Euthanasia involves intentionally ending a person's life to relieve suffering, a topic that stirs intense ethical and legal debates worldwide. The infographic breaks down key statistics, legal statuses, and moral considerations surrounding euthanasia. Visual data highlights diverse perspectives and the impact on patients, families, and healthcare systems.
Understanding Euthanasia: Key Concepts
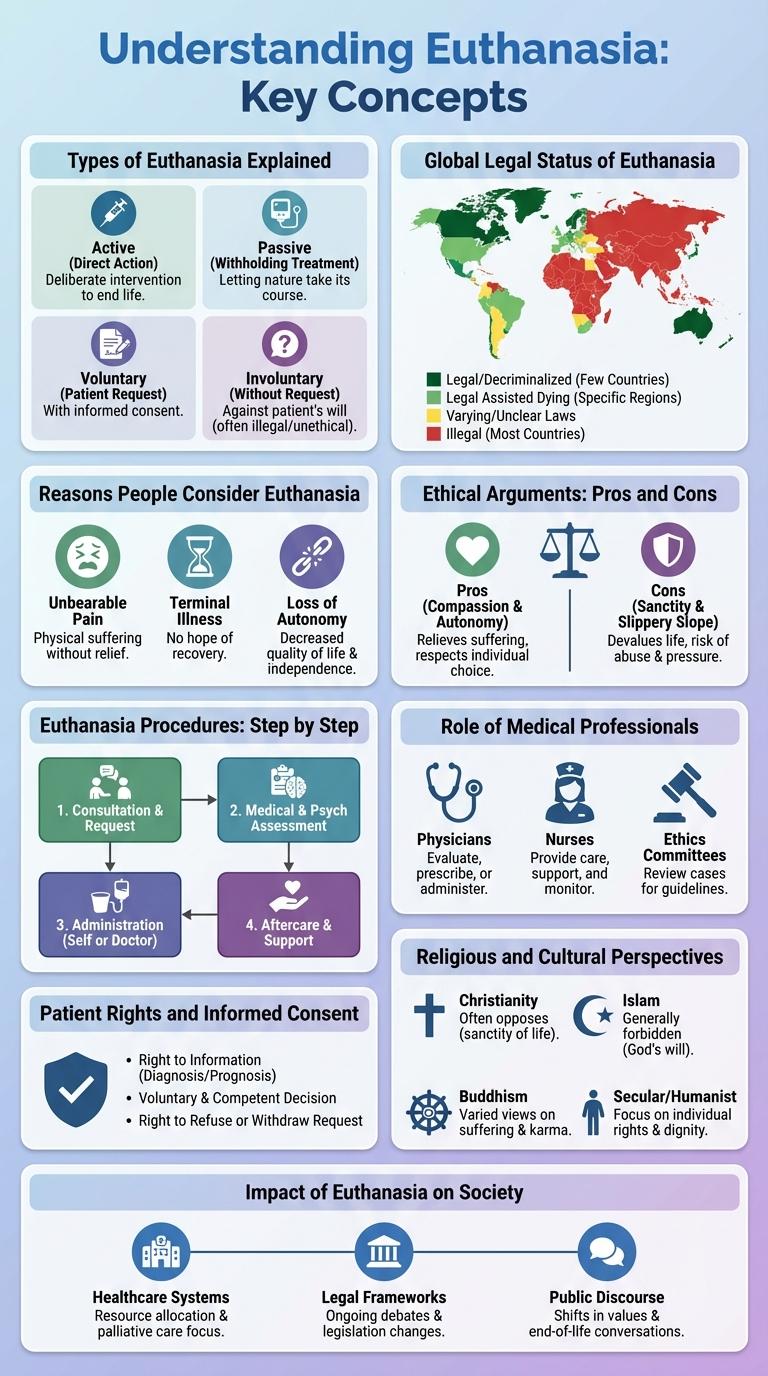
Euthanasia refers to the practice of intentionally ending a life to relieve pain and suffering. It is categorized into voluntary, non-voluntary, and involuntary euthanasia based on the patient's consent.
Voluntary euthanasia involves the explicit request of the patient, whereas non-voluntary occurs when the patient is unable to consent. Legal status and ethical debates surrounding euthanasia vary significantly across countries and cultures.
