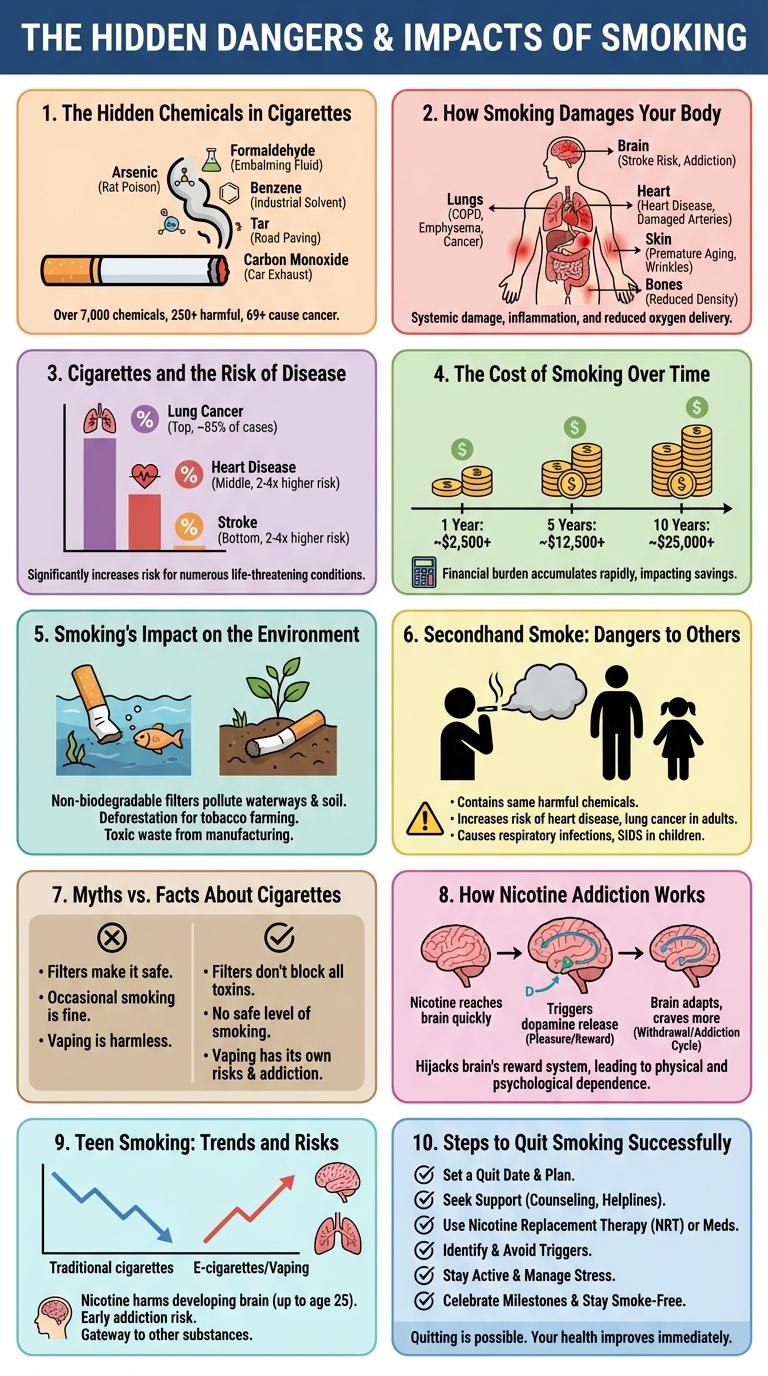
Cigarettes contain thousands of harmful chemicals that pose serious health risks, including cancer, heart disease, and respiratory issues. Smoking remains a leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide, impacting both smokers and those exposed to secondhand smoke. Understanding the dangers and statistics behind cigarette use highlights the urgent need for effective prevention and cessation efforts.
The Hidden Chemicals in Cigarettes
Cigarettes contain numerous hidden chemicals that pose significant health risks. Many of these substances are toxic and can cause serious diseases.
