Drug abuse impacts millions worldwide, leading to severe health, social, and economic consequences. Understanding the patterns, risks, and effects of substance misuse is crucial for prevention and intervention efforts. This infographic highlights key statistics and facts to increase awareness and promote informed decision-making.
Understanding Drug Abuse: Key Facts
| Key Fact | Data |
|---|---|
| Prevalence of Drug Abuse | Approximately 35 million people worldwide suffer from drug use disorders. |
| Commonly Abused Drugs | Opioids, cannabis, cocaine, and amphetamines. |
| Health Impact | Drug abuse accounts for over 450,000 deaths annually due to overdose and related diseases. |
| Risk Factors | Genetics, environment, mental health disorders, and early drug exposure increase susceptibility. |
| Treatment Access | Less than 20% of those affected receive adequate treatment and rehabilitation services. |
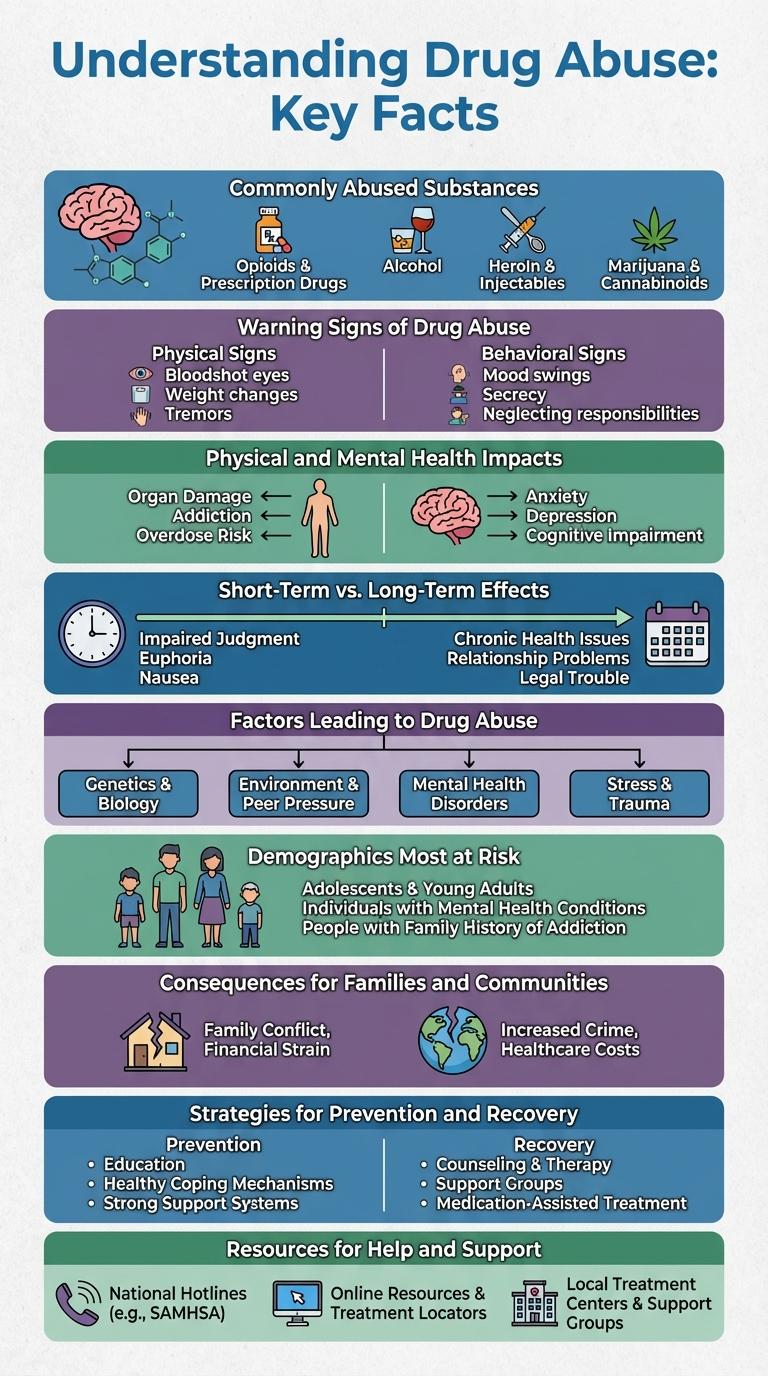
Commonly Abused Substances
Drug abuse involves the harmful or hazardous use of substances that alter the mind or body. Commonly abused substances include alcohol, prescription medications, and illicit drugs.
