Mpox, a viral infection caused by the monkeypox virus, has gained significant attention due to its symptoms and transmission methods. This infographic visually breaks down key facts about mpox, including its incubation period, common signs, and preventative measures. Understanding these elements helps raise awareness and promote effective health strategies.
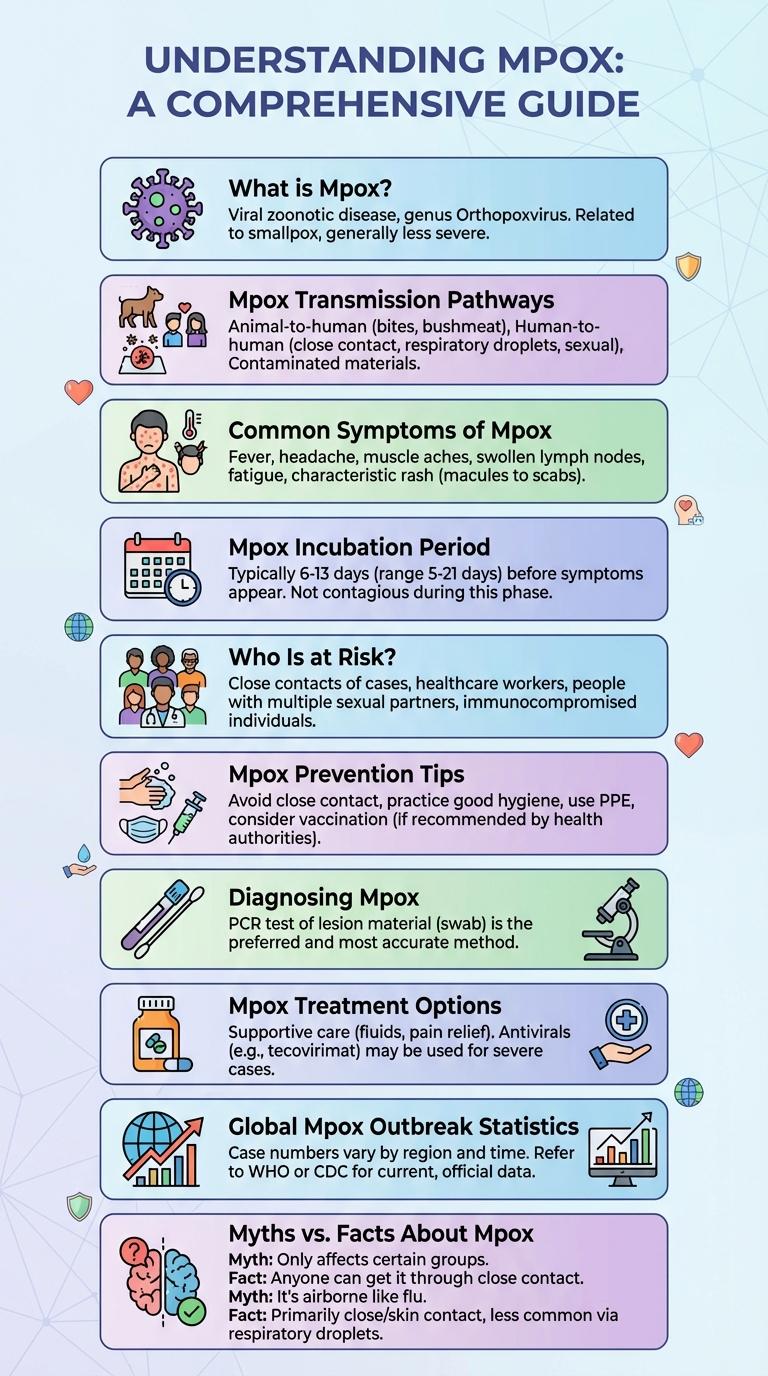
What is Mpox?
Mpox is a rare viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, part of the Orthopoxvirus genus. It primarily affects humans and certain animals, leading to symptoms similar to smallpox but generally less severe.
- Transmission - Mpox spreads through close contact with infected animals, humans, or contaminated materials.
- Symptoms - Common signs include fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches.
- Prevention - Avoiding contact with infected individuals and animals reduces the risk of infection.
Mpox Transmission Pathways
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, primarily spreads through close contact with an infected person's skin lesions, bodily fluids, or respiratory droplets. The virus can also transmit via contaminated objects like bedding or clothing.
Human-to-human transmission occurs during prolonged face-to-face interaction or direct contact with infected materials. Animal-to-human transmission happens through bites or scratches from infected animals, especially rodents and primates.
Common Symptoms of Mpox
Mpox is a viral disease characterized by specific symptoms that help in early identification. Recognizing the common symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Fever - A sudden onset of high fever is often the first sign of mpox infection.
- Rash - The appearance of a distinctive rash typically follows the fever, progressing from macules to pustules.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes - Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the neck and groin, are common during the early stages.
Mpox Incubation Period
What is the incubation period of mpox?
The incubation period of mpox typically ranges from 5 to 21 days. Most cases develop symptoms within 7 to 14 days after exposure.
Who Is at Risk?
Mpox primarily affects individuals who have close, personal contact with an infected person, including sexual contact. People with weakened immune systems and healthcare workers caring for patients with mpox are also at increased risk.
Recent outbreaks have shown higher transmission rates among men who have sex with men. However, anyone exposed to the virus through skin-to-skin contact or contaminated materials can contract mpox.
Mpox Prevention Tips
Mpox, a contagious viral disease, spreads through close contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects. Preventing mpox requires maintaining good hygiene, avoiding close physical contact with those showing symptoms, and using protective barriers during intimate encounters. Regular handwashing, disinfecting surfaces, and seeking timely medical advice upon symptom onset significantly reduce mpox transmission risk.
Diagnosing Mpox
Mpox is a viral disease diagnosed through clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Early identification is crucial for effective management and containment.
- Symptom Assessment - Initial diagnosis involves evaluating skin lesions characteristic of mpox, such as pustules and vesicles.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - PCR testing of lesion samples confirms the presence of the mpox virus with high accuracy.
- Serological Tests - Blood tests can detect antibodies to assess past exposure but are less useful for early diagnosis.
Timely laboratory confirmation supports accurate diagnosis and helps prevent the spread of mpox.
Mpox Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | Tecovirimat (TPOXX) is FDA-approved for mpox, reducing virus replication and severity. |
| Supportive Care | Pain management, hydration, and wound care to ease symptoms and prevent complications. |
| Vaccinia Immune Globulin (VIG) | Used in severe cases or immunocompromised patients to boost immunity against the virus. |
| Isolation and Hygiene | Prevent spread through strict isolation and maintaining good hygiene practices. |
| Monitoring and Follow-Up | Regular medical evaluation to track symptom progression and treatment response. |
Global Mpox Outbreak Statistics
The global mpox outbreak has affected over 85,000 confirmed cases across more than 110 countries as of 2024. The highest infection rates were reported in the United States, Brazil, and Spain, accounting for over 40% of total cases worldwide. Vaccination efforts and public health responses continue to evolve to control the spread and reduce mortality rates.
