Visual representations about death highlight complex emotions, cultural practices, and statistical data in a clear, engaging way. Infographics transform sensitive topics into accessible insights, offering viewers a holistic understanding of mortality trends and their societal impact. This approach enhances awareness, promotes informed discussions, and respects the profound nature of life's final chapter.
Understanding Death: Key Facts
Death is the permanent cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. It marks the end of life and is a universal experience for all living beings.
Understanding death involves recognizing its biological, psychological, and cultural aspects. Common causes include diseases, accidents, and aging. Knowledge about death helps in medical decision-making, grief processes, and ethical considerations surrounding end-of-life care.
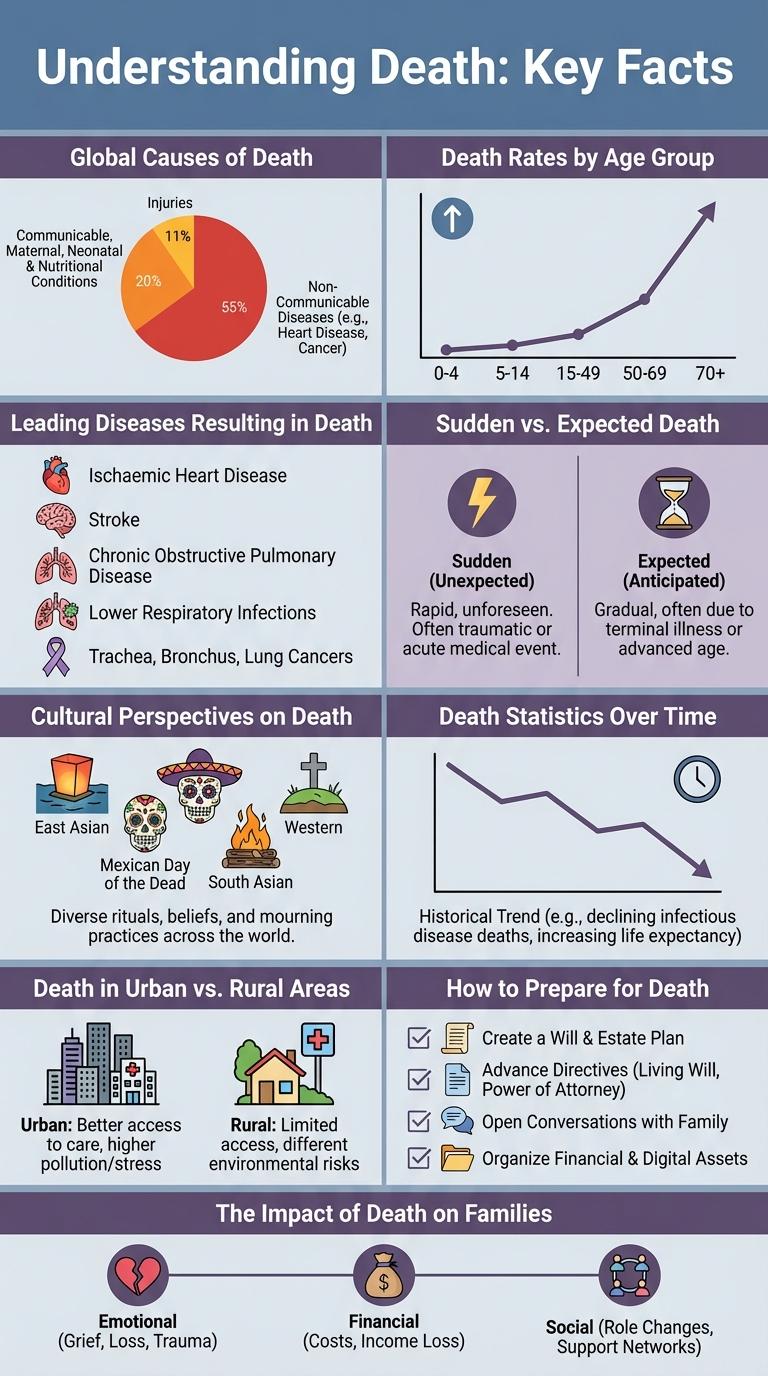
Global Causes of Death
| Cause of Death | Percentage of Global Deaths |
|---|---|
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 16% |
| Stroke | 11% |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) | 6% |
| Lower Respiratory Infections | 5% |
| Neonatal Disorders | 4% |
Death Rates by Age Group
Death rates vary significantly across different age groups, reflecting diverse health risks and life stages. Understanding these variations helps in targeting healthcare resources and preventive measures more effectively.
