Vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that promote overall health and well-being. Incorporating a variety of colorful vegetables into daily meals supports immune function and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Understanding their nutritional benefits through an engaging infographic can inspire healthier eating habits.
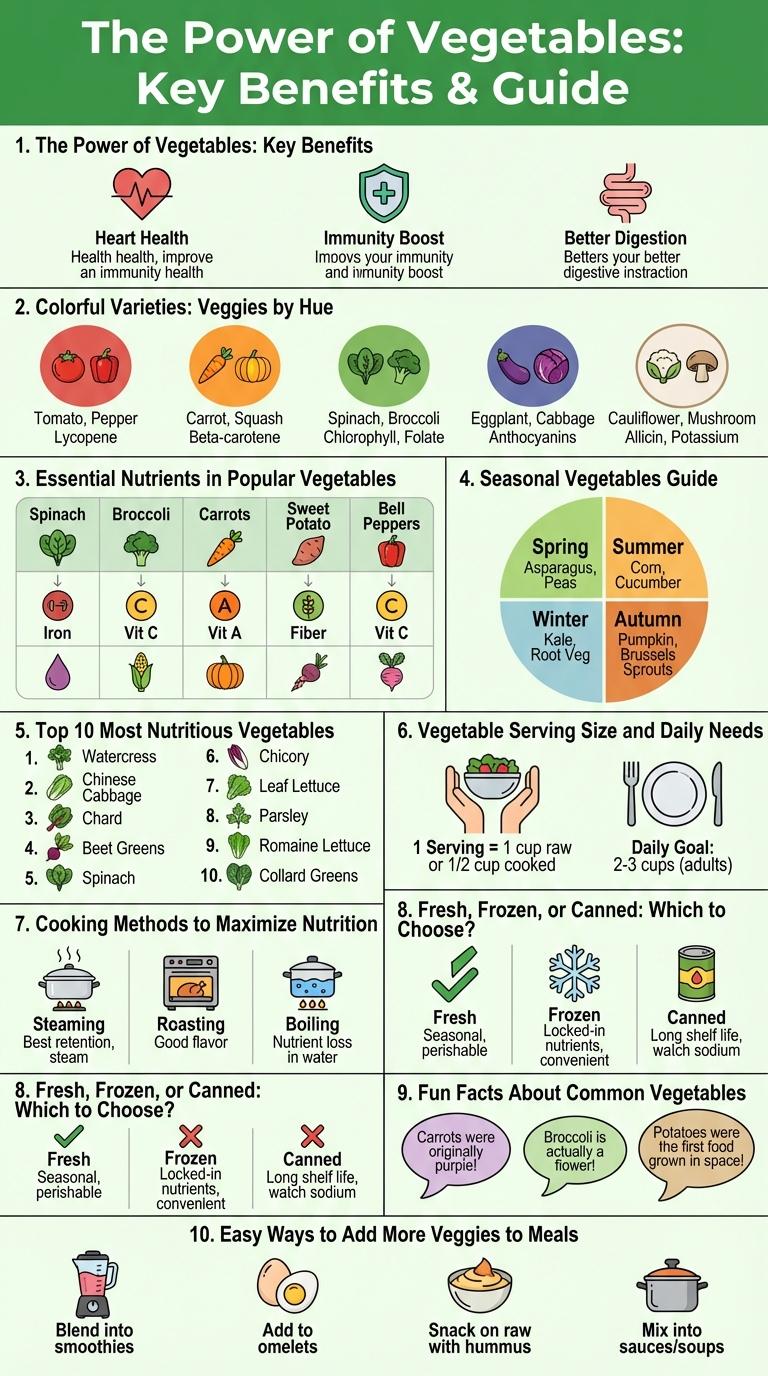
The Power of Vegetables: Key Benefits
Vegetables are rich sources of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Consuming a variety of vegetables supports immune function, improves digestion, and enhances skin health.
High in dietary fiber, vegetables aid in weight management and help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Regular vegetable intake lowers the risk of heart disease, hypertension, and certain types of cancer.