- Formaldehyde - Used in embalming, this chemical is a carcinogen present in cigarette smoke.
- Arsenic - A poisonous element often used in pesticides found in tobacco products.
- Cadmium - A toxic metal linked to kidney damage and lung disease found in cigarette smoke.
- Ammonia - Enhances nicotine absorption, increasing addiction potential.
- Carbon Monoxide - A harmful gas that reduces oxygen delivery to the body's organs.
Understanding these chemicals highlights the dangers hidden within every cigarette.
How Smoking Damages Your Body
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals like tar, nicotine, and carbon monoxide into your body. These substances damage your lungs, heart, and other vital organs over time.
The lungs suffer from reduced function and increased risk of diseases such as chronic bronchitis and lung cancer. Blood vessels narrow, raising the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Cigarettes and the Risk of Disease
Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of preventable diseases worldwide. Exposure to cigarette smoke significantly increases the risk of various chronic illnesses.
- Lung Cancer - Cigarette smoke contains carcinogens that lead to a high incidence of lung cancer among smokers.
- Heart Disease - Chemicals in cigarettes cause damage to the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) - Smoking causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to progressive lung damage and breathing difficulties.
The Cost of Smoking Over Time
Smoking cigarettes imposes a significant financial burden over time, with the average smoker spending thousands of dollars annually. The cumulative cost increases exponentially as the years of smoking add up, often exceeding tens of thousands over a lifetime. High cigarette prices, combined with healthcare expenses related to smoking-related illnesses, amplify the economic impact on individuals and society.
Smoking's Impact on the Environment
Smoking significantly contributes to environmental pollution through toxic cigarette waste and air contamination. Cigarette butts, the most littered item worldwide, contain harmful chemicals that leach into soil and waterways.
Each year, over 4.5 trillion cigarette butts are discarded globally, impacting ecosystems and marine life. The production and disposal of cigarettes release thousands of tons of toxic pollutants, including heavy metals and carcinogens. Forests suffer from deforestation linked to tobacco farming, reducing biodiversity and increasing carbon emissions.
Secondhand Smoke: Dangers to Others
Secondhand smoke poses serious health risks to non-smokers exposed to it. It contains harmful chemicals that can cause respiratory problems and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Causes Respiratory Issues - Exposure to secondhand smoke can lead to asthma, bronchitis, and other lung infections in both adults and children.
- Increases Heart Disease Risk - Non-smokers who inhale secondhand smoke face a higher chance of developing heart complications due to toxic chemicals.
- Harms Children's Health - Children exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to suffer from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and developmental problems.
Myths vs. Facts About Cigarettes
Cigarettes are often surrounded by myths that can mislead smokers and non-smokers alike. Understanding the facts is crucial to making informed decisions about health and lifestyle.
Myth: Smoking cigarettes only harms the lungs. Fact: Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals that damage nearly every organ in the body. Myth: Light or low-tar cigarettes are safer. Fact: These types do not reduce health risks and can still cause serious diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Myth: Smoking helps reduce stress and anxiety. Fact: Nicotine addiction can actually increase stress levels and cause mood swings over time. Myth: Quitting smoking is impossible for most people. Fact: Millions have successfully quit each year using proven methods such as counseling, medication, and support groups.
How Nicotine Addiction Works
How does nicotine addiction affect the brain?
Nicotine rapidly reaches the brain, stimulating the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter linked to pleasure. This process reinforces smoking behavior, making quitting difficult due to cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Teen Smoking: Trends and Risks
| Teen Smoking Trends | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Percentage of High School Students Who Smoke | 12% (2023, CDC) |
| Decline in Teen Smoking Rates Since 2010 | 60% reduction |
| Health Risks for Teen Smokers | Impact |
| Increased Risk of Lung Disease | 50% higher by age 30 |
| Higher Likelihood of Addiction | Nicotine dependence develops faster in teens |
