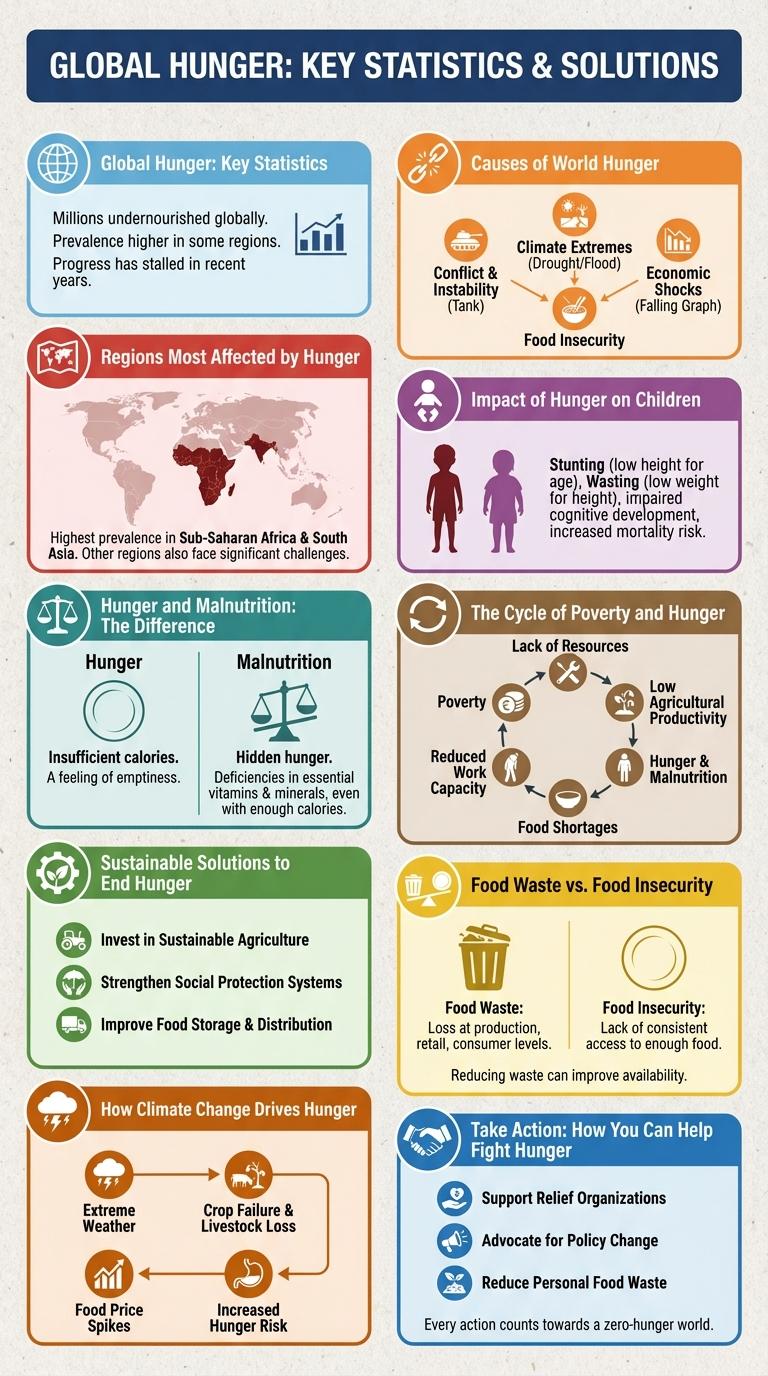
Hunger affects millions worldwide, leading to severe health and developmental challenges. Infographics visually convey the urgency and extent of this global issue through clear statistics and impactful imagery. Understanding these data highlights the critical need for sustainable solutions to combat food insecurity.
Global Hunger: Key Statistics
Global hunger affects over 820 million people worldwide, with the majority residing in developing regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Chronic undernourishment leads to increased mortality rates among children under five, with nearly 45 million children suffering from wasting. Efforts to combat hunger involve improving food security, boosting agricultural productivity, and addressing socio-economic inequalities.