Colorful Varieties: Veggies by Hue
Vegetables come in a wide spectrum of colors, each hue representing unique nutrients and health benefits. Exploring colorful varieties enhances both the visual appeal and nutritional value of meals.
- Red Vegetables - Contain antioxidants like lycopene that support heart health.
- Green Vegetables - Rich in chlorophyll, vitamins K and C, boosting immunity and bone strength.
- Orange and Yellow Vegetables - Packed with beta-carotene, promoting eye health and immune function.
Incorporating a rainbow of vegetables ensures a diverse intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
Essential Nutrients in Popular Vegetables
Vegetables are rich sources of essential nutrients that support overall health. Each type of vegetable offers unique vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Consuming a variety of vegetables ensures a balanced intake of vital nutrients.
- Spinach: High in Iron - Spinach provides a significant amount of iron which aids in oxygen transport and energy production.
- Carrots: Rich in Beta-Carotene - Carrots contain beta-carotene, essential for healthy vision and immune function.
- Broccoli: Excellent Source of Vitamin C - Broccoli delivers vitamin C that boosts immune defense and supports skin health.
Seasonal Vegetables Guide
Discover the benefits of eating seasonal vegetables for optimal freshness and nutrition. Seasonal vegetables vary throughout the year, offering a diverse range of flavors and nutrients. Enjoy a colorful plate by choosing vegetables at their peak each season for the best taste and health benefits.
| Season | Vegetables |
|---|---|
| Spring | Asparagus, Spinach, Peas |
| Summer | Tomatoes, Zucchini, Bell Peppers |
| Fall | Pumpkin, Brussels Sprouts, Carrots |
| Winter | Kale, Cabbage, Root Vegetables |
Top 10 Most Nutritious Vegetables
Vegetables are essential for a balanced diet, providing a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Consuming nutrient-dense vegetables supports overall health and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
The top 10 most nutritious vegetables include kale, spinach, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, sweet potatoes, bell peppers, garlic, onions, and asparagus. These vegetables are rich in fiber, vitamins A, C, K, and folate, as well as minerals like potassium and iron. Incorporating them into your meals boosts immune function, aids digestion, and promotes healthy skin and bones.
Vegetable Serving Size and Daily Needs
Vegetable serving sizes vary based on type but generally equal about one cup of raw or cooked vegetables. The USDA recommends adults consume 2 to 3 cups of vegetables daily to meet nutritional needs.
Dark leafy greens, colorful vegetables, and legumes provide essential vitamins and minerals in each serving. Choosing a variety of vegetables ensures intake of fiber, antioxidants, and other nutrients critical for health.
Cooking Methods to Maximize Nutrition
| Cooking Method | Nutrition Benefit |
|---|---|
| Steaming | Preserves water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and folate |
| Microwaving | Retains high levels of antioxidants by minimizing cook time |
| Sauteing | Enhances absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K with healthy oils |
| Roasting | Concentrates flavors and maintains fiber integrity |
| Boiling | Can cause nutrient loss; limit time to reduce vitamin depletion |
Fresh, Frozen, or Canned: Which to Choose?
Choosing between fresh, frozen, or canned vegetables depends on your nutritional needs, convenience, and cooking preferences. Each form has its own benefits and considerations when it comes to flavor, texture, and nutrient retention.
- Fresh Vegetables - Offer the highest vitamin content when consumed soon after harvest but can spoil quickly without proper storage.
- Frozen Vegetables - Retain most nutrients due to rapid freezing after harvest and offer long shelf life, making them convenient and healthy.
- Canned Vegetables - Provide a long-lasting pantry option with slightly lower nutrient levels and may contain added sodium or preservatives.
Fun Facts About Common Vegetables
Vegetables contain essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health and immunity. Carrots were first grown for their aromatic leaves and seeds rather than their roots. Tomatoes are botanically classified as fruits but are commonly used as vegetables in cooking.
