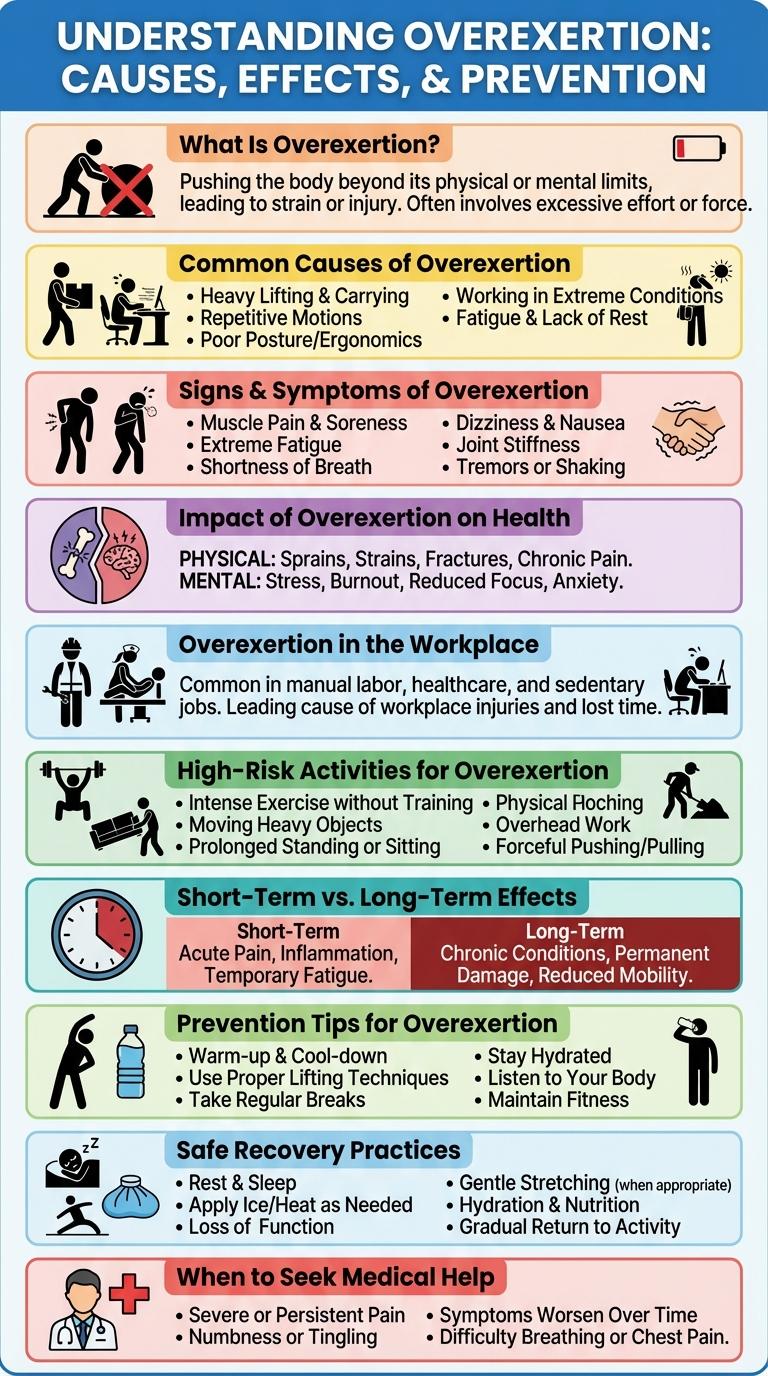
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to fatigue, muscle strain, or injury. This infographic highlights the common causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies to help maintain safe activity levels. Understanding these factors is essential for promoting long-term well-being and avoiding health risks associated with overexertion.
What Is Overexertion?
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to strain or injury. It commonly results from lifting heavy objects, repetitive motions, or enduring prolonged physical activity without adequate rest. Recognizing the signs early helps prevent severe muscle damage and chronic fatigue.
