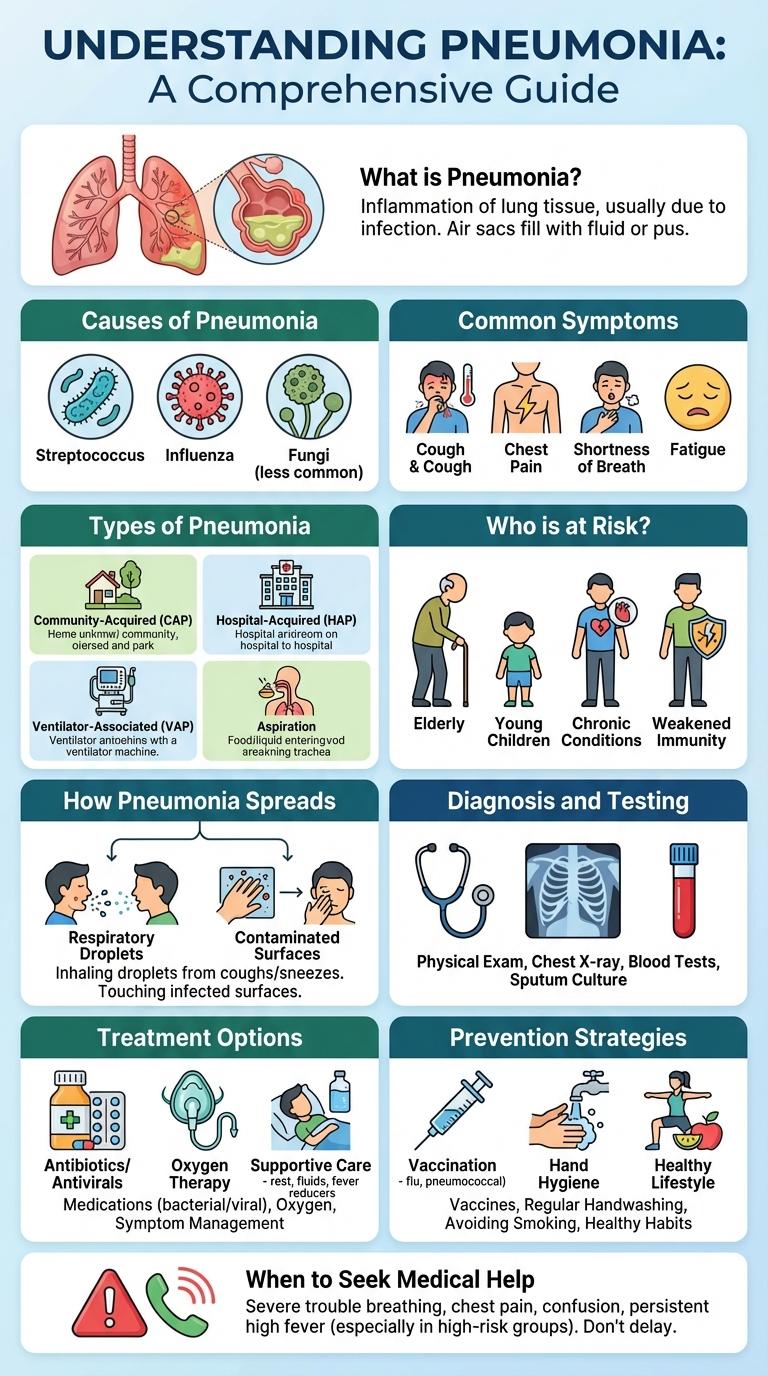
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that affects millions worldwide, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup in the air sacs. This infographic highlights key symptoms, causes, prevention tips, and treatment options to improve awareness and management. Understanding these critical points helps reduce the risk and promotes timely medical intervention.
What is Pneumonia?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which can fill with fluid or pus. |
| Causes | Caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or inhaled irritants. |
| Symptoms | Cough, fever, chills, difficulty breathing, chest pain. |
| Affected Areas | Alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs. |
| Risk Groups | Children under 5, elderly adults, immunocompromised individuals. |
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing symptoms like cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, each affecting the lungs differently.
Bacterial pneumonia often results from Streptococcus pneumoniae and is the most common cause in adults. Viral pneumonia can be triggered by influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, or coronaviruses, typically leading to milder symptoms. Fungal pneumonia occurs mainly in individuals with weakened immune systems and can be caused by organisms like Histoplasma or Cryptococcus.
Common Symptoms
Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes inflammation and impairs breathing. Common symptoms include persistent cough, high fever, and shortness of breath. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for prompt medical treatment and recovery.
Types of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing symptoms like cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. Different types of pneumonia are classified based on the cause and the setting in which the infection occurs.
The main types include bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and aspiration pneumonia. Each type requires specific diagnosis and treatment to effectively manage the condition and prevent complications.
Who is at Risk?
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that affects millions globally each year. Certain groups have a higher vulnerability due to age, health conditions, or environmental factors.
- Young Children and Elderly - Immature or weakened immune systems in these age groups increase their susceptibility to pneumonia infections.
- People with Chronic Illnesses - Conditions like asthma, diabetes, and heart disease compromise lung function and immune response, raising pneumonia risk.
- Smokers and Polluted Environment Residents - Tobacco use and exposure to air pollutants damage respiratory defenses, making the lungs prone to infection.
How Pneumonia Spreads
Pneumonia spreads through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Close contact with someone who has the infection increases the risk of transmission. Contaminated surfaces can also play a role in spreading the bacteria or viruses causing pneumonia.
Diagnosis and Testing
Pneumonia diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests to determine the presence and cause of lung infection. Accurate testing is essential for guiding treatment and improving patient outcomes.
- Chest X-ray - A chest X-ray is the primary imaging tool used to confirm pneumonia by revealing lung infiltrates or consolidation.
- Sputum Culture - Sputum samples are analyzed to identify bacterial pathogens and guide antibiotic therapy.
- Blood Tests - Blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC) and blood cultures, help detect infection severity and identify causative bacteria in the bloodstream.
Treatment Options
Pneumonia treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection, often involving antibiotics for bacterial cases. Viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications and supportive care to manage symptoms.
Hospitalization might be necessary for severe pneumonia to provide oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly improve recovery outcomes and reduce complications.
Prevention Strategies
Pneumonia prevention is essential to reduce hospitalizations and mortality worldwide. Effective strategies target vaccination, hygiene, and lifestyle changes to protect vulnerable populations.
- Vaccination - Immunization with pneumococcal and influenza vaccines significantly lowers the risk of pneumonia infection.
- Hand Hygiene - Regular handwashing with soap reduces the transmission of respiratory pathogens causing pneumonia.
- Smoking Cessation - Avoiding tobacco smoke improves lung health, decreasing susceptibility to pneumonia.
- Healthy Nutrition - A balanced diet strengthens immune defenses enabling better resistance to infections.
- Avoiding Exposure - Minimizing contact with sick individuals prevents the spread of pneumonia-causing bacteria and viruses.
Implementing these prevention strategies effectively decreases pneumonia incidence and improves public health outcomes.
