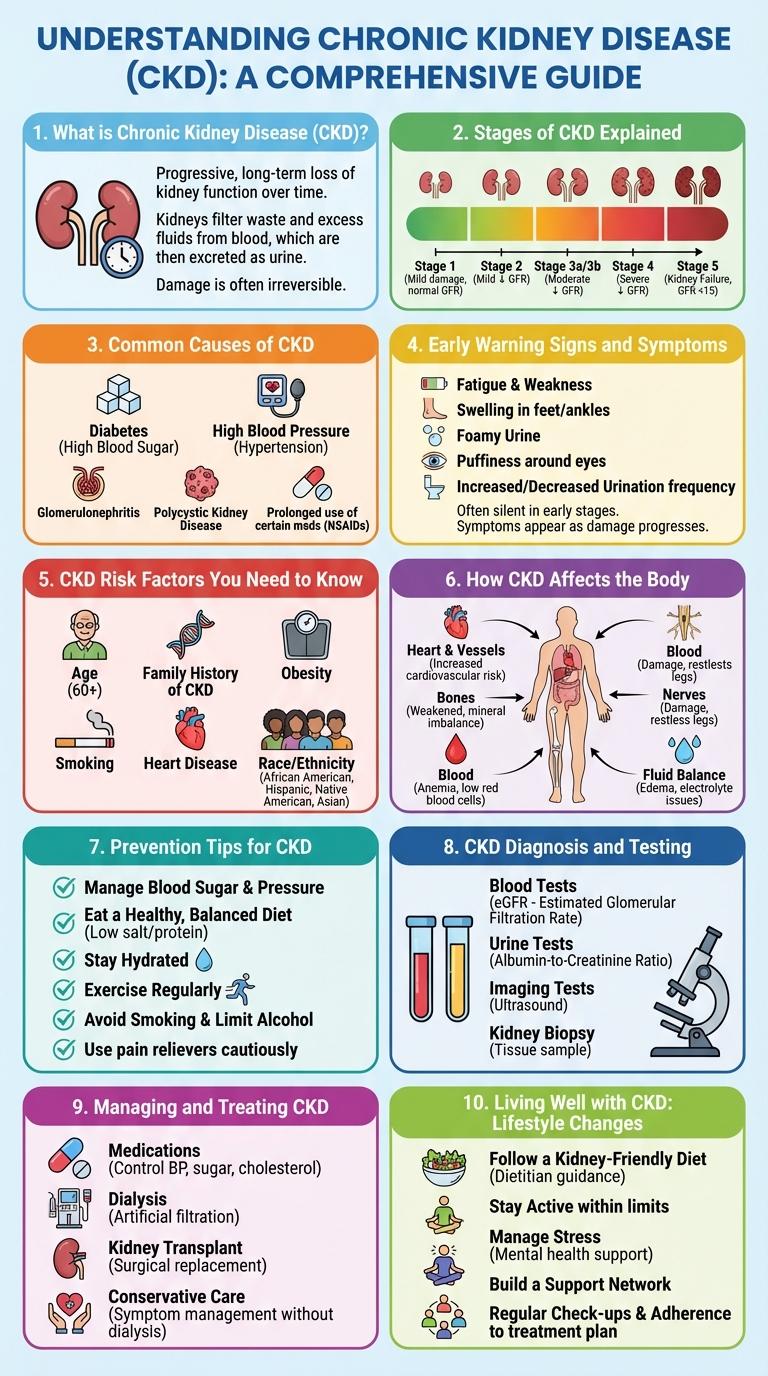
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects millions worldwide, progressively impairing kidney function and leading to serious health complications. Understanding the stages, symptoms, and risk factors of CKD is crucial for early detection and effective management. This infographic highlights key information to empower individuals in recognizing and addressing this silent but impactful condition.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose function over time. |
| Causes | Common causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, and glomerulonephritis. |
| Stages | CKD progresses through 5 stages based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) from mild damage to kidney failure. |
| Symptoms | Early stages often show no symptoms; advanced stages may cause fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination. |
| Impact | CKD can lead to kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplantation and increases risk for cardiovascular disease. |
Stages of CKD Explained
What are the stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)? Chronic Kidney Disease progresses through five stages based on kidney function and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Each stage indicates increasing kidney damage and decreasing function.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Kidney damage with normal or high GFR (>=90 mL/min). Kidney function appears normal but signs of damage exist. |
| Stage 2 | Mild reduction in GFR (60-89 mL/min). Early kidney damage with slight loss of function. |
| Stage 3 | Moderate decrease in GFR (30-59 mL/min). Noticeable loss of kidney function, may cause symptoms. |
| Stage 4 | Severe reduction in GFR (15-29 mL/min). Significant kidney failure requiring preparation for dialysis or transplant. |
| Stage 5 | End-stage renal disease (GFR <15 mL/min). Kidneys no longer function adequately, requiring dialysis or transplant. |
Common Causes of CKD
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) results from progressive kidney damage impairing renal function over time. Identifying the common causes of CKD helps in early detection and management to prevent kidney failure.
