Understanding hazards is essential for creating safe environments and preventing accidents. Infographics provide a clear visual representation of various types of hazards, their potential impacts, and effective safety measures. This infographic highlights key hazard categories to raise awareness and promote proactive risk management.
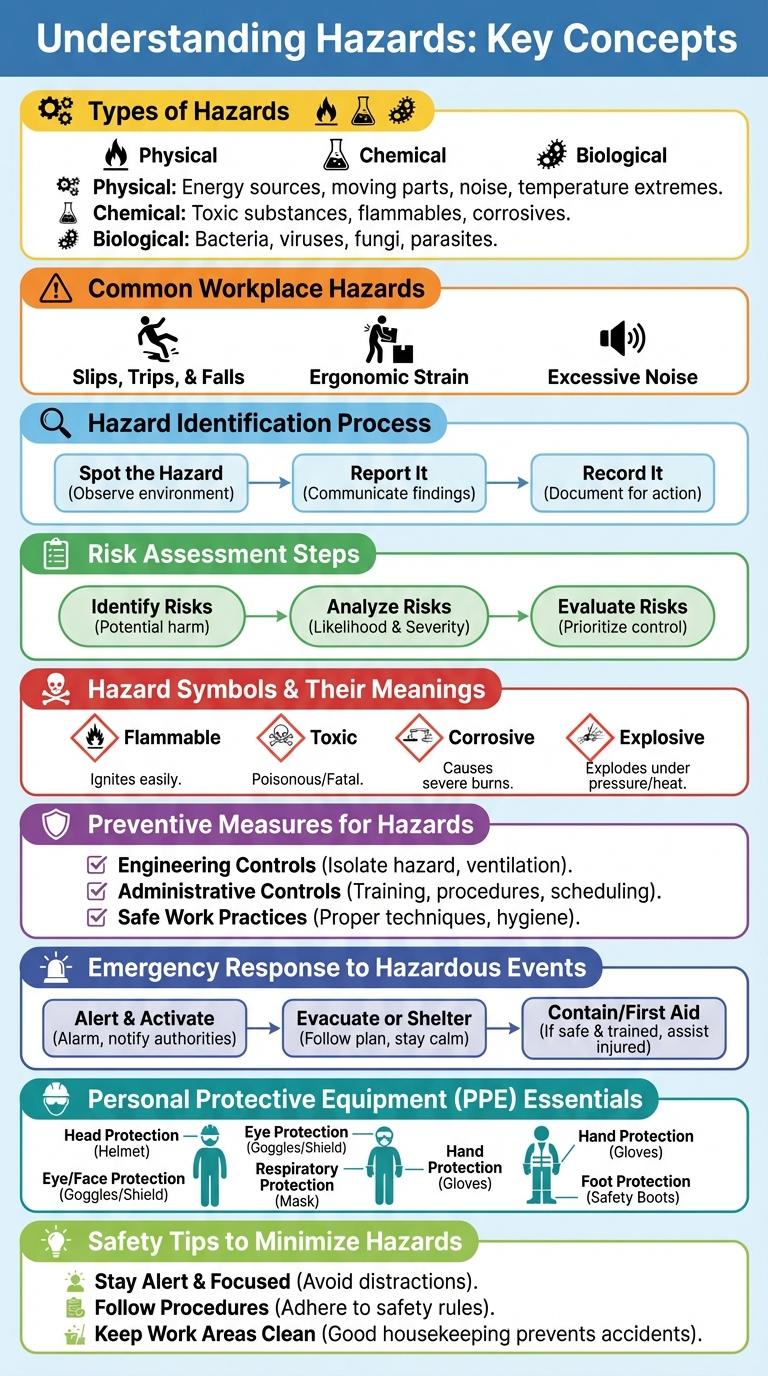
Understanding Hazards: Key Concepts
Hazards pose potential threats to safety, health, and the environment. Understanding hazard concepts helps in effective risk management and prevention.
