Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer are leading causes of death worldwide, impacting millions annually. This infographic visually presents critical data on their prevalence, risk factors, and prevention strategies. Understanding these elements is key to promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing the global burden of NCDs.
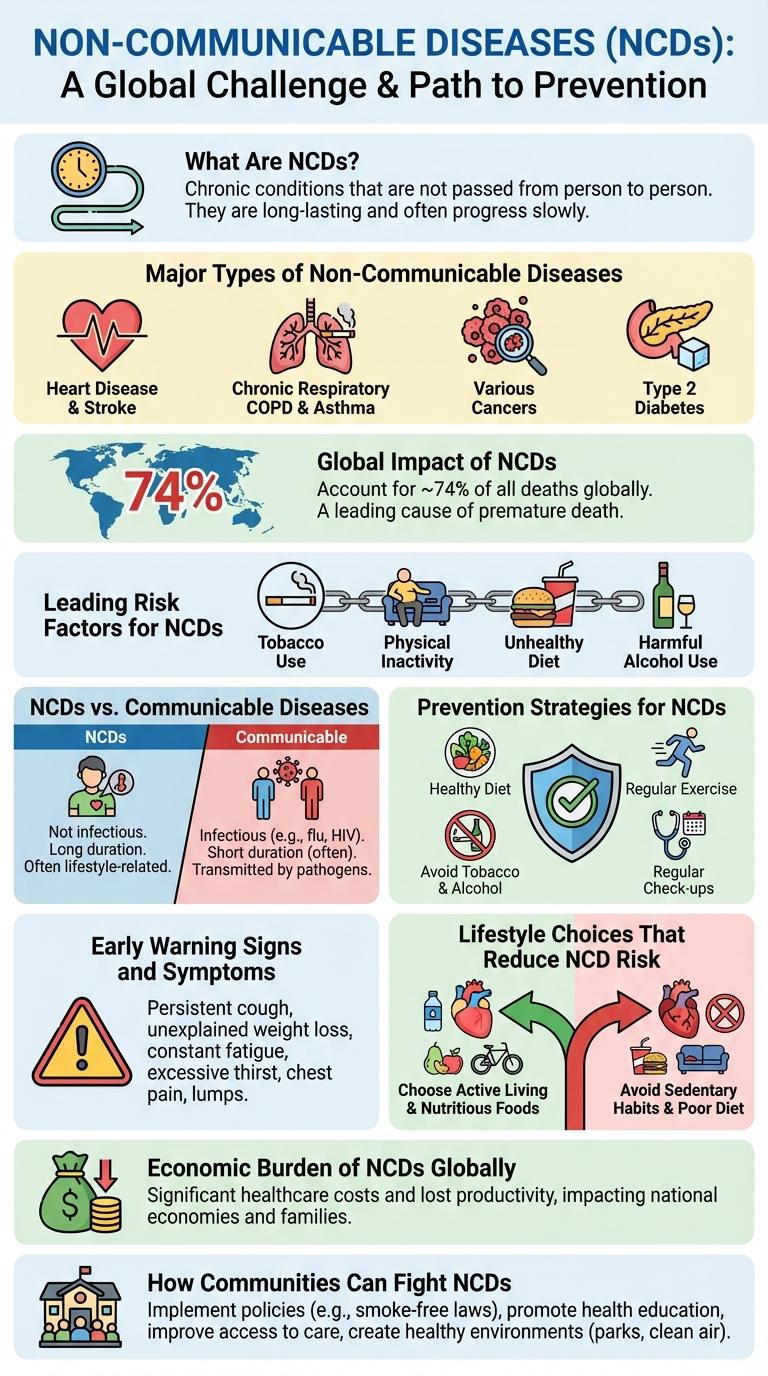
What Are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are medical conditions that are not transmitted from person to person. They typically have a long duration and slow progression, including heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases. NCDs are the leading cause of death globally, responsible for over 70% of all deaths each year.
