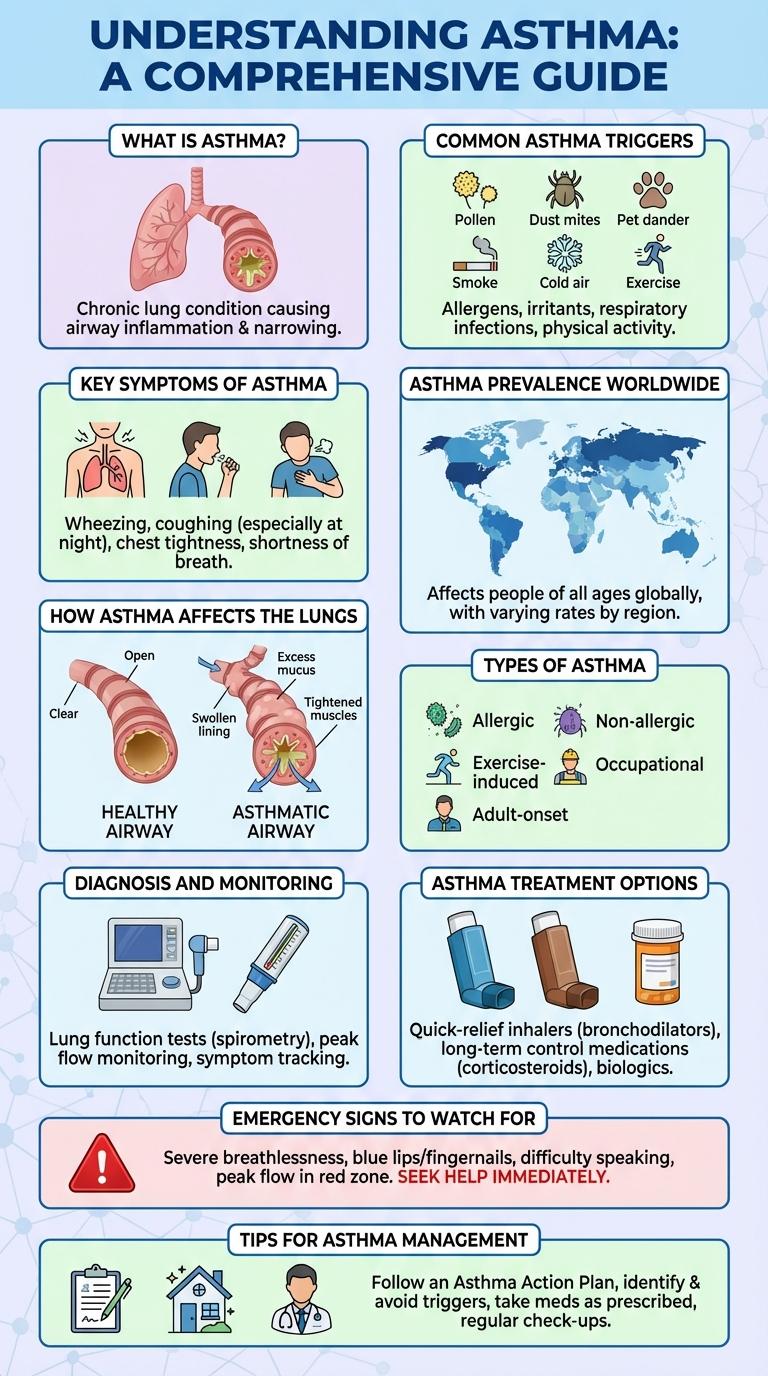
Asthma affects millions worldwide by causing airway inflammation and breathing difficulties. Understanding its triggers, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial for effective management. This infographic highlights key facts to raise awareness and support those living with asthma.
What is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, causing difficulty in breathing. It affects people of all ages and can range from mild to severe episodes.
Common symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Asthma triggers vary and may include allergens, exercise, cold air, and respiratory infections.
Common Asthma Triggers
Common asthma triggers include allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander that can cause airway inflammation. Respiratory infections, cold air, and physical activity are frequent non-allergenic triggers that exacerbate asthma symptoms. Exposure to tobacco smoke, strong odors, and pollution also significantly increase the risk of asthma attacks.
Key Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Key symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and persistent coughing, especially at night or early morning. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management and preventing severe asthma attacks.
Asthma Prevalence Worldwide
| Region | Asthma Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| North America | 7.7 |
| Europe | 6.2 |
| Asia | 4.5 |
| Africa | 4.2 |
| South America | 5.5 |
How Asthma Affects the Lungs
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that inflames and narrows the airways in the lungs. This inflammation causes swelling and increased mucus production, leading to breathing difficulties.
During an asthma attack, the muscles around the airways tighten, further restricting airflow. This results in symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Types of Asthma
What are the different types of asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by airway inflammation and constriction. Understanding the types helps in targeted treatment and management.
| Type of Asthma | Description |
|---|---|
| Allergic Asthma | Triggered by allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or mold. Common in individuals with other allergic conditions. |
| Non-Allergic Asthma | Triggered by factors like stress, exercise, cold air, or viral infections. Does not involve allergens. |
| Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction (EIB) | Occurs during or after physical activity. Causes shortness of breath and wheezing. |
| Occupational Asthma | Caused by exposure to irritants in the workplace. Symptoms improve when away from the triggering environment. |
| Severe Asthma | Persistent symptoms despite treatment. Requires specialized management and frequent monitoring. |
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Asthma diagnosis relies on a combination of medical history review and lung function tests to confirm airway inflammation and obstruction. Effective monitoring of asthma symptoms and lung performance is essential to manage and adjust treatment plans.
Diagnosis and monitoring tools help healthcare providers track disease progression and prevent acute exacerbations.
- Spirometry - Measures the volume and speed of air that can be inhaled and exhaled to assess airway obstruction.
- Peak Flow Monitoring - Patients use a peak flow meter daily to detect changes in airway narrowing at home.
- Exhaled Nitric Oxide Test - Detects airway inflammation by measuring nitric oxide levels in exhaled breath.
Asthma Treatment Options
Asthma treatment focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing attacks through medication and lifestyle adjustments. Effective management reduces flare-ups and improves overall lung function.
- Inhaled corticosteroids - These are the most common long-term control medications that reduce airway inflammation.
- Short-acting beta agonists (SABAs) - Used as quick-relief inhalers, they relax muscles around airways during asthma attacks.
- Leukotriene modifiers - Oral medications that help reduce inflammation and prevent asthma symptoms.
Emergency Signs to Watch For
Asthma emergencies require immediate attention to prevent severe complications. Recognizing the key warning signs can save lives by prompting quick action.
- Severe Shortness of Breath - Difficulty speaking full sentences indicates a serious asthma attack.
- Blue Lips or Fingertips - Cyanosis signals insufficient oxygen reaching the blood.
- Rapid Worsening of Symptoms - Sudden increase in wheezing or coughing demands urgent medical evaluation.
Seek emergency medical care immediately if any of these signs are observed to ensure safety and proper treatment.
