A sunog infographic visually presents crucial information about fire incidents, highlighting causes, prevention methods, and safety tips. It uses clear graphics and concise data to enhance public awareness and promote proactive measures against fire hazards. Understanding these elements through an infographic helps reduce risks and improve emergency responses effectively.
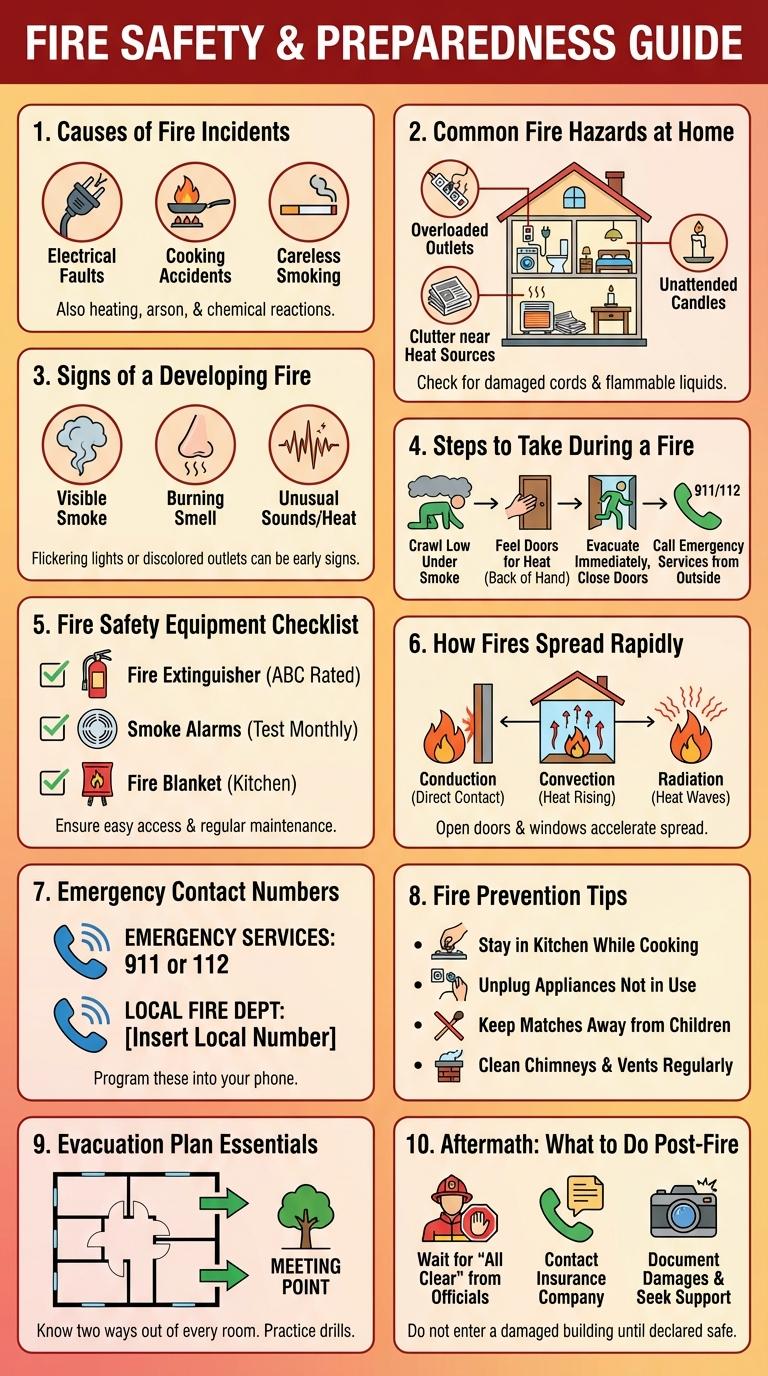
Causes of Fire Incidents
What are the primary causes of fire incidents? Fire incidents often result from electrical faults, unattended cooking, and improper handling of flammable materials. Understanding these causes helps in preventing potential fire hazards effectively.