Major Types of Non-Communicable Diseases
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are medical conditions that are not transmitted from person to person. They represent a significant global health burden with high rates of morbidity and mortality.
- Cardiovascular Diseases - These include heart attacks and strokes, caused by conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels.
- Cancer - A group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, affecting various organs and tissues in the body.
- Chronic Respiratory Diseases - Diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma that affect the lungs and airways.
- Diabetes - A metabolic disorder resulting in high blood sugar levels due to insulin dysfunction.
- Chronic Kidney Disease - Progressive loss of kidney function impacting waste elimination and fluid balance.
Understanding these major types is essential for effective prevention and management of non-communicable diseases worldwide.
Global Impact of NCDs
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular diseases, cancers, respiratory diseases, and diabetes account for over 71% of all deaths globally. These diseases impose a heavy economic burden, reducing global productivity and increasing healthcare costs.
Low- and middle-income countries bear 85% of premature NCD deaths, highlighting significant health disparities. Effective prevention and control strategies are crucial to reducing the increasing global toll of NCDs.
Leading Risk Factors for NCDs
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are driven by specific leading risk factors that significantly increase the probability of chronic conditions. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for effective prevention and health promotion strategies.
Identifying and addressing these risk factors reduces the global burden of heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases.
- Tobacco Use - Smoking and tobacco consumption contribute directly to cardiovascular diseases, lung cancer, and respiratory disorders.
- Unhealthy Diet - Diets high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats increase risks of hypertension, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
- Physical Inactivity - Sedentary lifestyles elevate the likelihood of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular complications.
NCDs vs. Communicable Diseases
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes are chronic conditions not transmitted from person to person. Communicable diseases, including influenza, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS, spread through infectious agents like bacteria and viruses. NCDs account for over 70% of global deaths, while communicable diseases remain a major health concern in low-income regions.
Prevention Strategies for NCDs
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer represent a leading cause of death globally. Prevention strategies focus on lifestyle modifications to reduce risk factors and improve overall health outcomes.
Key prevention methods include maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco use, and limiting alcohol consumption. Early screening and education on healthy habits are crucial to controlling the prevalence of NCDs worldwide.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer are leading causes of death worldwide. Early detection through recognizing warning signs significantly improves treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
Common early warning signs include unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, and chronic pain. Changes in bodily functions such as prolonged coughing, unusual bleeding, or sudden vision problems require prompt medical attention. Identifying symptoms early enables timely intervention and reduces the risk of severe complications.
Lifestyle Choices That Reduce NCD Risk
What lifestyle choices help reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs)? Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains significantly lowers the chances of developing NCDs. Regular physical activity and avoiding tobacco use further contribute to preventing heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
How does physical activity impact NCD prevention? Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week strengthens the cardiovascular system and improves metabolic health. Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Why is a healthy diet crucial for reducing NCD risks? Consuming foods low in saturated fats, sugars, and salt supports normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Nutrient-rich diets promote overall immune function and reduce inflammation, key factors in preventing chronic illnesses.
What role does avoiding tobacco play in NCD risk reduction? Tobacco use is a leading cause of lung cancer and chronic respiratory diseases, as well as increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Quitting smoking and minimizing exposure to secondhand smoke dramatically improve long-term health outcomes.
How important is managing stress for NCD prevention? Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy behaviors and physiological changes that increase disease risk. Implementing stress management techniques like mindfulness and adequate sleep supports heart health and boosts immune resilience.
Economic Burden of NCDs Globally
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) impose a significant economic burden worldwide, affecting both healthcare systems and productivity. The global cost of NCDs has increased dramatically, threatening sustainable development and economic growth.
- Cost of Treatment - NCDs account for over $2 trillion annually in healthcare expenses globally.
- Workforce Impact - Productivity losses due to NCD-related disability and premature death cost economies billions each year.
- Healthcare Resource Demand - Chronic disease management requires extensive long-term healthcare resources, straining health budgets in low- and middle-income countries.
