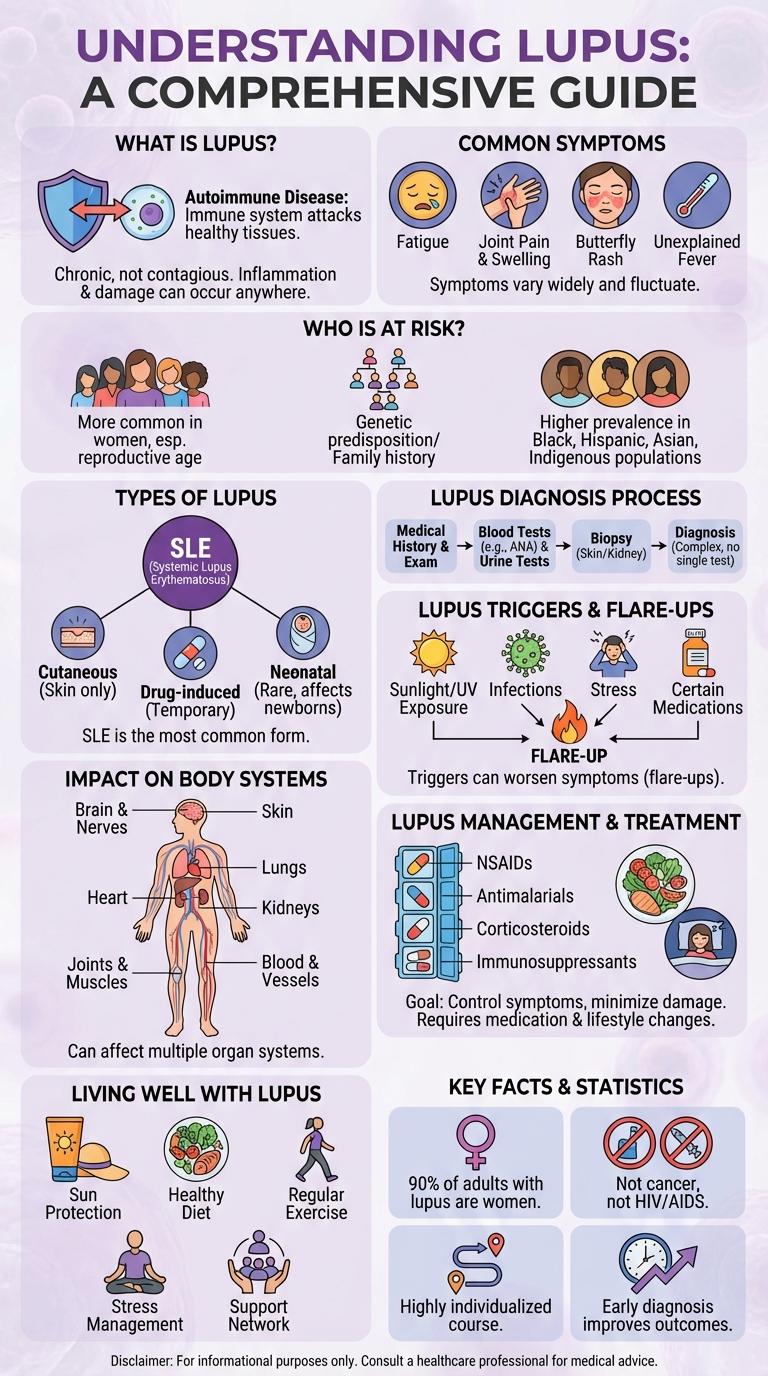
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by the body's immune system attacking healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and damage in various organs. Symptoms vary widely, including joint pain, skin rashes, and fatigue, making diagnosis challenging. Understanding lupus through clear, visual infographics helps raise awareness and educates about its impact and management.
What Is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues. It causes inflammation and damage in various parts of the body, including skin, joints, kidneys, and organs.
The most common form is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), affecting multiple organ systems. Symptoms often include fatigue, joint pain, and a characteristic butterfly-shaped rash on the face.
Common Symptoms of Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and affects multiple organs. Common symptoms include persistent fatigue, joint pain, and a distinctive butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose. Early detection of these symptoms is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Who Is at Risk?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect anyone, but certain groups have a higher risk of developing it. Women, particularly those of childbearing age, are the most commonly affected.
Risk factors include genetics, ethnicity, and environmental triggers. African American, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American individuals are more likely to develop lupus. Family history and exposure to UV light or certain medications can also increase susceptibility.
Types of Lupus
What are the different types of lupus? Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease with several distinct types, each affecting the body in unique ways. Knowing the types helps in understanding symptoms and treatment options.
| Type of Lupus | Description |
|---|---|
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | The most common and severe form, SLE affects multiple organs including skin, joints, kidneys, and heart. |
| Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus | This type primarily causes skin rashes and lesions, especially on sun-exposed areas. |
| Drug-Induced Lupus | Triggered by certain medications, this type produces lupus-like symptoms that fade after stopping the drug. |
| Neonatal Lupus | A rare condition seen in newborns, caused by antibodies passed from the mother, leading to skin rash and liver issues. |
Lupus Diagnosis Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History Review | Assessment of symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, skin rashes, and photosensitivity to identify lupus indicators. |
| Physical Examination | Evaluation of skin, joints, and other organs to detect signs linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). |
| Laboratory Tests | Blood tests including ANA (antinuclear antibody) test, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith antibodies, and complement levels to confirm autoimmune activity. |
| Urine Analysis | Detection of proteinuria or hematuria indicating kidney involvement commonly seen in lupus nephritis. |
| Imaging Studies | X-rays, echocardiogram, or chest CT to assess organ damage or inflammation associated with lupus. |
Lupus Triggers & Flare-Ups
Lupus is an autoimmune disease with symptoms that can worsen suddenly during flare-ups. Identifying common triggers helps manage and reduce the frequency of these episodes.
- Sunlight Exposure - Ultraviolet rays can cause skin rashes and increase disease activity in many lupus patients.
- Stress - Physical or emotional stress may provoke immune system responses leading to flare-ups.
- Infections - Viral or bacterial infections can activate lupus symptoms and worsen overall health.
Impact on Body Systems
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple body systems, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage. Understanding its impact on various organs can help in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Musculoskeletal System - Lupus commonly causes joint pain, swelling, and muscle inflammation leading to arthritis and reduced mobility.
- Cardiovascular System - Inflammation from lupus can affect the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of pericarditis, myocarditis, and atherosclerosis.
- Renal System - Lupus nephritis is a serious condition where the kidneys become inflamed, potentially leading to kidney failure without proper treatment.
Lupus Management & Treatment
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease requiring careful management to reduce symptoms and prevent flares. Effective treatment focuses on controlling inflammation and supporting overall health.
- Medications - Anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants help control lupus symptoms and prevent organ damage.
- Lifestyle Adjustments - Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and protecting skin from UV exposure reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life.
- Regular Monitoring - Frequent medical check-ups and lab tests detect changes early and guide treatment modifications.
Personalized care strategies improve long-term outcomes for individuals living with lupus.
Living Well With Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that requires careful management to maintain quality of life. Living well with lupus involves balancing medication, regular medical check-ups, and a healthy lifestyle tailored to reduce flare-ups. Support systems, stress management, and awareness of symptoms play crucial roles in managing daily challenges effectively.