Common Fire Hazards at Home
Common fire hazards at home include unattended cooking, faulty electrical wiring, and flammable materials placed near heat sources. Kitchen fires often result from grease buildup or leaving cooking unattended. Electrical fires may start from overloaded outlets or damaged cords, while candles and heaters pose risks if left too close to combustible items.
Signs of a Developing Fire
Recognizing the early signs of a developing fire is crucial for timely evacuation and prevention. Awareness of these indicators can save lives and reduce property damage.
- Smoke Presence - Thin, wispy smoke indicates a small fire beginning to grow.
- Unusual Heat - Increasing warmth or hot surfaces near materials signals fire development.
- Crackling Sounds - A faint crackling or popping sound can mean flames are spreading.
Steps to Take During a Fire
Fires require immediate and careful responses to ensure safety. Knowing the proper steps during a fire can save lives and reduce damage.
- Evacuate Immediately - Leave the building as quickly and safely as possible to avoid smoke inhalation and burns.
- Call Emergency Services - Dial the local fire department number to report the fire once you are safe outside.
- Stay Low to the Ground - Smoke rises, so staying close to the floor helps you avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
- Use a Fire Extinguisher if Safe - Attempt to put out small fires only if you are trained and the fire is controllable.
- Do Not Re-enter the Building - Wait for firefighters to declare the area safe before going back inside.
Fire Safety Equipment Checklist
Fire safety equipment is essential for preventing and controlling sunog (fire) incidents in homes and workplaces. Proper tools can minimize damage and protect lives.
- Fire Extinguisher - A portable device designed to extinguish small fires before they spread.
- Smoke Detector - An alarm system that senses smoke early to alert occupants of potential fire danger.
- Fire Blanket - A safety tool used to smother flames, especially effective for kitchen fires.
- Fire Hose - A high-pressure hose that delivers water to control large fires, ideal for commercial spaces.
- Emergency Exit Signs - Illuminated signs guiding people safely out of buildings during a fire emergency.
Regular maintenance and checks of fire safety equipment ensure they function correctly in case of sunog emergencies.
How Fires Spread Rapidly
Fires spread rapidly through the process of conduction, convection, and radiation, igniting nearby materials quickly. Flammable substances and oxygen availability significantly accelerate the fire's expansion.
Factors like wind and building structure influence the speed and direction of fire spread. Understanding these elements helps in effective fire prevention and control strategies.
Emergency Contact Numbers
Sunog, or fire emergencies, require immediate response to ensure safety and minimize damage. Knowing emergency contact numbers is crucial for quick assistance from fire departments and rescue teams. Keep these numbers handy to act swiftly during a sunog incident.
| Service | Emergency Contact Number |
|---|---|
| Fire Department | 911 |
| Police | 911 |
| Emergency Medical Services | 911 |
| Local Barangay Office | (Insert local number) |
| Disaster Risk Reduction Office | (Insert local number) |
Fire Prevention Tips
| Fire Prevention Tips | Details |
|---|---|
| Install Smoke Alarms | Place smoke alarms on every level of your home and inside bedrooms. Test them monthly and replace batteries annually. |
| Keep Flammable Items Safe | Store flammable liquids in proper containers away from heat sources and out of children's reach. |
| Maintain Electrical Safety | Avoid overloading outlets and replace worn or frayed electrical cords immediately to prevent electrical fires. |
| Practice Kitchen Safety | Never leave cooking unattended, keep flammable objects away from the stove, and have a fire extinguisher accessible in the kitchen. |
| Create an Emergency Plan | Develop and practice a fire escape plan with all household members, designating meeting points outside the home. |
Evacuation Plan Essentials
Creating a clear evacuation plan is crucial for safety during a sunog (fire). Knowing exit routes and designated meeting points can save lives in emergencies.
Essential elements include marked escape routes, fire extinguishers, and regular drills. Families and workplaces should review and practice these plans frequently to ensure preparedness.