Alcohol is the most widely used and abused substance worldwide, leading to numerous health and social problems. Prescription drugs such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants are frequently misused due to their availability and addictive properties.
Warning Signs of Drug Abuse
Drug abuse can significantly impact a person's health, relationships, and daily life. Recognizing the warning signs early can help prevent long-term damage and support timely intervention.
- Changes in Behavior - Sudden mood swings, secrecy, or withdrawal from social activities may indicate drug abuse.
- Physical Symptoms - Unexplained weight loss, bloodshot eyes, and poor hygiene are common physical warning signs.
- Decline in Performance - Decreased productivity at work or school and neglecting responsibilities can signal substance misuse.
- Financial Issues - Frequent borrowing of money or unexplained financial problems often accompany drug abuse.
- Legal Troubles - Increased encounters with law enforcement or risky behaviors may be related to drug use.
Early recognition of these warning signs is crucial for seeking help and preventing further harm.
Physical and Mental Health Impacts
Drug abuse significantly harms physical health, causing issues such as heart disease, liver damage, and respiratory problems. Mental health suffers through increased risks of anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairments. Long-term substance abuse often leads to chronic conditions that severely reduce quality of life and increase mortality rates.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effects
Drug abuse significantly impacts the body and mind, with effects varying between short-term and long-term use. Short-term effects may include impaired judgment, memory loss, and increased heart rate.
Long-term drug abuse often leads to chronic health problems such as liver damage, mental health disorders, and addiction. Understanding these differences is crucial for prevention and treatment efforts.
Factors Leading to Drug Abuse
What are the primary factors leading to drug abuse?
Drug abuse often stems from a combination of social, psychological, and environmental influences. Understanding these factors helps in creating effective prevention and treatment strategies.
| Factor | Impact |
| Peer Pressure | Encourages initial experimentation and continued use, especially among adolescents. |
| Mental Health Disorders | Conditions like depression and anxiety increase vulnerability to drug dependency. |
| Family Environment | Exposure to substance abuse or lack of support fosters higher risk of addiction. |
| Stress and Trauma | Chronic stress or traumatic experiences often trigger substance use as a coping mechanism. |
| Accessibility | Easy access to drugs raises the likelihood of abuse in communities. |
Demographics Most at Risk
Drug abuse affects various population groups, but certain demographics are more vulnerable. Understanding these groups helps target prevention and treatment efforts more effectively.
- Young Adults Aged 18-25 - This group shows the highest rates of drug experimentation and dependency.
- Low-Income Communities - Economic hardship often correlates with increased substance abuse prevalence.
- Individuals with Mental Health Disorders - Co-occurring mental health issues significantly raise the risk of drug abuse.
Consequences for Families and Communities
Drug abuse profoundly impacts families and communities, disrupting relationships and fostering instability. Emotional distress, financial hardship, and social isolation frequently afflict affected households.
Communities face increased crime rates, diminished economic productivity, and strained healthcare systems due to widespread substance abuse. Children in families affected by drug abuse often experience neglect and psychological trauma. Preventive measures and support services are essential to mitigate these consequences and promote community resilience.
Strategies for Prevention and Recovery
Effective strategies for drug abuse prevention include education programs, community support, and early intervention to reduce risk factors. Recovery methods emphasize counseling, medical treatment, and peer support groups to promote long-term sobriety. Combining prevention and recovery approaches creates a comprehensive framework to combat drug abuse and support affected individuals.