- Types of Hazards - Natural, technological, and human-made hazards vary in origin and impact.
- Risk vs. Hazard - Hazard is the source of harm, risk is the likelihood and consequence of that harm occurring.
- Exposure - The degree to which people or assets come into contact with hazards influences potential damage.
Effective hazard understanding supports preparedness, mitigation, and response strategies for minimizing adverse effects.
Types of Hazards: Physical, Chemical, Biological
What are the main types of hazards in the workplace? Hazards are classified into Physical, Chemical, and Biological types. Each type poses unique risks that require specific safety measures.
| Type of Hazard | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical | Includes hazards such as noise, radiation, extreme temperatures, and mechanical dangers that can cause injury or illness. |
| Chemical | Consists of harmful substances like acids, solvents, and toxic gases that can cause chemical burns, poisoning, or respiratory issues. |
| Biological | Involves exposure to bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that can lead to infections or allergic reactions. |
Common Workplace Hazards
Workplace hazards pose significant risks to employee safety and productivity. Recognizing common hazards helps in implementing effective prevention measures.
- Physical Hazards - Include slips, trips, falls, and exposure to loud noise that can cause injury or long-term health issues.
- Chemical Hazards - Involve exposure to harmful substances such as solvents, gases, and toxic fumes that affect respiratory and skin health.
- Ergonomic Hazards - Result from repetitive motions, poor workstation design, or improper lifting, leading to musculoskeletal disorders.
Hazard Identification Process
| Hazard Identification Process | |
|---|---|
| Step | Description |
| 1. Hazard Recognition | Systematic identification of potential sources of harm within the workplace or environment. |
| 2. Hazard Characterization | Analyzing the nature and properties of hazards including chemical, physical, and biological factors. |
| 3. Risk Assessment | Evaluating the likelihood and severity of adverse effects resulting from identified hazards. |
| 4. Documentation | Recording identified hazards, assessment results, and control measures for compliance and review. |
| 5. Continuous Monitoring | Ongoing observation and re-evaluation to detect new or changing hazards over time. |
Risk Assessment Steps
Risk assessment is a critical process in hazard management that identifies potential dangers and evaluates their impact. Understanding these steps helps in implementing effective safety measures to prevent accidents.
- Hazard Identification - Recognize and list all possible hazards in the workplace or environment.
- Risk Analysis - Evaluate the likelihood and severity of harm from the identified hazards.
- Risk Evaluation - Compare the analyzed risk against established safety criteria to decide necessary control measures.
Hazard Symbols & Their Meanings
Hazard symbols are visual representations designed to convey the risks associated with various substances or environments. These symbols provide essential warnings to ensure safety and prevent accidents in workplaces and public areas. Understanding hazard symbols facilitates proper handling, storage, and emergency response.
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Flammable | Indicates materials that can easily catch fire |
| Toxic | Represents substances that are poisonous if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed |
| Corrosive | Warns about chemicals that can cause severe skin burns or damage metals |
| Explosive | Marks materials that may explode under certain conditions |
| Radioactive | Indicates the presence of radioactive materials harmful to health |
Preventive Measures for Hazards
Hazards present significant risks in workplaces and homes, leading to injuries or property damage. Understanding preventive measures is essential to minimize these risks effectively.
Implementing proper safety training ensures everyone is aware of potential dangers. Regular inspections and maintenance help identify and address hazards before incidents occur. Utilizing personal protective equipment further reduces exposure to harmful conditions.
Emergency Response to Hazardous Events
Emergency response to hazardous events requires fast assessment and coordinated action to minimize harm and protect lives. Key responders include fire services, medical teams, and hazardous materials specialists, all working together to contain the hazard. Effective communication and proper use of protective equipment are essential components for a successful emergency intervention.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Essentials
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is vital for ensuring safety in hazardous environments. Proper use of PPE reduces the risk of injuries and exposure to harmful substances.
Essential PPE items include helmets, gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory masks. Selecting the right PPE depends on the specific hazards present in the workplace.