Common Causes of Overexertion
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to strain and injury. Common causes often involve repetitive motion, heavy lifting, and prolonged physical activity without adequate rest.
Poor posture and improper technique during tasks can also contribute significantly to overexertion injuries. Environmental factors such as extreme temperatures and lack of hydration increase the risk by taxing the body's ability to recover.
Signs & Symptoms of Overexertion
| Signs of Overexertion | Symptoms of Overexertion |
|---|---|
| Muscle fatigue | Persistent muscle soreness |
| Shortness of breath | Dizziness or light-headedness |
| Rapid heartbeat | Increased sweating |
| Clumsiness or loss of coordination | Headaches |
| Excessive weakness | Nausea or vomiting |
Impact of Overexertion on Health
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to various health complications. It significantly impacts overall well-being, highlighting the need for balanced activity and rest.
- Muscle Strain - Excessive physical effort causes muscle fibers to overstretch or tear, resulting in pain and limited mobility.
- Cardiovascular Stress - Overexertion can overload the heart, increasing the risk of arrhythmias and hypertension.
- Fatigue - Chronic overexertion leads to persistent tiredness, weakening the immune system and reducing productivity.
- Injury Risk - Pushing the body too hard raises the likelihood of accidents and long-term musculoskeletal injuries.
- Mental Health Effects - Physical overexertion can contribute to anxiety, stress, and decreased cognitive function.
Recognizing the signs of overexertion is essential to prevent serious health consequences.
Overexertion in the Workplace
Overexertion in the workplace occurs when employees push their physical limits, leading to muscle strains, sprains, and fatigue. It is one of the leading causes of workplace injuries, especially in physically demanding jobs such as construction and warehousing.
Common signs of overexertion include persistent muscle soreness, decreased productivity, and increased risk of accidents. Implementing proper ergonomics and regular breaks can significantly reduce the risk of overexertion-related injuries.
High-Risk Activities for Overexertion
Overexertion is a common cause of workplace injuries, resulting from excessive physical effort. Identifying high-risk activities helps prevent strain and promotes safety.
Certain tasks significantly increase the risk of overexertion due to their physical demands and repetitive motions.
- Heavy lifting - Involves carrying or moving loads that exceed safe weight limits, stressing muscles and joints.
- Repetitive motions - Performing the same movement repeatedly can cause muscle fatigue and strain over time.
- Prolonged standing or bending - Maintaining such positions for extended periods leads to muscle exhaustion and increased injury risk.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effects
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to fatigue and potential injury. Short-term effects include muscle soreness, cramps, and exhaustion, which often resolve with rest. Long-term effects can involve chronic pain, joint damage, and increased risk of musculoskeletal disorders, requiring medical intervention.
Prevention Tips for Overexertion
Overexertion occurs when the body is pushed beyond its physical limits, leading to fatigue, injury, or serious health issues. Recognizing the signs early can help prevent long-term damage and ensure optimal performance.
To prevent overexertion, maintain proper hydration and take regular breaks during physical activities. Use ergonomic techniques when lifting heavy objects and avoid sudden increases in intensity or duration of exercise. Listening to your body and resting when feeling fatigued can significantly reduce the risk of overexertion injuries.
Safe Recovery Practices
How can you ensure a safe recovery after overexertion?
Rest is crucial to allow muscles to repair and reduce inflammation. Hydration and proper nutrition support cellular recovery and energy replenishment.
What role does stretching play in recovery?
Gentle stretching helps maintain flexibility and prevents stiffness. It promotes blood circulation, which accelerates healing of overworked tissues.
Why is sleep important for recovering from overexertion?
Sleep facilitates physical and mental restoration through hormone regulation. Deep sleep cycles enhance muscle growth and tissue repair processes.
When should you seek medical attention after overexertion?
Persistent pain, swelling, or extreme fatigue lasting several days requires professional evaluation. Early intervention prevents complications and promotes effective healing.
How does pacing contribute to a safer recovery?
Gradually reducing activity intensity prevents re-injury and supports progressive adaptation. Listening to your body's signals helps avoid overdoing recovery efforts.
