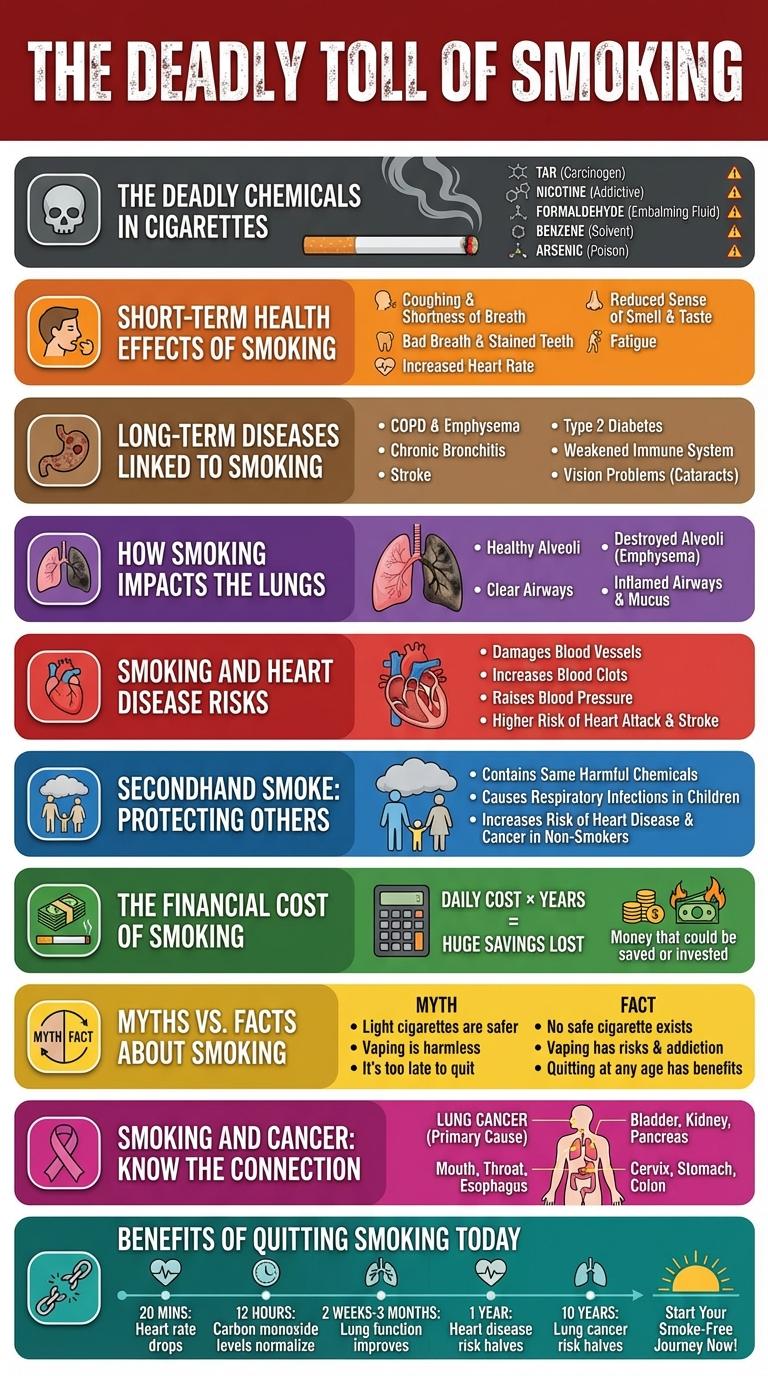
Smoking poses severe health risks that affect nearly every organ in the body, significantly increasing the chances of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke damage cells and reduce oxygen flow, leading to chronic conditions and premature death. Understanding these hazards visually through an infographic highlights the urgent need for prevention and smoking cessation.