- Diabetes Mellitus - High blood sugar levels damage kidney filters, making diabetes the leading cause of CKD worldwide.
- Hypertension - Elevated blood pressure strains blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to function properly.
- Glomerulonephritis - Inflammation of kidney filtering units disrupts normal filtration and leads to CKD.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease - A genetic disorder causing cyst growth in kidneys, impairing renal function progressively.
- Prolonged Obstruction - Conditions like kidney stones or enlarged prostate block urine flow, contributing to kidney damage.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) often progresses silently, making early detection crucial. Recognizing early warning signs can help slow disease progression and improve outcomes.
- Fatigue - Persistent tiredness results from kidney dysfunction affecting waste removal and red blood cell production.
- Swelling - Fluid retention causes swollen ankles, feet, or around the eyes due to impaired kidney filtration.
- Changes in Urination - Increased frequency, foamy urine, or blood in urine indicate kidney stress or damage.
- Persistent Itching - Toxin buildup in the bloodstream causes stubborn itching in CKD patients.
- Shortness of Breath - Fluid overload and anemia linked to CKD lead to breathing difficulties during exertion or rest.
Early medical consultation upon noticing these symptoms enables timely diagnosis and management of CKD.
CKD Risk Factors You Need to Know
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects millions worldwide, with risk factors significantly impacting its development. Key risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, family history of kidney disease, age over 60, and obesity. Understanding these factors helps in early detection and prevention of CKD progression.
How CKD Affects the Body
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) progressively impairs kidney function, reducing the body's ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. This buildup of toxins can cause complications such as high blood pressure, anemia, and weak bones. Over time, CKD may lead to kidney failure, impacting multiple organ systems including the heart and nervous system.
Prevention Tips for CKD
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects millions worldwide, often progressing silently until advanced stages. Early prevention plays a crucial role in reducing the risk and slowing disease progression.
Maintain a balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits and vegetables to support kidney health. Regular exercise and controlling blood pressure contribute significantly to preventing CKD.
CKD Diagnosis and Testing
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) diagnosis involves a combination of blood tests and urine analysis to assess kidney function. Early detection is crucial to prevent progression and manage complications effectively.
Blood tests measure creatinine levels to calculate the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), an essential indicator of kidney function. Urine tests check for protein, which can signal kidney damage even before symptoms arise. Imaging tests and kidney biopsy may be used in certain cases to determine the cause and extent of CKD.
Managing and Treating CKD
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) requires ongoing management to slow progression and prevent complications. Effective treatment focuses on controlling underlying causes and maintaining kidney function.
- Blood Pressure Control - Maintaining blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg reduces kidney damage and slows CKD progression.
- Dietary Management - Low sodium, protein moderation, and balanced electrolyte intake help preserve kidney health.
- Medication Therapy - Use of ACE inhibitors or ARBs protects kidney function and controls blood pressure effectively.