Infants and the elderly show the highest death rates due to vulnerability and chronic conditions. Middle-aged adults generally have lower death rates but face increasing risks from lifestyle-related diseases.
Leading Diseases Resulting in Death
Understanding the leading diseases that result in death is crucial for public health awareness and prevention efforts. Cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, remain the top causes of mortality worldwide.
Respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lower respiratory infections also contribute significantly to global deaths. Cancer, particularly lung, colorectal, and liver cancers, ranks among the leading killers across different regions.
Sudden vs. Expected Death
What distinguishes sudden death from expected death? Sudden death occurs without warning, often due to cardiac arrest or accidents. Expected death follows a known illness or decline, allowing preparation for end-of-life care.
Cultural Perspectives on Death
Death holds diverse meanings across cultures, shaping rituals and beliefs about the afterlife. In Mexico, the Day of the Dead celebrates and honors deceased loved ones with vibrant altars and offerings. In Japan, ancestral worship and ceremonies reflect a deep respect for family lineage and spiritual continuity.
Death Statistics Over Time
Death rates have shifted significantly due to advances in medicine and changes in lifestyle. Historical data highlights trends in causes and frequency of death worldwide.
Understanding death statistics over time reveals patterns that inform public health policies and resource allocation.
- Global Mortality Decline - The overall global death rate has decreased steadily from 20 per 1,000 in 1900 to 7.5 per 1,000 in 2020 due to improved healthcare.
- Infectious Disease Reduction - Deaths from infectious diseases dropped by over 60% since the mid-20th century thanks to vaccines and sanitation improvements.
- Rise of Chronic Diseases - Chronic illnesses such as heart disease and cancer have become leading causes of death, increasing from 30% to over 70% of all deaths since 1950.
Death in Urban vs. Rural Areas
Death rates and causes vary significantly between urban and rural areas, influenced by access to healthcare and lifestyle differences. Understanding these disparities helps target public health interventions effectively.
Urban areas typically report higher mortality from chronic diseases, while rural regions face increased deaths due to accidents and delayed medical care.
- Mortality Rate Differences - Rural areas often experience higher overall death rates compared to urban regions due to limited healthcare accessibility and emergency response times.
- Leading Causes of Death - Urban populations show higher instances of cardiovascular disease and cancer, whereas rural deaths more commonly result from accidents and respiratory diseases.
- Healthcare Accessibility - Urban residents benefit from proximity to hospitals and specialists, reducing mortality related to treatable conditions prevalent in rural zones.
How to Prepare for Death
Preparing for death involves practical, emotional, and legal steps to ensure a smooth transition for yourself and your loved ones. Understanding these steps can provide peace of mind and clarity during difficult times.
- Create a Will - A legal document that specifies how your assets and belongings will be distributed after your death.
- Discuss Wishes - Communicate your end-of-life preferences with family and healthcare providers to ensure your desires are respected.
- Organize Important Documents - Keep vital records such as insurance policies, financial statements, and medical directives in a secure, accessible place.
- Consider Funeral Arrangements - Plan or pre-pay for funeral services to alleviate the burden on loved ones during grieving.
- Seek Emotional Support - Engage with counselors or support groups to process feelings and foster acceptance of mortality.
Taking these proactive measures helps safeguard your legacy and provides comfort to those you leave behind.