Types of Euthanasia Explained
Euthanasia involves intentionally ending a life to relieve pain and suffering. Different types of euthanasia are categorized by consent and method used.
- Voluntary Euthanasia - Performed with the explicit consent of the patient who wishes to end their life.
- Non-Voluntary Euthanasia - Conducted when the patient is unable to give consent, such as in cases of unconsciousness.
- Involuntary Euthanasia - Done without the patient's consent and against their will, often considered unethical and illegal.
- Active Euthanasia - Involves direct intervention to cause death, such as administering lethal substances.
- Passive Euthanasia - Involves withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatments, allowing the patient to die naturally.
Global Legal Status of Euthanasia
What is the global legal status of euthanasia?
Euthanasia laws vary significantly worldwide, with some countries permitting it under strict conditions while others impose total bans. Understanding these legal frameworks helps clarify the ethical and medical implications surrounding euthanasia practices globally.
| Country/Region | Legal Status |
|---|---|
| Netherlands | Legal under strict regulatory frameworks since 2002 |
| Belgium | Legal and extended to minors under specific criteria |
| Canada | Legalized as Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) nationwide |
| United States | Legal in some states, including Oregon, Washington, and California |
| Japan | Not legally permitted; euthanasia remains illegal |
Reasons People Consider Euthanasia
Euthanasia remains a deeply personal and complex decision influenced by various factors. Many individuals facing terminal illnesses or unbearable pain contemplate this option to regain control over their final moments.
Chronic pain and lack of effective treatment drive many towards considering euthanasia. Psychological suffering, such as depression from prolonged illness, also plays a crucial role. Desire for dignity and avoidance of prolonged dependency motivates those seeking relief through euthanasia.
Ethical Arguments: Pros and Cons
Euthanasia remains a deeply controversial topic, involving complex ethical considerations. Supporters argue it respects individual autonomy and alleviates unbearable suffering.
Opponents highlight the moral risks, including potential abuses and the devaluation of human life. Ethical debates balance compassion with the sanctity of life principles.
Euthanasia Procedures: Step by Step
Euthanasia involves a carefully regulated process to ensure ethical and legal compliance. The procedures vary depending on jurisdiction but generally follow a structured step-by-step approach.
- Assessment and Consent - Medical professionals evaluate the patient's condition and confirm informed consent is given voluntarily.
- Legal Review - Legal requirements are verified, including documentation and approval from relevant authorities.
- Medication Administration - A qualified practitioner administers prescribed drugs to induce a peaceful and painless death.
Each step is designed to respect the patient's dignity while adhering to legal and ethical standards.
Role of Medical Professionals
| Role of Medical Professionals | Details |
|---|---|
| Assessment of Patient Requests | Evaluate patient's physical and mental health to confirm voluntary and informed consent for euthanasia. |
| Legal Compliance | Ensure all actions comply with state or country-specific euthanasia laws and guidelines. |
| Ethical Considerations | Balance professional ethics, patient autonomy, and compassionate care during decision-making. |
| Communication | Provide clear information to patients and families regarding prognosis, alternatives, and euthanasia procedures. |
| Procedural Responsibilities | Administer euthanasia in a medically appropriate manner ensuring patient comfort and dignity. |
Patient Rights and Informed Consent
Euthanasia involves complex ethical considerations centered on patient rights and informed consent. Patients must be fully informed about their medical condition, treatment options, and potential outcomes to make autonomous decisions. Informed consent ensures that patients voluntarily agree to euthanasia without coercion, respecting their dignity and personal choice.
Religious and Cultural Perspectives
Euthanasia raises profound ethical questions influenced by diverse religious and cultural beliefs. Understanding these perspectives helps clarify the global debate surrounding the practice.
- Christianity - Many Christian denominations oppose euthanasia, viewing life as sacred and divinely ordained.
- Islam - Islamic teachings strictly forbid euthanasia, emphasizing the sanctity of life and divine will.
- Hinduism - Hindu perspectives on euthanasia vary, with some accepting it under compassionate circumstances while others stress karma and the natural cycle of life and death.
- Buddhism - Buddhist views often discourage euthanasia, focusing on the importance of non-harm and the impact on spiritual karma.
- Cultural Differences - Cultural attitudes towards euthanasia differ widely, influenced by historical, social, and religious contexts affecting acceptance or rejection.
