Birth control methods vary widely, offering individuals numerous options to manage reproductive health effectively. Understanding the types, benefits, and potential side effects of each method helps make informed decisions tailored to personal needs. Visualizing this information through an infographic simplifies complex data, making it easier to compare and choose suitable contraception.
Understanding Birth Control Methods
Birth control methods help prevent unintended pregnancies by regulating fertility through various techniques. Understanding these methods enables individuals to choose options that best suit their health and lifestyle needs.
Common birth control methods include hormonal options like pills and patches, barrier methods such as condoms and diaphragms, and long-acting reversible contraceptives like IUDs and implants. Each method varies in effectiveness, usage, and potential side effects. Consulting healthcare professionals ensures informed decisions tailored to personal circumstances.
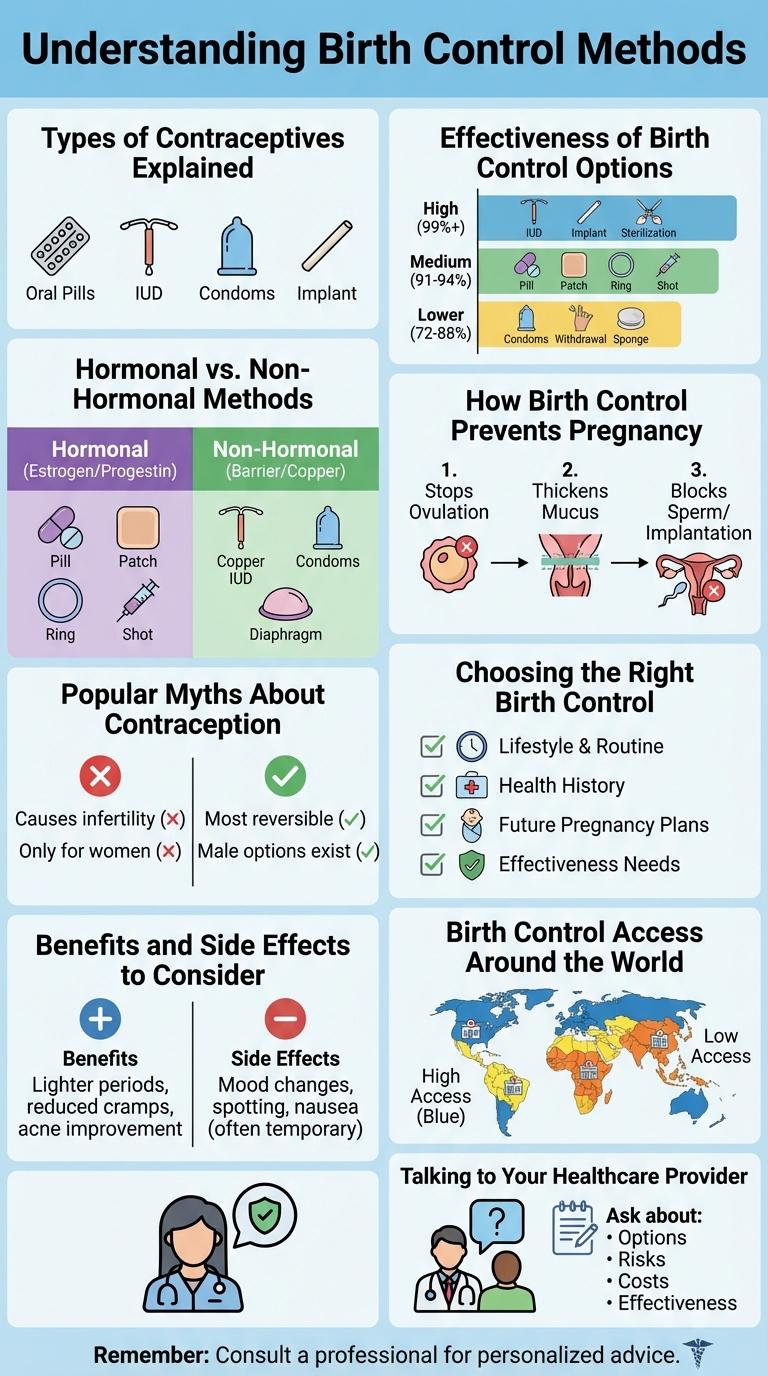
Types of Contraceptives Explained
Understanding different types of contraceptives is essential for making informed choices about birth control. Various methods cater to diverse needs, effectiveness, and preferences.