The Deadly Chemicals in Cigarettes
Cigarettes contain over 7,000 chemicals, with at least 70 known to cause cancer. Harmful substances such as tar, formaldehyde, arsenic, and ammonia damage the lungs and other organs. Smoking introduces these deadly chemicals into the body, increasing the risk of heart disease, respiratory problems, and multiple types of cancer.
Short-Term Health Effects of Smoking
Smoking immediately harms the body, causing numerous short-term health issues. These effects can reduce lung function, impair circulation, and weaken the immune system.
- Respiratory Irritation - Smoking causes coughing and throat irritation by damaging airway linings and increasing mucus production.
- Reduced Lung Capacity - Inhalation of smoke compounds limits oxygen intake, leading to shortness of breath and decreased stamina.
- Increased Heart Rate - Nicotine causes the heart to beat faster, raising blood pressure and stressing the cardiovascular system.
Long-Term Diseases Linked to Smoking
What are the long-term diseases linked to smoking? Smoking significantly increases the risk of developing chronic diseases that impact multiple organs. These illnesses lead to severe health complications and reduce life expectancy.
| Disease | Description |
|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | Smoking is the primary cause of lung cancer, responsible for about 85% of cases. |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) | Smoking causes COPD, which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, leading to breathing difficulties. |
| Heart Disease | Smoking greatly increases the risk of coronary artery disease and heart attacks. |
| Stroke | Smoking doubles the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels and increasing clot formation. |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | This condition narrows arteries in the limbs, caused largely by smoking, leading to pain and mobility issues. |
How Smoking Impacts the Lungs
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that damage lung tissue and reduce lung function. Tar and toxins in cigarette smoke cause inflammation and destruction of air sacs in the lungs.
Chronic exposure results in diseases like chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer. Smokers have a significantly higher risk of developing respiratory infections and long-term breathing difficulties.
Smoking and Heart Disease Risks
Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and reducing oxygen flow. Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, heavily influenced by tobacco use.
- Increased Heart Attack Risk - Smokers are twice as likely to suffer from a heart attack compared to non-smokers due to narrowed arteries.
- Elevated Blood Pressure - Chemicals in tobacco cause the heart to work harder by raising blood pressure and heart rate.
- Reduced Oxygen Carrying Capacity - Carbon monoxide from smoke binds with hemoglobin, lowering oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
Secondhand Smoke: Protecting Others
| Hazard | Impact on Others |
|---|---|
| Secondhand Smoke Exposure | Contains over 7,000 chemicals, including 70 known carcinogens |
| Health Risks for Non-Smokers | Increased risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory infections |
| Children's Vulnerability | Greater chance of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), asthma, and ear infections |
| Protective Actions | Enforce smoke-free environments at home, work, and public places |
| Community Benefits | Reduced air pollution and improved public health outcomes |
The Financial Cost of Smoking
Smoking inflicts a substantial financial burden on individuals and households. The average smoker spends over $2,000 annually on cigarettes, leading to significant economic strain. Medical expenses related to smoking-induced illnesses further amplify the overall financial cost.
Myths vs. Facts About Smoking
Smoking remains a leading cause of preventable diseases worldwide. Many myths about smoking obscure the true health risks.
One common myth claims light cigarettes are safer, but they deliver similar harmful chemicals as regular ones. Another misconception is that occasional smoking is harmless, yet even infrequent use increases heart disease risk. Quitting smoking significantly improves lung function and reduces cancer risks.
Smoking and Cancer: Know the Connection
Smoking is a leading cause of cancer worldwide, significantly increasing the risk of developing various types of cancer. Understanding the link between smoking and cancer helps in promoting healthier lifestyle choices.
- Increased Lung Cancer Risk - Smoking causes about 85% of lung cancer cases globally, leading to high mortality rates.
- Head and Neck Cancers - Tobacco use is strongly linked to cancers of the mouth, throat, and esophagus.
- Other Cancers Linked to Smoking - Smoking also increases the risk of bladder, pancreas, kidney, and stomach cancers.
Quitting smoking significantly reduces cancer risk and improves overall health.
