphtheria have dramatically declined globally because of successful vaccination campaigns. Maintaining vaccination efforts is essential to prevent their resurgence.
Recommended Vaccination Schedule
The recommended vaccination schedule ensures timely protection against infectious diseases for all age groups. Following this schedule supports public health by reducing the spread of preventable illnesses.
- Infants and Toddlers - Vaccines such as Hepatitis B, DTaP, and MMR are scheduled within the first two years to build early immunity.
- Adolescents - Tdap, HPV, and meningococcal vaccines are administered to protect during school years and reduce disease risk.
- Adults - Booster shots like Td, influenza, and COVID-19 vaccines maintain immunity throughout life and adapt to emerging health threats.
Major Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
Vaccines protect millions of people from serious diseases worldwide. They prevent the spread of major vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs) such as measles, polio, and influenza.
Measles causes severe respiratory symptoms and can lead to death if untreated. Polio attacks the nervous system, potentially causing paralysis. Influenza leads to seasonal epidemics affecting millions globally every year.
Vaccine Safety and Monitoring
Vaccines undergo rigorous safety testing before approval to ensure they are both effective and safe for public use. Continuous monitoring helps identify and manage any rare side effects after vaccines are administered.
- Pre-approval clinical trials - Vaccines pass through multiple phases of trials involving thousands of participants to assess safety and efficacy.
- Post-marketing surveillance - Health authorities track adverse events reported by healthcare providers and patients after vaccine distribution.
- Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) - A national system that collects data on possible vaccine side effects to detect and respond to safety concerns.
Ongoing research and transparent communication help maintain public trust in vaccine safety worldwide.
Innovations in Vaccine Technology
Innovations in vaccine technology have revolutionized disease prevention by enhancing efficacy and reducing development time. Breakthroughs like mRNA vaccines enable rapid design and customization against emerging pathogens.
Advances in nanoparticle delivery systems improve immune response and stability of vaccines. Novel platforms such as viral vectors and protein subunits expand protection against complex diseases.