- Hormonal Methods - These include pills, patches, injections, and implants that regulate hormones to prevent ovulation.
- Barrier Methods - Condoms and diaphragms create a physical barrier to stop sperm from reaching the egg.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) - T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus that provide long-term pregnancy prevention through hormonal or copper mechanisms.
Choosing the right contraceptive depends on individual health, lifestyle, and family planning goals.
Effectiveness of Birth Control Options
Birth control methods vary widely in their effectiveness, with some options providing nearly 100% protection against pregnancy when used correctly. Understanding the effectiveness rates helps individuals choose the most suitable method for their lifestyle and health needs.
Long-acting reversible contraceptives like IUDs and implants offer over 99% effectiveness, making them some of the most reliable options available. Barrier methods and fertility awareness have lower effectiveness rates but can be suitable for those seeking non-hormonal or temporary solutions.
Hormonal vs. Non-Hormonal Methods
What are the key differences between hormonal and non-hormonal birth control methods? Hormonal birth control uses synthetic hormones to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus. Non-hormonal methods avoid hormones and often create a physical barrier or alter the uterine environment to prevent pregnancy.
How effective are hormonal versus non-hormonal birth control options? Hormonal methods like the pill, patch, and implant generally have effectiveness rates above 90% with typical use. Non-hormonal methods, including condoms and copper IUDs, vary widely but can also exceed 90% effectiveness when used correctly.
How Birth Control Prevents Pregnancy
Birth control methods prevent pregnancy by interrupting the natural reproductive process. They use various mechanisms to stop fertilization or implantation of an egg.
- Hormonal Regulation - Birth control pills release hormones that inhibit ovulation, preventing eggs from being released.
- Barrier Protection - Condoms and diaphragms physically block sperm from reaching the egg.
- Alteration of Uterine Lining - Some methods thicken cervical mucus and thin the uterine lining to prevent sperm movement and egg implantation.
Popular Myths About Contraception
Birth control is surrounded by many misconceptions that can affect its usage and effectiveness. Understanding the facts helps individuals make informed decisions about contraception.
- Myth: Birth control causes infertility - Most contraceptive methods do not impact long-term fertility and normal fertility returns after stopping use.
- Myth: You don't need contraception during breastfeeding - While breastfeeding can reduce fertility, it is not a reliable contraceptive method on its own.
- Myth: Birth control pills protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - Contraceptives like pills do not prevent STIs; barrier methods are required for protection.
- Myth: Emergency contraception causes abortion - Emergency contraception prevents pregnancy and does not terminate an existing pregnancy.
- Myth: You can't get pregnant during your period - Pregnancy is possible during menstruation due to sperm survival and variable ovulation timing.
Choosing the Right Birth Control
| Birth Control Method | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Hormonal Pills | Daily use required; regulates menstrual cycles; no protection against STIs |
| Intrauterine Device (IUD) | Long-term protection, 3-10 years; hormonal or copper options; requires medical insertion |
| Condoms | Protects against STIs; single-use; accessible and non-hormonal |
| Implants | Up to 3 years of protection; hormonal; small, placed under skin |
| Natural Methods | Involves tracking fertility signs; no medical side effects; less reliable |
Benefits and Side Effects to Consider
Birth control offers effective prevention of unintended pregnancies and helps regulate menstrual cycles for many users. It can also reduce the risk of certain cancers, such as ovarian and endometrial cancer.
Common side effects include nausea, weight changes, and mood fluctuations, though these vary by individual and method used. Some methods carry risks like blood clots or hormonal imbalances, so consulting a healthcare provider is essential.
Birth Control Access Around the World
Access to birth control varies significantly across the globe, influenced by economic, cultural, and legal factors. Developed countries generally have widespread availability of contraceptives, while many low-income regions face limited access due to supply shortages and social stigma. Efforts to improve family planning services aim to reduce unintended pregnancies and support reproductive health worldwide.
