Infographics about autism provide clear, concise visuals to enhance understanding of this complex neurodevelopmental condition. They highlight key facts about symptoms, diagnosis, and support strategies to promote awareness and inclusivity. These resources help demystify autism and foster greater acceptance in diverse communities.
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
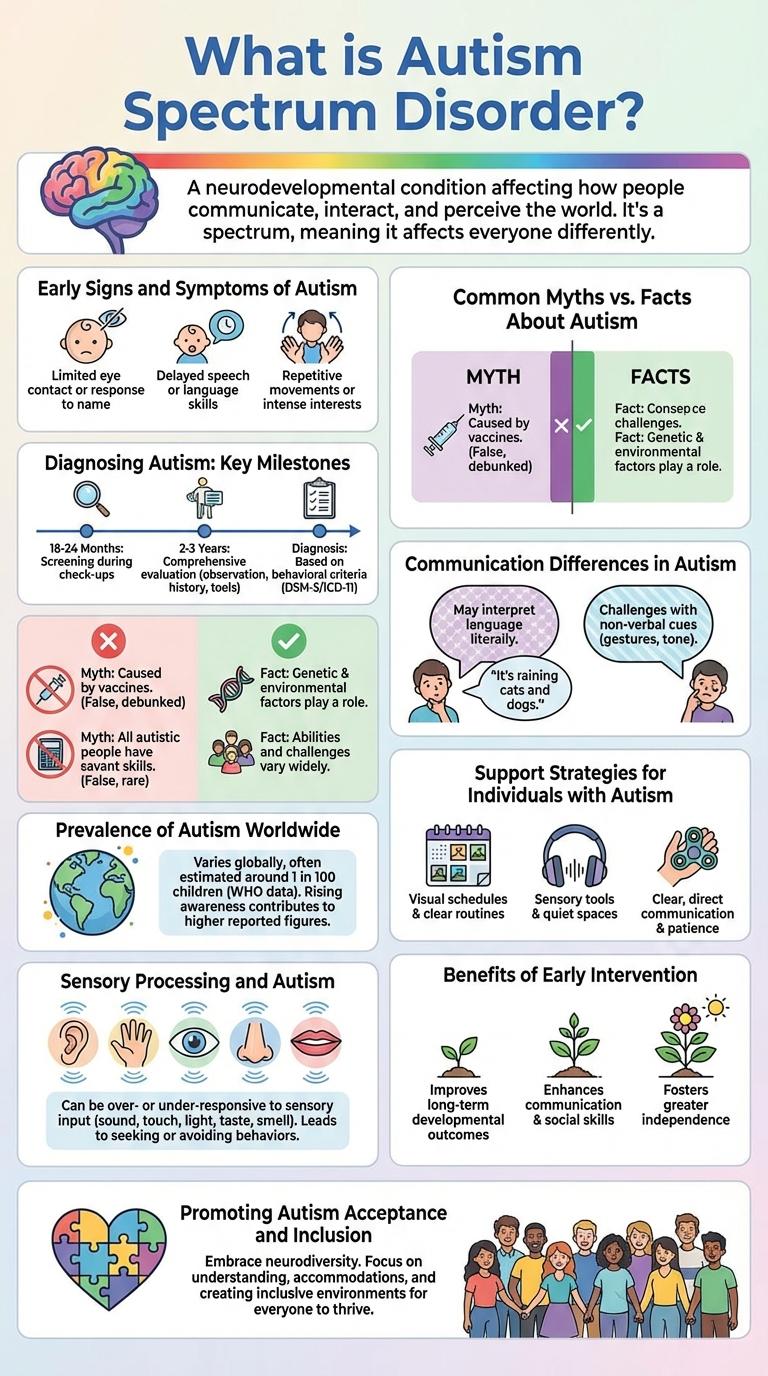
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition characterized by challenges with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Symptoms and severity vary widely, making each individual's experience unique. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for those with ASD.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) manifests early in childhood and affects social interaction and communication. Recognizing early signs can lead to timely interventions and better outcomes.
- Delayed Speech Development - Children may have limited or no verbal communication by 16 months.
- Avoidance of Eye Contact - Difficulty maintaining eye contact with caregivers and others is common.
- Repetitive Behaviors - Repeated movements like hand-flapping or rocking often indicate sensory processing differences.
- Limited Social Interaction - Children might show little interest in playing or engaging with peers.
- Resistance to Changes - Insistence on routines and distress over changes is frequently observed.
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and support planning.
Diagnosing Autism: Key Milestones
Diagnosing autism involves identifying key developmental milestones related to social interaction, communication, and behavior. Early detection is crucial for providing timely support and interventions.
Common signs include delayed speech, limited eye contact, and repetitive behaviors. Healthcare professionals use structured assessments and observations to confirm the diagnosis.
Common Myths vs. Facts About Autism
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) affects communication and behavior but varies widely among individuals. Understanding autism requires separating widespread myths from scientific facts.
Myth: People with autism lack empathy. Fact: Many individuals with autism experience deep empathy but express it differently.
Myth: Autism only affects children. Fact: Autism is a lifelong condition that continues into adulthood, requiring ongoing support.
Prevalence of Autism Worldwide
Autism affects approximately 1 in 100 children globally, with prevalence rates varying by region. Studies indicate a rising trend in diagnosis due to enhanced awareness and improved screening methods. Early diagnosis and intervention significantly improve outcomes for individuals with autism worldwide.
Communication Differences in Autism
Communication differences are a core aspect of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), affecting how individuals express and interpret language. These variations often influence social interactions and understanding of verbal and nonverbal cues.
- Delayed Speech Development - Many autistic individuals experience delays in speech milestones compared to neurotypical peers.
- Use of Alternative Communication - Some rely on augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) methods like picture systems or speech-generating devices.
- Literal Interpretation - People with autism often interpret language literally, which can affect understanding of idioms or sarcasm.
Sensory Processing and Autism
Sensory processing challenges are common in individuals with autism, affecting how they perceive and respond to sensory stimuli. Understanding these differences is key to providing supportive environments and interventions.
Autistic individuals may experience hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity across various senses, impacting daily functioning and comfort.
- Sensory Overload - Many autistic people become overwhelmed by loud noises, bright lights, or strong smells, leading to distress or avoidance behaviors.
- Sensory Seeking - Some individuals actively seek intense sensory experiences, such as rocking or spinning, to self-regulate or feel grounded.
- Impact on Communication - Sensory processing differences can influence social interaction and communication, as sensory input affects attention and emotional responses.
Support Strategies for Individuals with Autism
| Support Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Structured Routine | Establish clear, consistent daily schedules to reduce anxiety and improve predictability. |
| Visual Supports | Use visual aids like charts, pictures, and symbols to enhance understanding and communication. |
| Social Skills Training | Implement targeted programs to develop interpersonal skills and improve social interaction. |
| Sensory Integration Therapy | Provide interventions addressing sensory processing challenges to improve comfort and focus. |
| Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) | Design customized learning approaches tailored to the strengths and needs of each individual. |
Benefits of Early Intervention
Early intervention for autism significantly enhances developmental outcomes. Children receiving timely support often show improved communication and social skills.
Targeted therapies during early childhood promote brain plasticity, allowing for better adaptation and learning. Early support reduces the severity of symptoms and fosters independence. Families benefit from guidance and resources, creating a more supportive environment for the child.