Causes of World Hunger
World hunger primarily stems from poverty, limiting access to sufficient food and resources. Conflict disrupts food production and distribution, exacerbating hunger crises globally.
Climate change reduces crop yields through extreme weather, droughts, and floods. Inefficient food systems and waste also contribute significantly to food shortages worldwide.
Regions Most Affected by Hunger
Hunger remains a critical issue affecting millions worldwide, with certain regions experiencing higher levels of food insecurity. Understanding these regions is essential to addressing global hunger effectively.
Sub-Saharan Africa is the most affected region, with over 20% of its population facing chronic hunger. South Asia follows closely, where poverty and conflict contribute significantly to food scarcity. Conflict-affected areas in the Middle East also experience severe hunger crises due to displacement and disrupted food supplies.
Impact of Hunger on Children
Hunger significantly affects the physical and cognitive development of children worldwide. Millions of children suffer from malnutrition, leading to long-term health and educational challenges.
- Stunted Growth - Chronic hunger causes impaired physical development, resulting in reduced height and weakened immune systems.
- Cognitive Impairment - Malnutrition during early childhood negatively impacts brain development, lowering IQ and academic performance.
- Increased Mortality - Hunger contributes to higher child mortality rates by making children more vulnerable to diseases and infections.
Hunger and Malnutrition: The Difference
Hunger refers to the physical sensation of discomfort or weakness caused by insufficient food intake. Malnutrition occurs when the body lacks essential nutrients, leading to impaired growth and health problems. Understanding the difference is vital for addressing global food security and health challenges effectively.
The Cycle of Poverty and Hunger
How does the cycle of poverty contribute to persistent hunger? Poverty limits access to nutritious food, making it difficult for individuals to maintain healthy diets. This lack of adequate nutrition weakens health and reduces the ability to work, deepening poverty.
What role does poor health play in the hunger cycle? Malnutrition leads to increased susceptibility to diseases, which decreases productivity. As health deteriorates, earning capacity diminishes, reinforcing the cycle of poverty and hunger.
How does education affect hunger and poverty? Limited access to education reduces job opportunities and awareness about nutrition. Without education, families often cannot improve their economic situation or food security.
Why is food insecurity a critical aspect of the poverty-hunger cycle? Erratic food supply causes chronic hunger and malnutrition, impacting physical and cognitive development. Food insecurity impedes economic progress by reducing workforce effectiveness.
What interventions help break the cycle of poverty and hunger? Programs that improve education, healthcare, and food access empower communities. Sustainable agricultural practices and social safety nets also reduce hunger and poverty over time.
Sustainable Solutions to End Hunger
| Sustainable Solution | Impact on Ending Hunger |
|---|---|
| Climate-Resilient Agriculture | Increases crop yield and food availability despite changing climate conditions |
| Food Waste Reduction | Recovers edible food to feed millions, reducing pressure on food systems |
| Investment in Smallholder Farmers | Boosts local food production and strengthens rural economies |
| Improved Food Distribution Networks | Ensures equitable access to nutritious food in remote and urban areas |
| Nutrition Education Programs | Promotes sustainable dietary practices and reduces malnutrition risks |
Food Waste vs. Food Insecurity
Food waste and food insecurity represent two critical challenges in global hunger. Addressing both issues is essential to ensure sustainable food systems and reduce hunger worldwide.
- Food Waste Volume - Approximately one-third of all food produced globally is wasted, equating to 1.3 billion tons annually.
- Food Insecurity Prevalence - Over 820 million people worldwide suffer from chronic hunger and lack reliable access to nutritious food.
- Resource Impact - Wasted food consumes about 25% of freshwater and contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing food waste can improve food availability and help alleviate food insecurity across vulnerable populations.
How Climate Change Drives Hunger
Climate change exacerbates hunger by disrupting weather patterns critical for agriculture, leading to droughts and floods that reduce crop yields. These extreme conditions decrease food availability, pushing vulnerable populations toward food insecurity.
Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall threaten staple crops like wheat, rice, and maize, intensifying malnutrition worldwide. Increased frequency of natural disasters damages infrastructure, limiting access to food markets and aid distribution.
